Microcontrollers: Definition, Working, and Elements
A microcontroller (MCU) is a compact integrated circuit essential for embedded systems, controlling specific operations. This article delves into the definition, functioning, and key elements of microcontrollers, such as the processor, memory, and I/O peripherals. Explore how microcontrollers work, their applications, and the vital components that make them function effectively.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
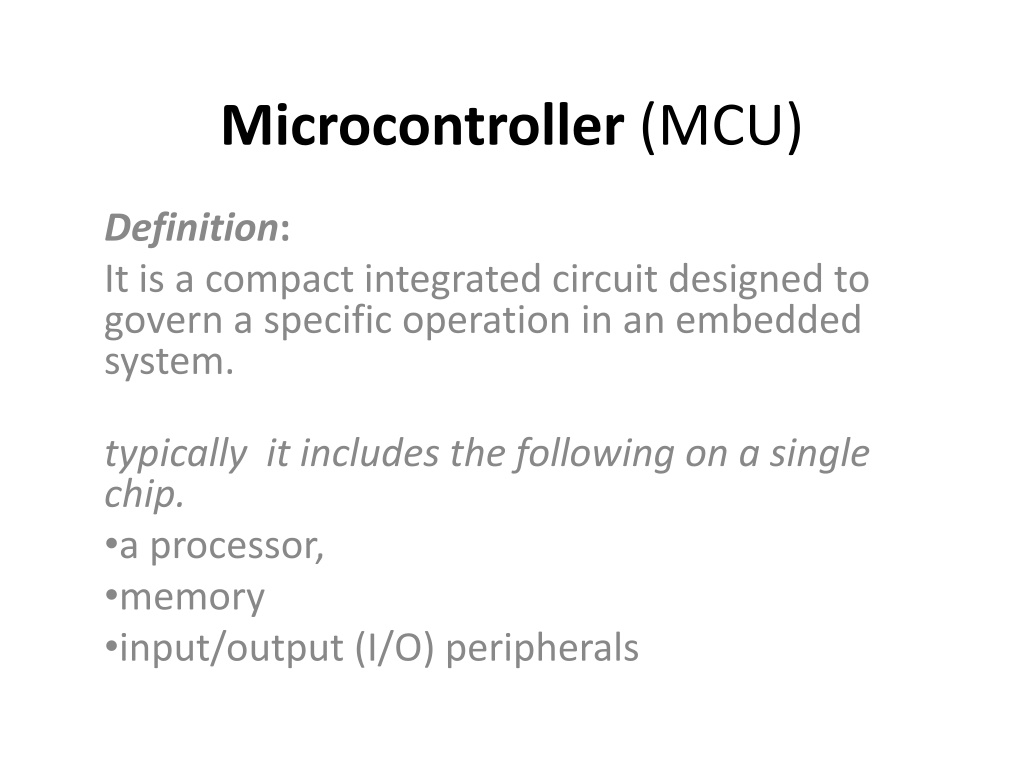
Microcontroller (MCU) Definition: It is a compact integrated circuit designed to govern a specific operation in an embedded system. typically it includes the following on a single chip. a processor, memory input/output (I/O) peripherals
Microcontrollers Also know as embedded These are simple miniature personal computers (PCs) designed to control small features of a larger component are found in vehicles, robots, office machines, medical devices, mobile radio transceivers, vending machines and home appliances etc.
How do microcontrollers work? How do microcontrollers work? It is embedded inside of a system to control a singular function in a device. It works by interpreting data it receives from its I/O peripherals using its central processor. The temporary information it receives is stored in its data memory, where the processor accesses it and uses instructions stored in its program memory to decipher and apply the incoming data. It then uses its I/O peripherals to communicate and enact the appropriate action.
Elements of a microcontroller Elements of a microcontroller 1. The processor (CPU) -- A processor can be thought of as the brain of the device. -- It processes and responds to various instructions . -- This involves performing basic arithmetic, logic and I/O operations as well as data transfer operations.
2. Memory -- is used to store the data that the processor receives . Two main memory types: a) Program memory: This stores long-term information about the instructions that the CPU carries out. -- It is a non-volatile memory. b) Data memory: This is required for temporary data storage while the instructions are being executed. Data memory is volatile,
3. I/O peripherals -- The input and output devices are the interface for the processor to the outside world. -- The processor receives that data and sends the necessary instructions to output devices that execute, tasks external to the microcontroller.
Microcontroller features Microcontroller features vary by application. Options range from the simple 4- bit, 8-bit or 16-bit processors to more complex 32-bit or 64-bit processors. Microcontrollers can use volatile memory types such as random access memory (RAM) non-volatile memory types eg programmable read-only (EEPROM). flash memory, erasable memory (EPROM) and
Microprocessor It is a controlling unit of a micro-computer, fabricated on a small performing ALU (Arithmetic Logical Unit) operations and communicating with the other devices connected to it. chip capable of Microprocessor consists of an ALU, register array, and a control unit.
Elements of a Microprocessor Elements of a Microprocessor
How does a Microprocessor Work? The microprocessor follows a sequence: Fetch, Decode, and then Execute. The instructions are stored in the memory in a sequential order. The microprocessor fetches those instructions from the memory, then decodes it and executes those instructions till STOP instruction is reached. Later, it sends the result to the output port
Difference between Microcontroller and Microprocessor Microcontroller and Microprocessor both terms seem similar but there is a huge difference between these two ICs. Microprocessor only have CPU in the chip like most of the Intel Processors but Microcontroller also have RAM, ROM and other peripherals along with the CPU or processor. Both ICs have different applications. They can be differentiated in terms of Applications, structure, internal parameters, power consumption, and cost
Applications of Microprocessor and Microcontroller The microprocessor used in : an application where the task is not predefined and it is assigned by the user. in computers, mobiles, video games, TVs, etc where the task is not fixed and it depends on the user. where intensive processing is required.
Applications of Microprocessor and Microcontroller The microcontroller: The microcontroller: is designed for a specific task and once the program is embed on MCU chip, it can t be altered easily. The according to its application. Hence, it does some processing, based on the input given to the microcontroller and gives the predefined results as an output. process of the microcontroller is fixed
Microprocessor Development Tools Software Tools Assembler Linker Loader Compiler Libraries Pre-compiled IP Simulator IDE
Hardware Tools In Circuit Emulator (ICE) Logic Analyzer Microprocessor Development Systems System Development Systems