Respiration and Fermentation Overview
In this content, you will find an overview of respiration and fermentation processes, including aerobic and anaerobic respiration, the production of ethanol, and the distinctions between different types of respiration. The content also discusses the influence of temperature on these processes. Explore the concepts of respiration, cellular metabolism, and energy production in organisms.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
2.2.5 Respiration Follow-Me iQuiz
Q. Yeast cells produce ethanol in fermentation. Is this process affected by temperature? Explain your answer. Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Write a balanced equation to summarise aerobic respiration. Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Where in the cell does the first stage of respiration occur? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
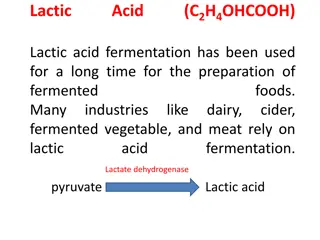
Q. Give two industrial uses of the anaerobic respiration of yeast. Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the final product of the first stage of respiration under aerobic conditions? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Pyruvic acid is used for the second stage of respiration. Where does this second stage take place? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. If conditions in a human muscle cell become anaerobic pyruvic acid is converted to another substance. Name this other substance. Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. When lactic acid builds up in the blood, a person is in oxygen debt. This debt must eventually be paid. Suggest how the debt is paid. Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the first stage process of respiration called? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. In the first stage of respiration there is a release of ATP as glucose is converted to another substance. Name this other substance. Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. To what is pyruvic acid converted under anaerobic conditions in yeast? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Under aerobic conditions pyruvic acid is converted to an acetyl group and in the process a small molecule is released. Name this molecule. Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. In respiration acetyl co-enzyme A enters a cycle of reactions. What name is given to this cycle? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. To what is pyruvic acid converted under anaerobic conditions in a human muscle cell? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Is oxygen required for the first stage of respiration? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. To what might pyruvic acid be converted, in the absence of oxygen? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Where in the cell does Krebs Cycle take place? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the cytosol? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is fermentation? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Is oxygen required for the second stage of aerobic respiration? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Suggest a situation in which some cells in the human body may not be able to engage in the second stage of aerobic respiration. Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What term is used to describe respiration in which only Stage 1 occurs? Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name an organism that is used in industrial fermentation. Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Aerobic requires oxygen; Anaerobic does not Lactic acid; Ethanol + Carbon dioxide Cytoplasm minus organelles; Liquid part of cytoplasm Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic respiration; Respiration that produces ethanol and CO2 or lactic acid Ethanol and CO2 Mitochondrion Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Anaerobic: Fermentation Glycolysis No Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Kreb s cycle Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Baking; Brewing Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Yeast C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Kreb s cycle Yeast Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Lack of oxygen; Strenuous exercise; Restricted blood supply Carbon dioxide Yes Cytoplasm Lactic acid Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Cytoplasm Lactic acid
CONGRATULATIONS You re Brilliant
Incorrect Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again