Pavement Deterioration Model & Maintenance Decision Tree
The Pavement Deterioration Model provides forecasts on future pavement conditions using deterministic and probabilistic modeling techniques. It also discusses Maintenance Decision Trees outlining treatments, costs, and applications based on road conditions. The decision tree helps in determining maintenance strategies based on factors like road width, PSI, RUT, and more. Explore transportation engineering concepts and calculations to determine total maintenance costs for road segments.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
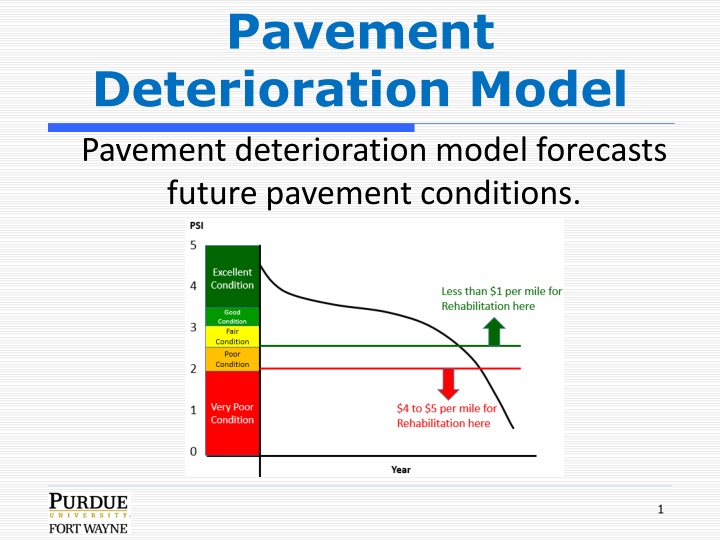
Pavement Deterioration Model Pavement deterioration model forecasts future pavement conditions. 1
Pavement Deterioration Model, Modeling Techniques Deterministic : A deterministic model is one in which every set of variable states is uniquely determined by parameters in the model and by sets of previous states of these variables Probabilistic or Stochastic: In probabilistic model, randomness is present, and variable states are not described by unique values, but rather by probability distributions. Markov process is commonly used probabilistic technique.
Maintenance Decision Tree Details and Applications Treatment Est. Type Cost/Mile GM General Maintenance Procedure Asphalt Patching Pothole Repair Crack Sealing Road Striping Chip Seal Micro-surface Thin Overlay (<2 ) Surface Preparation (mil, level, full-depth reclamation, or combination thereof) Thick Overlay (>2 ) Seal Coat 1-R plus shoulder or widening requirements Applicable on roads in good condition with shoulder needs 2-R plus shoulder or widening requirements Applicable on narrow roads with shoulder or widening needs Complete Reconstruction $0 1-R GM General Maintenance 1-R Preventive Rehabilitation $60,000 3-R 2-R 2-R Minor Rehabilitation $250,000 4-R 3-R Preventive Rehabilitation with Shoulder Needs $350,000 4-R Major Rehabilitation $650,000 5-R 5-R Full Reconstruction $1,200,000 3
Maintenance Decision Tree 5-R PSI < 1.0 Road Width <= 28 Road With > 28 4-R 1.0 <= PSI < 2.0 2-R Road Width <= 28 Road With > 28 Road Width <= 26 Road Width > 26 Road Width <= 28 Road Width > 28 Road Width <= 26 Road Width > 26 4-R RUT >0.3 2-R 2.0 <= PSI < 2.5 Rural Roads 3-R RUT < =0.3 1-R 4-R RUT >0.3 2-R 2.5 <= PSI < 3.0 3-R Rut < =0.3 1-R Road Width <= 26 Road Width > 26 3-R PSI => 3.0 GM 4
Transportation Engineering CE Lecture 1 Maintenance Decision Tree, Example Segment # 1 2 3 4 5 6 Road Width 29 29 29 25 25 25 PSI Length Rut 2.2 2.1 2 3 4.5 3.5 0.1 2 1 2 3 1 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.2 0.2 0.2 1 5 2 4 3 6 Determine total cost to maintain all the segments? 5
Transportation Engineering CE Lecture 1 Maintenance Decision Tree, Example, solution Segment # Road Width PSI Length Rut Treatment Cost $250,00 0 *0.1 1 2.2 0.1 29 0.4 2-R 2 3 4 5 6 2.1 2 3 4.5 3.5 2 1 2 3 1 29 29 25 25 25 0.4 0.4 0.2 0.2 0.2 Determine total cost to maintain all the segments? 6
Optimization Model, Example Total Needs: $15 M Available Budget: $3 M Figure: Schematic of an Optimization Model 7
Optimization Model, Methodology 8
Optimization Model, Capital Improvement Plan (CIP) Segment ID Road Name 222-1 3 6 19-1 222 Year1 Year2 Year3 GM GM GM GM 1-R Year4 GM GM 1-R GM GM Year5 GM GM GM 1-R GM 1-R GM GM GM GM Chalk Bluff Road/"78" Rd GM Albin/LaGrange Rd Black hills Rd Old Highway Birns West Chalk Bluff Road/"78" Rd GM GM GM GM 9
Optimization Model, Formulation Maximize Subject to 10
Transportation Engineering CE Lecture 1 Optimization Model, Example Segment # 1 2 3 4 5 6 Length , miles 0.1 2 1 2 3 1 PSI 1 2.2 2.1 2 3 4.5 3.5 5 2 4 3 6 Determine overall pavement condition? 11
Transportation Engineering CE Lecture 1 Optimization Model, Example If we have 3 segments, how many possible combinations? If we have 17 segments, how many possible combinations? Draw a curve of possible options against number of segments. 12
Transportation Engineering CE Lecture 1 Pavement Management Systems, dataset required 1.IRI, Rut, PCI, Road width, AADT 2.Pavement deterioration model 3.Pavement performance model 4.Maintenance decision tree 5.Maintenance cost 6.Maintenance improvement matrix 7.Available budget 13
PMS Deliverables pavement condition report Electronic Data Electronic GIS Maps & Video Logs 14
Software Required? VBA in Excel Optimization Software 15