Ocean Water Chemistry: Salinity, Saltiest Body of Water, and Gases
Delve into the complexity of ocean water chemistry, including the significance of salinity levels, the saltiest body of water on Earth at Don Juan Pond in Antarctica, the composition of salts in ocean water, and the role of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide. Discover how these factors shape the characteristics of ocean water and impact marine ecosystems.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ocean Water Chemistry ocean composition text pgs. 127-133
Salinity- the amount of salt dissolved in water Bowling Ball clip Salinity in the ocean is between 34 and 37 ppt (parts per thousand). That would be about 35 grams per liter. Near the surface, rain, snow, and ice melting add more fresh water. Rivers dumping into the ocean (like an estuary) create lower levels of saline. Areas high in evaporation and closer to the poles (below 1 km) are the highest in salt. Where is the saltiest body of water?______
Did you guess? Don Juan Pond isn t just an awesome name for a little pool of water; it s also the name of one of the most interesting ponds out there for astrobiologists. At 40 percent salinity, the pond is the saltiest body of water on the planet. It s 18 times saltier than the ocean. Even though it s in Antarctica, it s so salty that it never freezes in conditions that get to 40 degrees below zero. But how does it get all that salt? New research from Brown University seems to have uncovered the answer, and it could mean that ponds like Don Juan Pond are possible on Mars.
The substance that you know as table salt, sodium chloride, is the most abundant salt in ocean water. When sodium chloride dissolves in water, it separates into sodium and chloride particles called ions. Other salts, include magnesium chloride, potassium chloride, sulfur chloride, and calcium chloride. Together sodium and chloride make up almost 86% of the ions in dissolved ocean water. These minerals in the water make it more dense than fresh water.
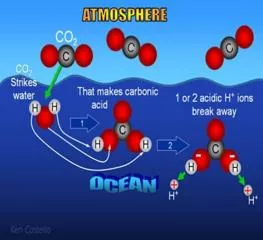
Gases in Ocean Water Three gases found in the ocean are nitrogen (N), oxygen, and carbon dioxide. Oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide(CO2) are necessary for living things found there. Oxygen and nitrogen come from the atmosphere and from algae in the ocean. Algae uses sunlight to carry out photosynthesis, releasing oxygen into the water. Oxygen is more scarce in ocean water than it is in air and is most plentiful near the surface. Carbon dioxide on the other hand, is about 60 times more plentiful in the oceans as in the atmosphere. Algae need CO2 for photosynthesis. Animals such as corals also use CO2 , which provides the carbon to build their hard skeletons.
Temperatures in Ocean Water mini-lab on density differences Ocean temperatures vary; closer to the equator are warmer temperatures, while closer to the poles temperatures are colder. Temperatures decrease with depth. Temperatures are important because they determine how much dissolved oxygen is available for living organisms.
Density Differences Flow : Gulf Stream
Changes with Depth James Cameron's Challenger Deep Dive Temperature Decreases There are 3 different temperature zones in the water column. The 1stzone called the surface (sunlight) zone extends from the surface to about 100-500 meters. Next is the transition (twilight) zone which extends from the bottom of the surface zone to about 1 km down. Temperatures can drop quickly here to as low as 4 C . Finally, is the deep (midnight) zone where temperatures are about 3.5 C or colder. 10000 feet below sea level Ocean Zones
Pressure Increases Water Pressure Experiment Pressure is a force exerted by the weight of water above pressing down. Pressure increases continuously from the surface to the deepest part of the ocean. The average depth of the ocean floor is 3.8 kms. There the pressure is about 400 times greater than air pressure on the Earth s surface. Effects on Human Body scuba diver and pressure clip
Apply what you have learned! For Fun: Cracking Egg under water egg