Modern Organizational Structure for Today's Challenges
Explore the evolution of organizational design, from Fayol's principles to modern approaches focusing on customer satisfaction and rapid change management. Learn about key concepts such as division of labor, job specialization, and managing resources effectively in response to dynamic market demands.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Structuring Organizations for Today s Challenges Chapter 8
Building or Reorganizing from the Bottom Up
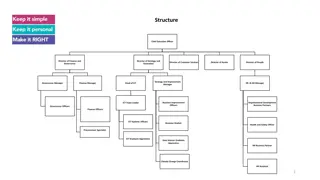
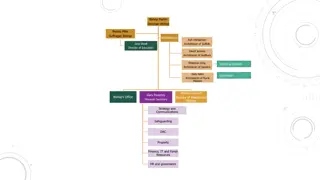
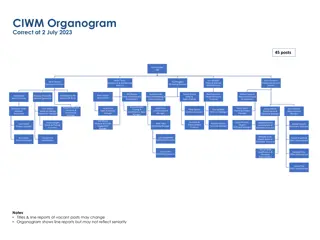
Structuring an Organization Division of Labor: dividing tasks among workers Job Specialization: dividing tasks into smaller jobs Departmentalization: creating individual departments for specialized tasks Assigning authority and responsibility Resource allocation Designing procedures to accomplish goals Aided by an organizational chart
Managing Change More rapid than ever before Customers, Technology, Global Business environment Past: companies structured to manage employees Modern: companies structured to please the customer
Fayols Principles of Organization Before the 20thcentury, most businesses were small, and relatively easy to manage and organize Mass production and economies of scale 1919 published General and Industrial Management Popularized after WWII in the US
Organizational Principles Unity of Command: worker reports to one boss Hierarchy of Authority: workers should know to whom they report to Division of Labor: functions divided into areas of specialization The general interest is greater than the individual interest Authority (and responsibility) Degree of Centralization Clear communication channels Order: materials and people maintained in right place Equity: employees deserve to be treated with respect and justice Esprit de corps
Weber and Organizational Theory The Theory of Social and Economic Organizations Company works most efficiently when workers are just told what to do Less decision-making the better Uneducated and untrained workers Similar ideas to Fayol s, plus: Job descriptions Written rules, decision guidelines, and detailed records. Consistent procedures, regulations, and policies. Staffing and promotion based on qualifications.
Structuring an Organization: Organizational Chart Hierarchy Chain of Command assigning authority and responsibility Division of Labor: dividing tasks among workers Job Specialization: dividing tasks into smaller jobs Departmentalization: creating individual departments for specialized tasks Bureaucracy
Reducing Bureaucracy Empowerment of employees
Centralized vs Decentralized authority Decision-making from the top or delegating to lower managers
Store manager has authority to buy, price, and promote merchandise Why?
Span of Control How many people should a manager supervise? Depends on levels of Standardization of jobs Less standardization means less span of control However, empowering workers allows for broader span of control Also, more educated workers Information technology
Tall (Mechanic)vs Flat (Organic) Hierarchy Level of hierarchy Layers and number of managers Level of empowerment
Departmentalization options Function Product Customer Group Geographic location Process Hybrid
Function (Traditional) President Finance HR Acct. Production Mktg
Product Johnson & Johnson: https://www.jnj.com/healthcar e-products CEO Consumer Products Medical Devices Pharmaceuticals Mk Prd Fin Mk Prd Fin
Consumer group / Market CEO Commercial Residential Govern ment Agric. Mk Prd Fin Mk Prd Fin
Geography CEO EMEA Latin Am. N. Amer. Asia Pac.
Process CEO Customer Acquisition Order Fulfillment R&D
Line Direct two-way lines of responsibility, authority, and communication running from the top to the bottom of the organization Reporting to one supervisor No specialists to provide support to managers No legal, accounting, HR, or IT
Line-and-Staff Line: responsible for directly achieving organizational goals Staff: advice and assist