Motion: Speed vs. Velocity in Physics
Differences between speed and velocity in physics, focusing on magnitude and direction. Learn about motion maps, acceleration, forces at play, and practice problems to enhance your understanding of these important concepts in physics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Review Choose A = Speed B = Velocity Magnitude and direction Scalar Vector Magnitude only
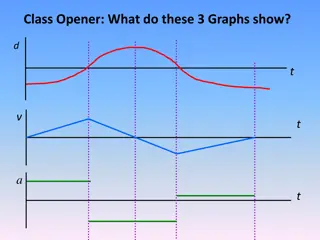
What is a motion map? A motion map represents the position, velocity, and acceleration of an object at various clock readings. Represents position and velocity only. It s like taking a snapshot photo of a moving object. Each image reveals the position of the object at one-second intervals.
How fast an object changes is its velocity. Three ways for Acceleration to occur: 1. Object Speeds up , + acceleration) 2. Object Slows down, - acceleration) 3. Object Changes direction Is the slope of a velocity vs. time graph
Vf - Vi time The unit for acceleration is calculated by dividing the unit for velocity (m/s) by the unit for time (s) You get m/s/s , we write m/s2 we say meters per second squared
A force that pulls us downward toward the center of the Earth. Falling objects accelerate DOWNWARD at the rate of gravity, or 9.8 m/s2.
In distance vs. time graphs, acceleration is displayed with a curve, because it is gradual. D D t t + or - acceleration + or acceleration?
Practice Problems A. If an object starts from rest and accelerates to 60 m/s in 10 seconds, what was the acceleration? B. What is the acceleration of a bus that increases its speed by 14m/s in 4 seconds?
Practice Problems C. A biker starting from rest reaches a final speed of 3.0 m/s in 3 seconds. What is the acceleration of the biker? D. The fastest land mammal, the cheetah, can accelerate at a rate of 30 m/s/s. How fast will the cheetah be going after 2 seconds if the cheetah started from rest?
Practice Problems E. A rocket ship is traveling at 18,000 m/s when it turns on its rocket thrusters. After 50 seconds the space ship has reached a speed of 28,000 m/s. What is the ship s acceleration? F. A roller coaster has a velocity of 40 mi/hr at the bottom of the hill. It slows to a velocity of 12 mi/hr during the 7 seconds it takes to reach the top of the next hill. What is its acceleration?