Mastering Pronouns: A Comprehensive Guide
Understand the nuances of pronoun usage with this detailed guide, covering pronoun cases, usage in questions and clauses, compound structures, elliptical constructions, pronoun-antecedent agreement, and more. Enhance your writing skills by mastering pronoun rules and applications.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Everyday Writer Andrea A. Lunsford PRONOUNS
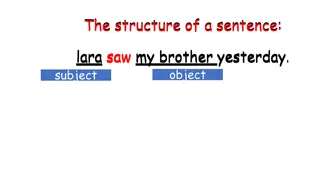
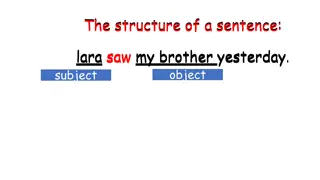
PRONOUN CASE Pronouns acting as subjects are in the subjective case; those acting as objects are in the objective case; those acting as possessives are in the possessive case. She was passionate about recycling. The boss surprised her with a big raise. The sound of his voice came right through the walls.
WHO, WHOEVER, WHOM, AND WHOMEVER In questions, answer the question using a personal pronoun. If the answer is he, she, or they, use who; if it is him, her, or them, use whom. Who did you visit? I visited them. Whom Who Whom do you think wrote the story? I think she wrote the story.
WHO, WHOEVER, WHOM, AND WHOMEVER In dependent clauses, determine its purpose in the clause. *Trick if you can put a person s name in, use who; if not, use whom. who Anyone can hypnotize someone whom wants to be hypnotized. John wants to be hypnotized. whomever The minister smiled at whoever she greeted. John she greeted (???)
CASE IN COMPOUND STRUCTURES Take the other words out to see what case it should be. her The boss invited she and her family to dinner. The boss invited she to dinner???? me Come to the park with Ann and I. Come to the park with I?????
CASE IN ELLIPTICAL CONSTRUCTIONS When an elliptical construction (words are understood and left out) ends in a pronoun, put the pronoun in the case it would be in normally. His sister has always been more athletic than he [is]. Willie likes Lily more than she [likes Willie].
WE AND US BEFORE A NOUN How would it sound without the noun? We Us fans never give up hope. Us never gives up hope???? us The Rangers depend on we fans. The Rangers depend on we???
PRONOUN-ANTECEDENT AGREEMENT Pronouns and antecedents (the words they replace) agree when they match up in person, number, and gender. The boys picked up their music. The audience fixed its attention on center stage. One of the ballerinas lost her balance. Some of the furniture was showing its age.
CLEAR PRONOUN REFERENCE Ambiguous antecedents the bridge The car went over the bridge just before it fell into the water. Vague use of it, this, that, and which and being late My mother forgot to wake me up, and I was late for class which made me mad.
CLEAR PRONOUN REFERENCE Indefinite use of you, it, and they people Commercials try to make you buy without thinking. Possessive antecedents Alexa her In Alexa s formal complaint, she showed why the test was unfair.