Magnetism: Introduction to Key Concepts
Delve into the fundamentals of magnetism with a focus on magnets, magnetic fields, and induced vs. permanent magnets. Explore the concepts of attraction, repulsion, magnetic materials, and the behavior of different metals in the presence of magnets. This lesson sets the foundation for a deeper understanding of electromagnetic principles.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
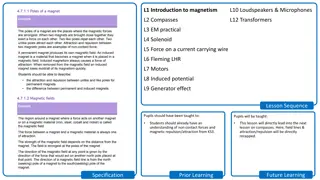
L1 Introduction to magnetism L10 Loudspeakers & Microphones L2 Compasses L12 Transformers L3 EM practical L4 Solenoid L5 Force on a current carrying wire L6 Fleming LHR L7 Motors L8 Induced potential L9 Generator effect Lesson Sequence Pupils should have been taught to: Pupils will be taught: Students should already have an understanding of non contact forces and magnetic repulsion/attraction from KS3. This lesson will directly lead into the next lesson on compasses. Here, field lines & attraction/repulsion will be directly recapped. Future Learning Specification Prior Learning
SciDoc Introduction to magnetism Introduction to magnetism Last Lesson Last Term Last Year Stretch & Challenge I do We do You do Do Now Test I do We do You do Do Now
SciDoc Introduction to magnetism Introduction to magnetism Keywords Learning Objectives Keywords Repel Attract North South Pole Permanent Induced Field Recall that like poles repel and unlike poles attract. Describe the difference between an induced magnet and a permanent magnet. Draw the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet. I do We do You do Do Now Test I do We do You do Do Now
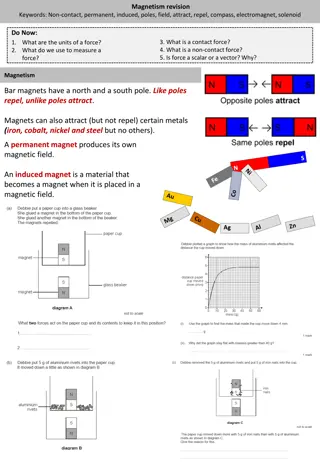
SciDoc T/N: Magnets T/N: Magnets Bar magnets have a north and a south pole. Like poles repel, unlike poles attract. Stretch: Do the magnets below attract or repel? I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
T/N: Magnetic metals T/N: Magnetic metals Magnets can also attract (but not repel) certain metals (iron, cobalt, nickel and steel but no others). SciDoc Stretch: Stretch: Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. Will it feel a larger or smaller magnetic force than the same amount of iron? Why? Ag I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
A permanent magnet produces its own magnetic field. SciDoc An induced magnet is a material that becomes a magnet when it is placed in a magnetic field. Stretch: What is the equation that links word done, force and distance? A magnet exerts a force of 3N over a distance of 5cm. How much work is done? I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
A magnetically soft material loses its induced magnetism. SciDoc Stretch: Are the nails below soft or hard? Why? A magnetically hard material will retain some of its magnetism. I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc What is a magnetic field? What is a magnetic field? The region around a magnet where it has a magnetic effect is called its magnetic field. When a magnetic material is placed in a magnetic field it will experience a force. N S The iron filings feel the effect of the magnetic field and show the direction of the forces in this region. I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Stick in the diagram Stick in the diagram Stretch: The magnetic field is strongest where the field lines are closest together. strongest field at poles strongest field at poles S N Where is the magnetic field strongest? Label this on your diagram. Super stretch: What does the magnetic field look like if two north poles are next to each other? weakest field further away from poles I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Task Task Complete the worksheet I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Basic answers Basic answers 1. 1. Non Non- -contact force. contact force. 2. 2. Newton. Newton. 3. 3. Like poles repel, unlike poles attract. Like poles repel, unlike poles attract. 4. 4. Iron, cobalt, nickel (and steel). Iron, cobalt, nickel (and steel). 5. 5. Bar magnet. Bar magnet. 6. 6. Magnetic field lines. Magnetic field lines. 7. 7. North on left hand side, South on right hand side (field North on left hand side, South on right hand side (field lines flow from North to South). lines flow from North to South). I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Medium answers Medium answers 8. a) False 8. a) False 9. Near the poles. The magnetic field lines are closest 9. Near the poles. The magnetic field lines are closest together. together. 10. A permanent magnet produces its own magnetic field. 10. A permanent magnet produces its own magnetic field. 11. An induced magnet is a material that becomes a magnet 11. An induced magnet is a material that becomes a magnet when it is placed in a magnetic field. when it is placed in a magnetic field. 12. Attraction. 12. Attraction. 13. They go into the shape of the magnetic field lines. 13. They go into the shape of the magnetic field lines. b) False b) False c) True d) False e) True c) True d) False e) True I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Hard answers Hard answers 14. Bar number 2. 1 and 3 repel each other; iron cannot be repelled by a magnet. 15. 16. a) Both are non-contact forces. Both forces get weaker the further away objects are. Magnetism can be repulsive, gravity is only attractive. Mass causes force of gravity, magnetic materials cause magnetism. b) Both are non-contact forces. Both forces get weaker the further away objects are. Both can be attractive or repulsive. Electric charges cause electrostatic forces, magnetic materials causes magnetism. I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Struggle time! Struggle time! Exam question so exam conditions! You have 10 minutes. I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Like poles repel [1] So the box wouldn t close [1] I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc As paper increases decrease in force needed [1] Force levels off after 50 sheets [1] I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Newtonmeter shows the weight of the top magnet. Top magnet and newtonmeter separate before magnets separate [1] Force between magnets is greater than force between magnet and hook [1] I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc 30 sheets of paper. [1] 30 0.1 [1] = 3 mm [1] I do We do You do LO: Test I do We do You do LO: