Nurturing the Future: Exploring the Global Precision Agriculture Market
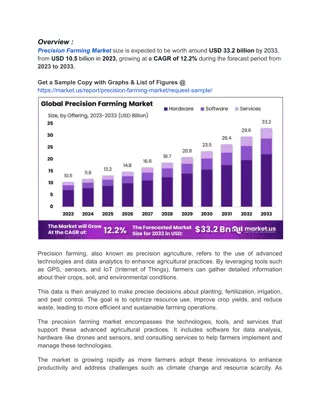
According to a BIS Research report, the Precision Agriculture Market was valued at $9,591.8 million in 2023, and it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.71% and reach $41,265.0 million by 2033 during the forecast period of 2023-2033.
Uploaded on | 2 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Nurturing the Future: Exploring the Global Precision Agriculture Market Precision Agriculture, also known as precision farming or smart farming, is transforming the agricultural landscape by leveraging technology to optimize crop production, minimize resource use, and enhance farm efficiency. By integrating advanced technologies such as GPS, sensors, drones, AI, and data analytics, precision agriculture enables farmers to make data-driven decisions, monitor crop health, and manage field variability with unprecedented accuracy and precision. The global market of precision agriculture is experiencing rapid growth as farmers and agricultural stakeholders embrace digitalization and innovation to address the challenges of feeding a growing population while minimizing environmental impact. The Essence of Precision Agriculture Precision Agriculture represents a shift from traditional farming practices to a more data-driven and technology-enabled approach to agriculture. According to a BIS Research report, the Precision Agriculture Market was valued at $9,591.8 million in 2023, and it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.71% and reach $41,265.0 million by 2033 during the forecast period of 2023-2033. At its core, precision agriculture aims to maximize crop yields, minimize input costs, and optimize resource use by: Site-Specific Management: - Precision agriculture tailors practices to specific field conditions. - Considers variability in soil types, moisture levels, and crop health. - Customizes planting, irrigation, fertilization, and pest management. Data-Driven Decision-Making: - Collects data from satellite imagery, soil sensors, and weather stations. - Analyzes data for actionable insights and recommendations.
- Optimizes farm operations and improves productivity. Automation and Robotics: - Robotics, automation, and autonomous systems revolutionize farm operations. - Perform tasks like planting, spraying, harvesting, and monitoring. - Enhance efficiency, accuracy, and precision. - Reduce labor costs and increase operational efficiency. Want to stay ahead of your competitors? Download FREE Sample PDF report on Precision Agriculture Market Research. Global Precision Agriculture Industry Segmentation Segmentation by Technology Type: - GPS/GNSS Technology - Remote Sensing - Variable Rate Technology (VRT) Segmentation by Application: - Crop Monitoring and Management - Soil Management - Livestock Monitoring Segmentation by End-User: - Large-Scale Farms - Smallholder Farmers - Agricultural Service Providers North America and Europe lead the market, driven by advanced farming practices, strong digital infrastructure, and supportive government policies. Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are experiencing rapid growth, fueled by increasing investment in agriculture, rising awareness of precision farming benefits, and adoption of digital technologies among farmers. Future Challenges and Opportunities While the global market of precision agriculture presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation, several challenges must be addressed, including: Cost and Accessibility: - High initial cost of precision agriculture technologies. - Challenges in connectivity, digital literacy, and infrastructure. - Limits adoption, especially among smallholder farmers and in developing regions. Data Privacy and Security: - Concerns about data privacy, ownership, and security. - Challenges in collection, storage, and sharing of farm data. - Clear guidelines and regulations needed to address concerns and build trust. Integration and Interoperability: - Challenges in integrating diverse precision agriculture technologies. - Issues with compatibility, interoperability, and data exchange. - Standardization efforts and open-source platforms can facilitate integration and collaboration among stakeholders. Conclusion
The Global Precision Agriculture Industry is poised for exponential growth as farmers and agricultural stakeholders embrace digitalization, innovation, and sustainability to address the challenges of feeding a growing population while minimizing environmental impact. By harnessing the power of advanced technologies such as GPS, sensors, drones, and AI, precision agriculture enables farmers to optimize crop production, conserve resources, and enhance farm profitability and resilience. As precision agriculture continues to evolve and expand, stakeholders across the agricultural value chain must collaborate to overcome challenges, bridge digital divides, and unlock the full potential of smart farming for a more sustainable and food-secure future.