Lessons Learned and Benefits in Early Childhood Data Systems
This presentation explores the importance of integrated data systems in early childhood education, emphasizing the need for linking data across different programs. It highlights the challenges of separate data systems and the benefits of an Integrated EC Data System. The status of state data systems for Early Intervention and Early Childhood Special Education is also discussed, pointing out the need for improved data linkages.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Center for IDEA Early Childhood Data Systems Including Early Intervention in Early Childhood Integrated Data Systems: Lessons Learned and Benefits Realized Stockholm Sweden, June 2016 Missy Coffey Cochenour, M.A. Kathleen Hebbeler, Ph.D Abby Schachner, Ph.D
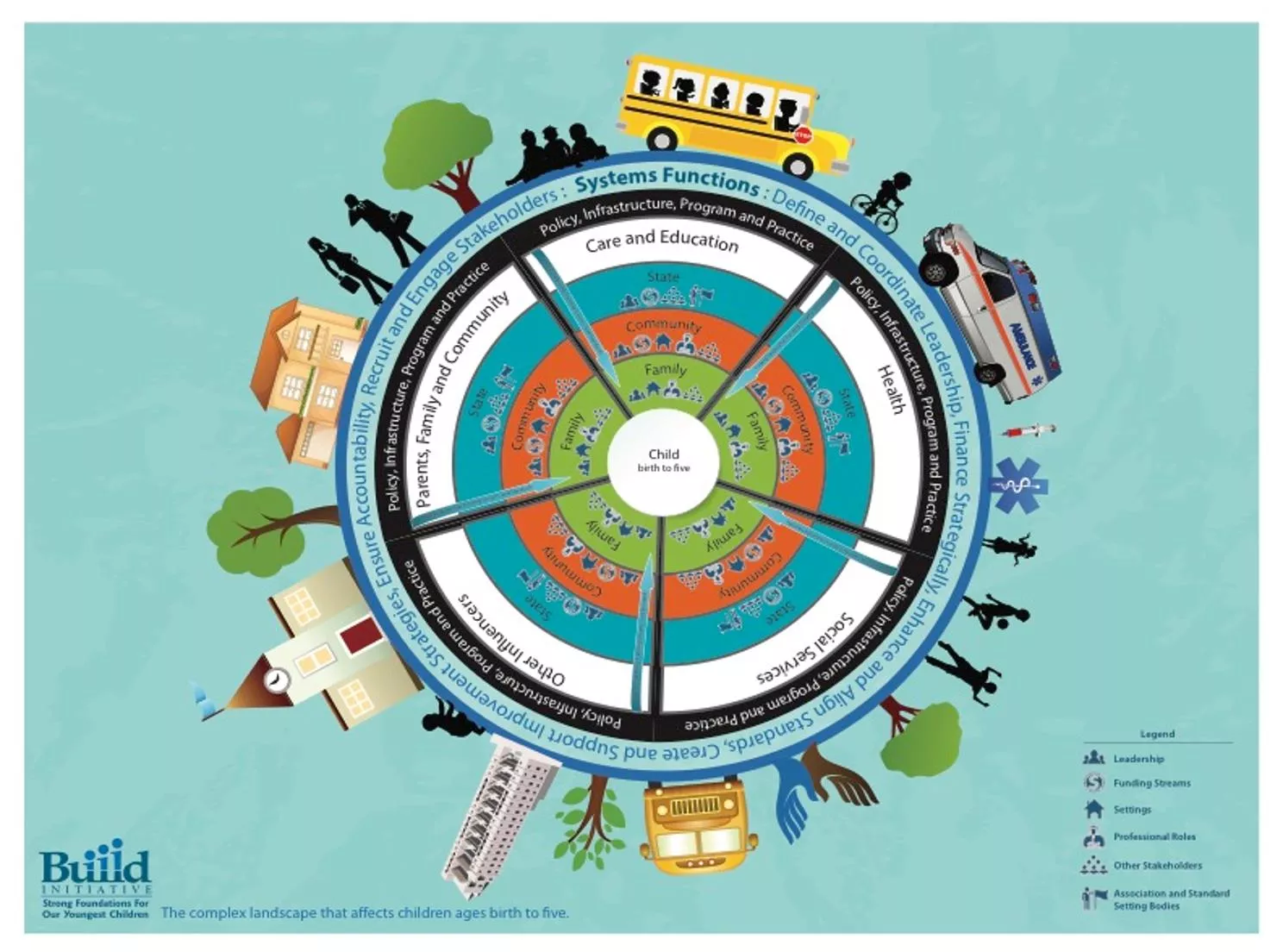
12,499,000 children under the age of 5 are in a regular child care arrangement 771,049 children enrolled in Head Start each year Over 150,000 children are enrolled in Early Head Start 2 2 http://www.buildinitiative.org/Portals/0/Uploads/Documents/SystemsDiagram.pdf
Understanding Early Intervention (EI) Early Childhood Special Education (ECSE) in the U.S. 3
What are the consequences of separate programs with separate data systems? We do not know: How many children with disabilities are being served in multiple programs How many children are served across all programs Important questions about early childhood education across programs cannot be answered without integrated data E.g., Which children with disabilities attend high-quality early childhood programs and services? 4
What is an Integrated EC Data System? Collects, integrates, maintains, stores, and reports information from multiple early childhood programs Includes data on the individual child, the family, the classroom, the program/providers, and other services Reference: https://slds.grads360.org/#communities/pdc/documents/4441 5
Status of State Data Systems for EI and ECSE Because EI (0-3) and (3-5) are separate programs, they also have a need to link data Online needs assessment developed by DaSy workgroup Completed by state early intervention Early Childhood Special Education coordinators Asked about status of data systems 6
Status of State Data Systems for EI and ECSE Data on children, programs, workforce are contained in different data systems Often, not even all data on children reside in the same data system Only about one-third of states have linked data across EI and ECSE Linkages with K12 education data are more common for ECSE than for EI 7
Status of State Data Systems for EI and ECSE: Linking across the system For EI, few states have linkages with other EC data, and for ECSE, almost half have linkages with state Pre-K Linkages with health data are more common for EI than for ECSE Only few states have linked EI or ECSE data to social services data Abbreviations: SCHIP = State Children s Health Insurance Program; WIC/SNAP = Women, Infants, and Children/Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program. 8
EI and ECSE link with multiple programs Note: The thickness of the lines represents the relative proportion of states with linkages. 9
Multiple Benefits of Having Integrated Data Data systems serve multiple purposes: Accountability Program operations Program improvement Knowledge development 10
Benefit: Program Operations Children transition to ECSE at 36 months How many children will be turning 3 in next 6 months? How many of these children have had a transition plan developed? How many of these children have had an evaluation completed? How many of these children are eligible for 3-5 services? Benefits: Improved management of transitions Better transitions for children and families 11
Benefit: Program Improvement Children are served in multiple programs meaning multiple influences on child outcomes What are the outcomes for children with various combinations of services and programs (e.g., child care and EI)? Do some combinations produce poorer or stronger outcomes than others? What needs to be done to improve less effective programs/services so that all children experience good outcomes? 12
Benefit: Knowledge Development Linking 0-3 data to 3-5 data to K-12 data provides answers to critical questions such as: How many children who receive 0-3 services receive special education services between 3-5, in kindergarten, in third grade, in eighth grade, etc.? How many children who received EI or ECSE were reading on grade level in Grade 3? What are their characteristics? What are the characteristics of the services they received as young children? 13
General Lessons Learned Privacy and confidentiality issues are challenging An ECIDS does not replace effective program-level data systems in fact, it requires one There has been a cultural shift from data for data s sake to one of using data for: Accountability Program operations Program improvement Knowledge development 14
Integrating EI/ECSE with Other Programs Multiple layers of decisions need to be made in developing an ECIDS (e.g., data governance, structure of data system) Development of an ECIDS requires ongoing stakeholder engagement from programs that are potential data contributors. Some programs may not be ready to share data in the early phases but might be ready later Minimal research on the state-level data driven decision making for states to use in building an ECIDS (e.g. collaboration, data literacy skills, data anxiety and self-efficacy) 15
Resources ECIDS Toolkit http://dasycenter.org/2014-early-childhood-integrated-data-systems-ecids- toolkit-2/ What is an ECIDS https://nces.ed.gov/programs/slds/pdf/whatisanecids.pdf DaSy Framework http://dasycenter.org/resources/dasy-framework/ DaSy Needs Assessment Report http://dasycenter.org/idea-part-c-and-part-b-619-state-data-systems-current- status-and-future-priorities/ 16
For More Information Visit the DaSy website at: http://dasycenter.org/ Visit the State Longitudinal Data System State Support Team website at: https://nces.ed.gov/programs/slds/techassistance.asp Email us: Missy Coffey Cochenour missy.cochenour@aemcorp.com Kathleen Hebbeler kathleen.hebbeler@sri.com Abby Schachner abby.schachner@sri.com 17
References 1. Child care services statistics retrieved from http://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2013/demo/p70- 135.pdf Head Start Services statistics retrieved from http://eclkc.ohs.acf.hhs.gov/hslc/data/pir Early intervention and early childhood special education statistics retrieved from http://www2.ed.gov/about/reports/annual/osep/2015/parts-b-c/37th-arc-for-idea.pdf Cochenour, M., Chatis, C., Irvine, S., Sellers, J., and Duarte, S. (2014). What is an Early Childhood Integrated Data System? U.S. Department of Education. Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics. Retrieved from https://slds.grads360.org/#communities/pdc/documents/4441 Derrington, T., Spiker, D., Hebbeler, K., & Diefendorf, M. (2013). IDEA Part C and Part B 619 state data systems: Current status and future priorities. Menlo Park, CA: SRI International. Retrieved from https://slds.grads360.org/#communities/pdc/documents/4441 2. 3. 4. 5. 18
The contents of this presentation were developed under a grant from the U.S. Department of Education, #H373Z120002. However, those contents do not necessarily represent the policy of the U.S. Department of Education, and you should not assume endorsement by the Federal Government. Project Officers, Meredith Miceli and Richelle Davis. 19