Kinematics and Free Fall Physics Concepts for Test Preparation
Lab homework due tomorrow. First test next Thursday covers graphs of motion and 1D kinematics with multiple choice questions and kinematic problems. Understand the three main kinematic equations for constantly accelerated motion and gravitational acceleration. Learn about free fall and solve a free fall example. Test your understanding by answering questions on object motion under gravity. The content includes explanations, examples, and solutions to help you prepare effectively.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
General announcements Please turn in lab HW for tomorrow is posted on class Website. First test is next Thursday 9/5 will cover graphs of motion and 1D kinematics See class Website class pdfs 1D Kinematics for more (e.g. multiple choice questions, more practice problems) plus your textbook Expect: 4-5 multiple choice, some graph analysis, and 2-4 kinematic problems that will require ALL 3 equations (know them!) Come talk to me today or tomorrow if you receive extra time Chipotle night tonight from 5:30-7
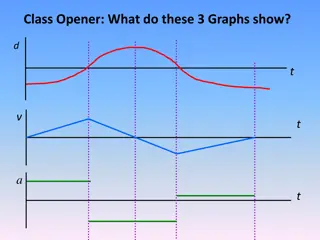
Using kinematic equations 3 main kinematic equations for constantly accelerated motion: ( )+1 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2= v1 2+2a x2-x1 2 x2= x1+v1Dt 2a Dt v2= v1+a Dt v2 YOU need to know these for the test. Remember: x is position (x1means position at time 1, etc) change in position (x2 x1) is displacement during time ? (t2 - t1) + sign means in the + direction; - sign means in the direction **** negative acceleration does not have to mean slowing down!!! If in free fall, a = -9.8 m/s2the whole time, assuming up is positive.
Free fall A special case of kinematics is for objects moving under the influence of gravity only An object affected by only gravity is said to be in free fall By the way, it doesn t actually have to be falling down to be in free fall just free of any other influences For now, we ll consider the effects of air resistance to be insignificant and therefore ignore it Question: if I drop a heavy object and a light object from the same height, which one will hit the ground first? Test it! Test it!
Gravitational acceleration Gravity causes objects to accelerate If we re close to sea level, we consider the Earth s gravitational acceleration to be constant For our purposes, we will assume the magnitude of this acceleration is always g = 9.80 m/s2and it always points towards the Earth s center (so if + is up) Next unit, we ll talk about why! ag=-9.8? m/s2 Some notes: Final velocity (at ground) is NOT zero! Velocity at the top is ?
Free fall example #1 Wile E. Coyote steps off a cliff after giving up pursuit of the Roadrunner (we ll assume his initial velocity is essentially 0 m/s). After 3.5 seconds, he hits the canyon floor below. How tall is the cliff, and how fast was he going when he hit the ground?
Free Fall Example #1 - solution Where is the reference point and which direction is positive? Where is the reference point and which direction is positive? Origin is at the bottom of the cliff, and up is positive Origin is at the top of the cliff, and down is positive + + yo= 0.00m y = ? vo= 0.00m /s v =? a = 9.80m /s2 t = 3.5s y =1 yo=? y = 0.00m vo= 0.00m /s v =? a = -9.80m /s2 t = 3.5s 0.00 = yo+1 2(9.80)(3.52) y = 60m v = (9.80)(3.5) v = 34m /s 2(-9.80)(3.52) 0.00 = yo-60.025 60m = yo v = (-9.80)(3.5) v = -34m /s
Problem 2.51 (modified) A tennis player throws a ball straight up. It leaves the hand 2.0 m above the ground and takes 4.0 seconds to return to the starting height. (note: remember sign and units for all numeric answers!) a) What is the ball's acceleration on the way up? b) What is the ball's acceleration at the top of its flight? c) What is the ball's acceleration on the way down? d) What is the velocity of the ball when it reaches its maximum height? e) What is the initial velocity of the ball? f) What is the ball's maximum height?
Problem 2.51 continued New set-up: The ball is again thrown upward. At a particular point in time, the velocity is registered at +12 m/s upward. If the stopwatch starts at that point: g) How fast is it moving after 0.3 seconds? h) How fast is it moving after it has traveled 0.2 meters? i) How long will it take to get to the point where it is moving at -4 m/s? j) Where will it be after the first 0.7 seconds?
Problem 2.51 solution See posted solution on class Website
the well problem Go to https://youtu.be/pey37CeaFVw?t=70. From what you find there, how deep is the well? (Kindly note that this video is from the last episode ever of the TV show iZombie, and that the speed of sound is 330 m/s.) hint: the problem has two parts - how do you need to split it up and why?
the well Problem - solution See solution posted on class Website (Note that the pebble in the well problem on the Website is the same problem as this one with slight modification in the sense that it actually tells you it takes 8 seconds of total elapsed time for the sound of the splash to get back to you. The solution to the problem is essentially the same, though.)