Overview of Gram-Negative Enteric Bacilli
Gram-negative bacilli are a diverse group of bacteria, including enteric and non-enteric bacilli. Common characteristics include being aerobic or facultative anaerobes, fermenting glucose, and being part of the normal flora of the human and animal gastrointestinal tract. Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a significant member, with various strains causing intestinal and extraintestinal infections. Klebsiella species, such as K. pneumoniae, are also notable for causing infections like pneumonia and urinary tract infections.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
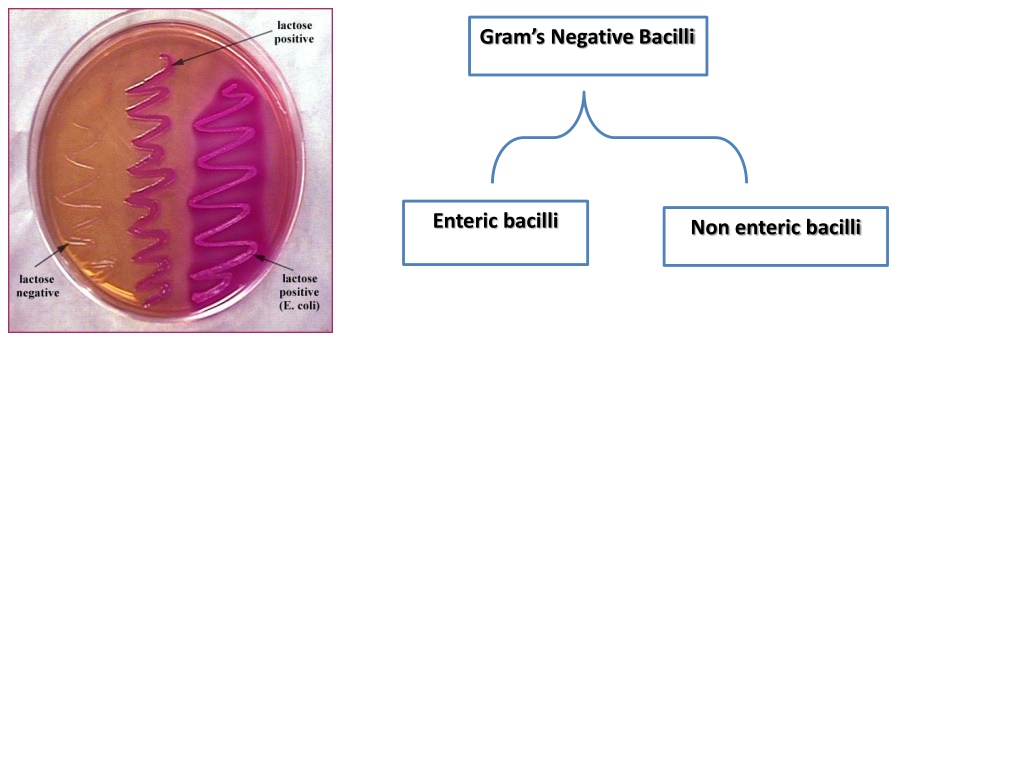
Grams Negative Bacilli Enteric bacilli Non enteric bacilli Late-lactose fermenting (LLF): NLF after 24h, LF after 48h. Non-lactose fermenting (NLF) Lactose fermenting (LF) E. coli (Escherichia coli). Others e.g. Salmonella, Shigella, proteus,Yersinia. Citrobacter Klebsiella species. Serratia Enterobacter species.
lactose fermenting Non lactose fermenting
Family: Enterobacteriaceae (ENTERIC BACILLI, COLIFORM). GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS * G ve bacilli or coccobacilli. * Aerobic or Facultative anaerobes. * Ferment glucose and produce acid + gas. * Oxidase ve, catalase +ve * Most of them are normal flora of human & animal GIT. * Grow well on MacConkey s agar. * Transmission either endogenous or person to person especially in hospital.
E. coli (Escherichia coli) Normal flora of human and animal GIT, human female genital tract. Under electron microscope
E. coli (Escherichia coli) There are many STRAINS SEROTYPED according to O Ag, H Ag, K Ag. Most strains are Motile, un-capsulated. Produced dry colonies.
E. coli (Escherichia coli) infections DISEASES EXTRAINTESTINAL infections INTESTINAL infections
E. coli (Escherichia coli) infections 1)INTESTINAL infections:(caused by some strains) (e.g. Traveler's diarrhea, dysentery, hemorrhagic infection). Source of infection either human or animal product. E. coli serotypes Enterotoxigenic E.coli (ETEC) Enteroadhesive E. coli (EAEC) Enteroinvasive E.coli (EIEC) Enteropathogenic E.coli (EPEC) Enterohemorrhagic E.coli (EHEC)
E. coli (Escherichia coli) infections 2) EXTRAINTESTINAL infections Wound infections, Pneumonia, Bacteremia, Septicemia, UTI . Its the common cause of G-ve nosocomial infection.
Klebsiella spp Klebsiella pneumoniae, K.oxytoca, K.ozaenae Normal flora of GIT. Non - motile. Capsulated by large capsule. Mucoid colonies. Causes Necrotizing Pneumonia, Nosocomail infections like UTI mainly in debilitated patients.
Laboratory Diagnosis 1) Specimens (site of infection e.g. urine, blood, pus etc). 2) Staining Gram s stain: Enterobacteriaceae resemble each other morphologically under microscope. So it is difficult to diagnose by microscope.
Laboratory Diagnosis Staining Capsular stain: Klebsiella stained by this stain, bacilli surrounded by hallo zone.
Laboratory Diagnosis 3) Culture: 37C , 24-48h A) Differential media: 1)MacConkey s agar (selective and differential media): A.) Lactose fermenter (Pink colonies after 24 hrs.): E. coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter. B.) Late lactose fermenter (Pink after 48 hrs.): Serratia, Citrobacter. C.) Non lactose fermenter (Pale colonies after 24 or 48 hrs.): Proteus, Salmonella, Shigella.
Laboratory Diagnosis MacConkey agar (selective and differential media) Bile salt: Inhibit G-ve other than Enterobacteriaceae Crystal violet: Inhibit G+ve bacteria Neutral red: Fermentation indicator Lactose: Differential between genera Nutrient agar
Laboratory Diagnosis Dry, discreet pink colonies E.coli on MacConkey s agar (pink colony due to lactose fermentation
Laboratory Diagnosis Klebsiella on MacConkey s agar (pink mucoid colony due to lactose fermentation
Laboratory Diagnosis 2) EMB (Eosin Methylene Blue) contain special dye: E.coli colonies appears green metallic sheen Others no green metallic sheen colonies or colorless. E.coli on EMB
Laboratory Diagnosis B) Non differential medium: Like Blood agar Enterobacteriaceae appears (large, gray, smooth)
4) Biochemical tests : 1- (IMViC) test: used to differentiate between E. coli and Klebsiella. Indole:- Tryptophan (a.a) Tryptophanase Indole add Kovac s reagent red ring (+ve). Methyl red:- Glucose phosphate broth (fer.) Acid (decrease PH) Methyl red red (+ ve), yellow (-ve) Voges proskauer:- Glucose ph. broth (fermentation) acetyl methyl carbinol (5% naphthol) + (40% KOH) dark brown (+ve), (-ve) brown-green Citrate: Simmon Citrate agar(utilize citrate) citrase Blue (+ ve), Green (- ve). Media contains bromthymol blue indicator.
Laboratory Diagnosis 4) Biochemical tests : 1- (IMViC) test: used to differentiate between E. coli and Klebsiella. Bacteria I M V C - (green) With growth E. coli + (red ring) + (red) - (yellow) - (colorless ring) + (blue) Without growth Klebsiella - (yellow) + (red)
Laboratory Diagnosis Indole test
Laboratory Diagnosis Methyl red test
Laboratory Diagnosis Voges-proskauer test
Laboratory Diagnosis Citrate test
Laboratory Diagnosis 4) Biochemical tests : API 20E system :( API= analytic profile index) This become popular for rapid identification of members of the Enterobacteriaceae and other Gram-negative bacteria. Plastic strips consist of 20 small wells containing dehydrated media components(consist of 20 tests). Not 100% specific.
Laboratory Diagnosis 5) Motility test (at 37C ): E.coli causes inverted tree (Christmas tree) due to it s motility (+ve), while Klebsiella doesn t as it is not motile (-ve). Semisolid medium motility test (inverted Christmas tree
Thank you Thank you