Molecular Advances in Phytosystematics Course Overview
Phytosystematics is a science focusing on plant taxonomy and classification, aiming to establish evolutionary relationships among plant species. Scientists use genetic analysis and physical characteristics to group plants into related taxa. Functional evolution, parallelism, and rapid divergence influence common traits. Key features like vessel presence, petal characteristics, and fruit types aid in plant identification. Conservative organs remain relatively unchanged over time, aiding in taxa differentiation. Vegetative characters are crucial in classifying lower plants. Effective taxonomy relies on characters of high taxonomic value.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Class MS Class MS Semester II Semester II Course Title: Molecular advances in Phytosystematics Course Title: Molecular advances in Phytosystematics Instructor: Dr. Instructor: Dr. Arusa Arusa Aftab Aftab Department of Botany Department of Botany Lahore College for Women University Lahore Lahore College for Women University Lahore
Phytosystematics is a science within botany, including traditional taxonomy, and it is a study nomenclature and classification of plants. Its main goal is to establish a system that reflects evolutionary relationships between various plant species and plant groups. of the description, identification,
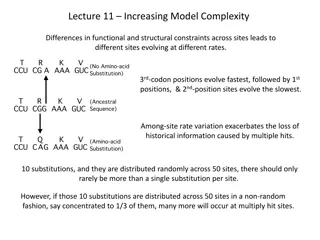
Classification scientists group the plants into related taxa. plants are classified based on how similar they are. Historically, examining the physical characters of plants but modern classification uses variety of techniques including genetic analysis. is the process by which similarity was determined by
All those characters which have well defined and obvious function and strongly selected during evolution Functional evolution parallelism and extremely rapid divergence in many cases so possession of such characters in common is not a good decision. group the channelized form during in of convergence,
Presence of vessels in gymnosperms and pteridophytes Lack or fusion of petals Explosive fruits
Conservative organs and characters are those which tend to remain unchanged for long period development . So it is particularly used for the identification of different member of taxa. But a conservative character vary from one taxon to another. of time during the evolutionary
For example in lower plants as flowering is less and reproductive organs are short lived so classification as compare to the angiosperm. vegetative characters are used for
Those characters which have high taxonomic value are good characters Those characters which have lessesr taxonomic importance known as bad character. Good character of one taxon is may be a bad character for other taxon As lysine synthesis pathway in plants and fungi is quite different so they placed in different sub kingdoms. animals some bacteria. Some bacteria and traditional fungi show the same pathway as plants so classification base on single character is not a good idea. Slime as both do not synthesis lysine but molds resembles with the
So important and should keep in consideration as structure, carbohydrates reserve and nucleic acid etc. But some characters have grate importance in higher hierarchy like ovary position ( superior or inferior) in angiosperms. As it remain same in species of same taxa. different variable characters are also cytoplasm ultra structure, wall flagella cell constituents,
Speciation , the process for the formation of new species by evolution is usually done by two ways Abrupt speciation Gradual speciation
In gradual speciation changes occur due to gradual change in a species due to some factors such as recombination , mutation and selection . Ecotypication and evolution of geographical races are early stages of speciation . During genetic interbreed become isolated this incompatibility, and process subgroups and evolve unable genetically a to specially and
In genetically chromosome difference. Alloploidy is the best known process for abrupt change as it change the phenotype of plant. Hybridization is also a process for abrupt change. abrupt speciation may number initial due isolation change chromosome is in be to or
Four different methods are used to deduce phylogenetic pathway like Fossil evidence Phenetic data Chemical and ultrastructure data Cladistics data All these are used to construct evolutionary classification .