Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Radiology
MRI is a powerful diagnostic tool utilizing magnetism, radio waves, and a computer to generate detailed images of body structures. Discover the importance of protons in MRI, its historical significance, key components, and working principles.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
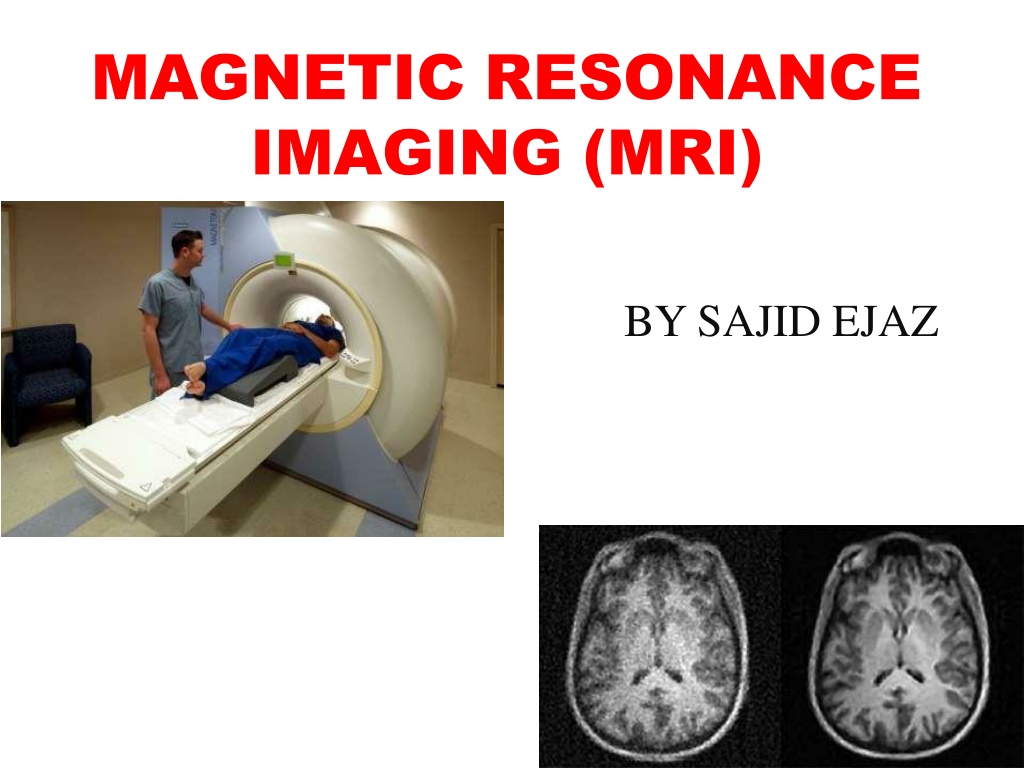
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) BY SAJID EJAZ
INTRODUCTION MRI is a technique in radiology which uses magnetism, radio waves and a computer to produce images of body structures. Human body is mainly composed of fat and water, which makes the human body composed of about 63% hydrogen Why Are Protons Important to MRI? Positively charged. Spin about a central axis. A moving (spinning) charge creates a magnetic field. The straight arrow (vector) indicates the direction of the magnetic field.
USES MRI scans are used as an extremely accurate method of detecting disease throughout the body. Head trauma, Brain Aneurysms, Stroke, Tumors of the brain, and Spine tumors, are all abnormalities that are detected by a MRI scan.
HISTORY The first MRI image was published in 1973. The first studies perform on human were published in 1997. Created by Dr Raymond V. Damadian, Dr.Larry Minkoff and Dr.Michael Goldsmith. In 2003,the 2003 nobel prize in physiology or medicine was awarded to paul C Lauterbur and peter mansfiled. Made new mr imaging techniques. Faster and more effcinet
COMPONENTS A magnet which produces a very powerful uniform magnetic field. Gradient Magnets which are much lower in strength. RF Coils to transmit radio frequency. A very powerful computer system, which translates the signals transmitted by the coils.
THE MAGNET The most important component of the MRI scanner is the magnet: The magnets currently used in scanners today are in the 0.5 T to 2.0 T range (5,000 to 20,000- gauss). Higher values are used for research(up to 9T. While Earth magnetic field: 0.5-gauss
GRADIENT MAGNET These magnets have a much lower magnetic field and are used to create a variable field.
RF COILS Transmission of radio frequency
PRINCIPAL OF MRI Spinning Atoms (hydrogen) face outside magnetic field. Energy Absorption by RF Coils. Resonance of Hydrogen atoms Measured by RF antenna which the received signal is sinusoidal in shape. Imaging by The computer which receives mathematical data, which is converted through the use of a Fourier transform into an image.
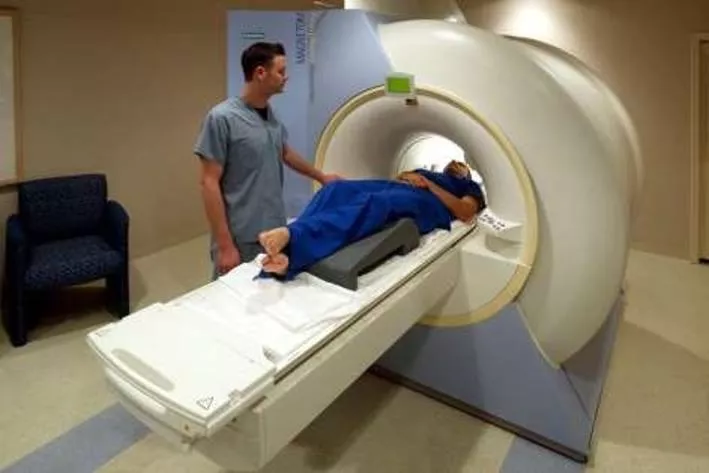
HOW DOES THE MRI WORK Put subject in big magnetic field. Transmit radio waves into subjects. Receive radio waves that has been re- transmitted by the subject. Store the data &repeat step 2. Process raw data to reconstruct images. Getting high resolution image.
When placed in a large magnetic field, hydrogen atoms have a strong tendency to align in the direction of the magnetic filed Inside the bore of the scanner, the magnetic field runs down the center of the tube in which the patient is placed, so the hydrogen protons will line up in either the direction of the feet or the head. The majority will cancel each other, but the net number of protons is sufficient to produce an image.
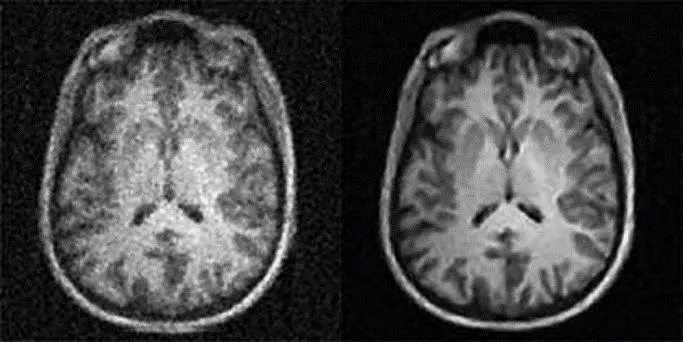
BASIC MRI SCANS T1-weighted: Differentiate fat from water. Water is darker,fat is brighter. Provide good grey matter/white matter contrast in brain. T2-weighted: Differentiate fat from water. Fat shows darker,and water lighter. Good for imaging edma. Abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin or in one or more cavities of the body.
ADVANTAGES Provide very detailed diagnostic pictures of most of the important organs and tissues in your body. Ability to diagnose, visualize, and evaluate various illnesses. Are generally painless. Did not use radiation and are therefore suitable for use in children and pregnant women.
DISADVANTAGES Limited availability. It is a lengthy procedure eg, a pituitary gland MRI scan can take up to 30 minutes . MRI scanning cannot be performed in the presence of foreign bodies or metallic implants eg,pacemakers . It is relatively expensive compared with other forms of imaging.