Introduction to Lipid Biosynthesis and Fixed Oils in Pharmacognosy Lecture
In this lecture by Asst. Prof. Dr. Ibrahim Salih, the focus is on lipid biosynthesis, specifically the three phases involved: glycerol formation, fatty acid biosynthesis, and triglyceride production. The classification of fixed oils into drying, semi-drying, and non-drying categories based on their oxygen absorption abilities is discussed. Additionally, tests such as acid value, saponification, and iodine number are explained to assess the quality of fixed oils. Physical properties and methods of obtaining fixed oils from plants are also covered.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PHARMACOGNOSY THREE STAGE SEMESTER 1 LECTURE 6 Asst.Prof Dr. Ibrahim Salih
- - Caster oil Caster oil
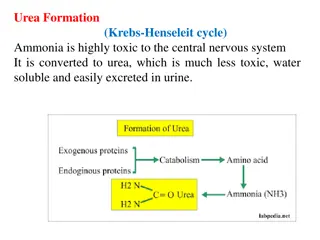
Biosynthesis of lipids : The biosynthesis of Lipids involving three ( phase involving several steps. 1 1- - First : 2 2- - Second : 3 3- - Third : triglycerides . Fixed oil Classification of fixed oils : - - Dring - - Semi dry oils - - No This classification depend on the ability of oils to absorption of oxygen from and unsaturated bounds to make oxygenated compounds and by polymerize process form solid and fine layer . Biosynthesis of lipids : The biosynthesis of Lipids involving three (3 3) ) phases : phase involving several steps. First : Glycerol formation . Second : Biosynthesis of fatty acids . Third : Combination of glycerol and fatty acids to produce triglycerides . Fixed oil Classification of fixed oils : Dring oils Semi dry oils No dring This classification depend on the ability of oils to absorption of oxygen from aire and unsaturated bounds to make oxygenated compounds and by polymerize process form solid and fine layer . phases : each each Glycerol formation . Biosynthesis of fatty acids . Combination of glycerol and fatty acids to produce oils dring oils oils aire , , where the oxygen saturate the double where the oxygen saturate the double
The tests of fixed oils : 1 1- - Acid value or Acid number : The number of milligram of potassium hydroxide required to neutralize the free acids in ( the substance , this indicates the amount of free acids present in the oil . 2 2- - Saponification The number of milligrams of potassium hydroxyl required to neutralized the free acids and their saponify 3 3- - Iodine number : The number of grams of iodine absorbed under prescribed condition , by indicate the degree of unsaturated . The tests of fixed oils : Acid value or Acid number : The number of milligram of potassium hydroxide required to neutralize the free acids in (1 1) one gram of the substance , this indicates the amount of free acids present in the oil . Saponification value or number : The number of milligrams of potassium hydroxyl required to neutralized the free acids and their saponify in one ( Iodine number : The number of grams of iodine absorbed under prescribed condition , by 100 indicate the degree of unsaturated . ) one gram of value or number : in one (1 1) gram of substance . ) gram of substance . 100g of the substance this g of the substance this
Physical properties of fixed oils : 1- melting point . 2- Specific gravity . 3- Refractive index . 4- Flavor . 5- Taste . * * The methods of Fixed oils obtain from plants . 1- By hydrolic presses [Expression] . If expression carried out in cold condition is called (virgin oil) but when carreidout in heat conditions is called [hot-pressed oil] 2- By organic solvents * The example of plants are contain the fixed oils : 1- Caster oil : from seeds of Ricinuscommunis L . Physical properties of fixed oils : The methods of Fixed oils obtain from plants .
Fam Caster seeds are contain Caster oil is a pale yellowish or almost colorless , transparent , and a bland Caster oil is composed of mixture of diglyceried lipase in the duodenum to exert a cathartic effects . Caster oil is used as stimulant cathartic agent . - - Olive oil from [ Is called sweet oil , is a pale yellow or light greenish yellow , oily liquid , whose odor is slight but characterizes and whose taste is bland to faintly acrid . . Fam : Euphorbiaceous Caster seeds are contain 45 Caster oil is a pale yellowish or almost colorless , transparent , vicid and a bland chavacteristic Caster oil is composed of mixture of triglycerid diglyceried , , 15 lipase in the duodenum to relase exert a cathartic effects . Caster oil is used as stimulant cathartic agent . Olive oil from [Oleaeuropa Is called sweet oil , is a pale yellow or light greenish yellow , oily liquid , whose odor is slight but characterizes and whose taste is bland to faintly acrid : Euphorbiaceous 45- -55 55% of fixed oil . % of fixed oil . vicid liquid , it has a faints mild odor chavacteristic taste . liquid , it has a faints mild odor taste . triglycerid and is hydrolyzed by relase ricin and 15% is % is tricicinolein tricicinolein is hydrolyzed by ricin oleic which oleic which Oleaeuropa] ]Fam Fam : :Oleaceae Oleaceae
Uses of olive oil Consider a pharmaceutics aid , it is used as a plasters and liniments , It is also a preparation of soaps , Is a nutrient and used widely as a salad oil - - Palm oil It's fixed oil obtain from the fleshy part ( [ [Elaeisguineenss - - Used in Food preparation for over - - It contain unsaturated fatty acids such as linoleic Medical uses : 1 1- - Prevents the formation of thrombus in blood vessels . 2 2- - Cardio tonic . 3 3- - Anticancer agents . Uses of olive oil Consider a pharmaceutics aid , it is used as a plasters and liniments , It is also a demlent preparation of soaps , Is a nutrient and used widely as a salad oil Palm oil It's fixed oil obtain from the fleshy part (mesocarp Elaeisguineenss L.] Used in Food preparation for over 5,000 It contain unsaturated fatty acids such as palmatic linoleic acid , Medical uses : Prevents the formation of thrombus in blood vessels . Cardio tonic . Anticancer agents . demlent , and laxative and in the , and laxative and in the mesocarp) of the fruit of ) of the fruit of L.]Fam Fam : :polnaceae polnaceae . . 5,000 years . years . palmatic , oleic , , oleic , acid , Lauric Lauric acid acid stearic stearic acid addition to vitamin E . acid addition to vitamin E .
Waxes Are esters are resulting from the reaction of high molecular weight weight ( Waxes are found in the outer cell walls of epidermal tissue especially in fruits and leaves . * * The function of waxes for plant and pharmacology : - - Its used for protection of loss of water from plant parts . . - - Used in pharmaceutical to produce harden ointments and cosmetics creams . Waxes Are esters are resulting from the reaction of high molecular weight chain acids and high molecular weight (Primary straight chain alcohols) . Waxes are found in the outer cell walls of epidermal tissue especially in fruits and leaves . The function of waxes for plant and pharmacology : Its used for protection of loss of water from plant parts chain acids and high molecular Primary straight chain alcohols) . Used in pharmaceutical to produce harden ointments and cosmetics creams .