Ionic Bonding and Lattice Energy
Explore the world of ionic bonding through images and explanations. Learn how electrons are transferred to form ions, the arrangement of ions in a crystal lattice, and the concept of lattice energy in ionic compounds. Discover the formation of formula units, examples of bond pairs, and the significance of lattice energy values in compound strength.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
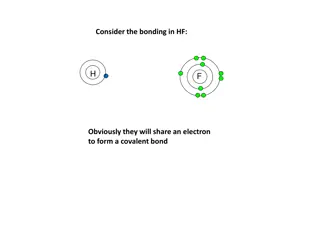
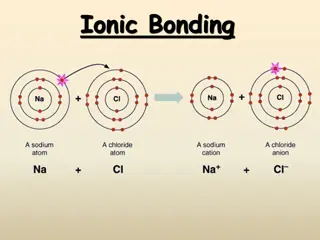
Formation of Bond Electrons are transferred from an atom of low electronegativity to one of high electronegativity Anion (-) and cation (+) formed Opposite charges attract called an electrostatic force
Formula Unit Simplest ratio of atoms in an ionic compound Charges combine to form a net of zero Formulas are not molecules: they do not show exact numbers of atoms just ratios Another term for an ionic compound is salt
Example Show how the bond forms in each pair and tell the formula unit Ca and F K and O Al and O
Ions Arrangement Opposite ions arrange themselves with each positive ion surrounded by negative ions and each negative surrounded by positive ions Where potential energy is lowest This arrangement is called a crystal lattice
Lattice Energy Energy released when one mole of an ionic compound is formed from its ions Values will always be negative, because energy is released The larger the negative value for the lattice energy, the stronger the ionic bond in the crystal is
Lattice energy Compound (kJ/mol) NaCl NaBr CaF2 CaO LiCl LiF MgO KCl 787.5 751.4 2634.7 3385 861.3 1032 3760 715
The notation for sodium chloride, NaCl, stands for one . A) Formula unit B) Molecule C) Crystal D) Atom
In a crystal of an ionic compound, each cation is surrounded by a number of . A) Molecules B) Positive ions C) Dipoles D) Negative ions
Compared with the neutral atoms involved in the formation of an ionic compound, the crystal lattice that results is . A) Higher in potential energy B) Lower in potential energy C) Equal in potential energy D) Unstable
The lattice energy of compound A is greater than that of compound B. What can be concluded from this fact? A) Compound A is not an ionic compound B) It will be more difficult to break the bonds in compound A than in compound B C) Compound B is probably a gas D) Compound A has larger crystals than compound B
The forces of attraction between molecules in a molecular compound are . A) Stronger than the attractive forces in ionic bonding B) Weaker than the attractive forces in ionic bonding C) Approximately equal to the attractive forces in ionic bonding D) Equal to zero
What type of force holds atoms together in an ionic bond? A) Van der Waals B) Dipole-dipole C) Electrostatic D) Hydrogen bonding
What type of bonding holds a polyatomic ion together? A) Ionic B) Metallic C) Covalent D) Hydrogen Bonding
Using the table below, which substance is held together by the strongest ionic bond? A) NaCl B) CaO C) KCl D) MgO E) LiCl

 undefined
undefined