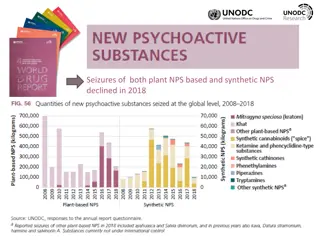
New Psychoactive Substances (NPS) and Their Categories
New Psychoactive Substances (NPS) are substances of abuse not regulated by international drug conventions, posing significant public health risks. These substances can fall under categories like synthetic cannabinoids, stimulants, hallucinogens, and depressants, each with unique risks and effects. Synthetic cannabinoids, for example, can lead to a range of clinical events and health issues, including overdose risks. Recognizing and addressing the dangers associated with NPS is crucial for harm reduction efforts.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
New psychoactive substances (NPS) Eliza Kurcevi Eurasian Harm Reduction Association
Definition of NPS - Substances of abuse, either in a pure form or a preparation, that are not controlled by the 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs or the 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances, but which may pose a public health threat. (UNODC) - A new narcotic or psychotropic drug, in pure form or in preparation, that is not controlled by the United Nations drug conventions, but which may pose a public health threat comparable to that posed by substances listed in these conventions. (EMCDDA) - Narcotic drugs or psychotropic substances made available or used from the early to mid-2000s for their psychoactive properties. These drugs are not scheduled or have only been listed since 2015 under the international drug control conventions of 1961 and 1971, and could pose similar threats to public health as do substances scheduled under these conventions. ( New psychoactive substances: challenges for drug surveillance, control, and public health responses , The Lancet, 2019 Amy Peacock, Raimondo Bruno, Natasa Gisev, Louisa Degenhardt, Wayne Hall, Roumen Sedefov, Jason White, Kevin V Thomas, Michael Farrell, Paul Griffiths)
European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (2020), European Drug Report 2020: Key Issues Summary, Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg.
European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (2020), European Drug Report 2020: Key Issues Summary, Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg.
NPS categories Synthetic cannabinoids Stimulants (synthetic cathinones) Hallucinogens (dissociatives and classic hallucinogens) Depressants (including opioids and benzodiazepines)
Synthetic cannabinoids NAMES: Spice, K2, Kronic, JWH, Black Mamba, Amsterdam Gold, smoking/ herbal mixtures Powders are typically dissolved in solvent, sprayed on inert plant material and then smoked. Could be ingestion of pills or powders, and vaping using solutions containing synthetic cannabinoids. CLINICAL EVENTS: Elevated mood, relaxation, altered perception, agitation, restlessness, anxiety, panic attacks, confusion, tachycardia, hypertension, catatonia, chest pain, heart palpitations, myocardial infarction, stroke, seizure, delirium, psychosis, suicidal ideation, hallucination, hyperthermia, nausea or vomiting, liver dysfunction, renal dysfunction, acute kidney injury, respiratory distress, rhabdomyolysis, more frequent drug use RISK OF OVERDOSE: toxic reactions, seizures, kidney damage, elevated blood pressure, reduced blood supply to the heart DUAL DIAGNOSIS: drug dependence and at least one mental-health disorder
Stimulant NPS (synthetic cathinones) NAMES: bath salts , Mephedrone (Meow Meow, 4-MMC), Methylone, Alpha-PVP, MDPV They are typically in a powder, capsule, tablet, liquid, or crystal form, and are primarily consumed by swallowing or snorting, as well as by injecting and smoking. CLINICAL EVENTS:Increased alertness, energy, confidence, and sociability, and suppression of appetite and fatigue, hypertension, tachycardia, cardiac arrest, chest pain, heart palpitations, headaches, agitation, paranoia, aggression, confusion, nausea or vomiting, anxiety, panic attacks, depression, insomnia, hallucinations, delusions, seizures, kidney injury, paranoid delusions, reduced consciousness, reduced motor control, muscle spasm or tremor, psychosis, mania, serotonin syndrome, increased sex drive (chemsex and slamming), more frequent drug use Risk of HIV, hepatitis, and other infectious diseases from shared needles. DUAL DIAGNOSIS: drug dependence and at least one mental-health disorder
Hallucinogen NPS NAMES: They can be divided into two main types: 1) dissociatives (methoxetamine M-ket, Mexxy, METH-O) and 2) classic hallucinogens (2C drugs, NBOME drugs) Hallucinogen NPS might be a powder, liquid, tablet, or capsule, or on blotter paper, and depending on the drug, are mostly swallowed, snorted, smoked, or injected CLINICAL EVENTS: euphoric, empathetic, altered consciousness, and love, delirium, hallucinations, psychosis, anxiety, paranoia, dissociation, agitation, aggression, seizure, confusion, headache, tachycardia, hypertension, nausea or vomiting, rhabdomyolysis, kidney injury, hyperthermia, frightening perceptions, troubling thoughts or feelings, dizziness, weakness, blurred vision Even moderate doses of NBOME can increase the risk of overdose (intense confusion, severe agitation, seizure, kidney failure, nausea and vomiting, rapid heart rate, rapid or difficulty breathing, overheating, attempted suicide)
CNS depressant NPS Names: 1) Opioids (fentanyl, carfentanyl) and 2) benzodiazepines (etizolam, phenazepam) These NPS can be sold under their own name but have also been detected as counterfeit prescription medicines (eg, in tablets or capsules), or adulterated with or sold as more established illicit drugs (eg, in powder form). They are mostly swallowed, snorted, injected or placed on the skin (skin patch). CLINICAL EVENTS: Pain relief and sedation, respiratory and CNS depression, respiratory arrest, reduced consciousness, disorientation, confusion, tachycardia, hypertension, nausea or vomiting, psychosis, delirium, hallucinations, anxiety, agitation, depression, paranoia, aggression When people overdose on fentanyl, their breathing can slow or stop. This can decrease the amount of oxygen that reaches the brain, a condition called hypoxia. Hypoxia can lead to a coma and permanent brain damage, and even death.
Access to Naloxone (medication used to reverse the effects of an opioid, or synthetic opioid, overdose) Supervised injection facilities On- and off- site drug checking services Comprehensive drug education Clinical management and protocols Harm reduction strategies Sexual health settings Low threshold settings and drop-in centers (the provision of sterile injection equipment/kits, condoms, as well other drug use equipment (pipes for smoking, etc.) and the dissemination of information on safe drug use Peers involvement Psychosocial support: integration of psychologists, psychotherapists to the harm reduction teams Pharmacological interventions