Instantaneous Velocity and Speed in Physics
Instantaneous velocity and speed are essential concepts in physics that describe how fast an object is moving at a specific moment in time. From understanding average speed and velocity to calculating instantaneous values, this content delves into practical examples with ant paths, sloth movements, and a thrilling race scenario up a mountain.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
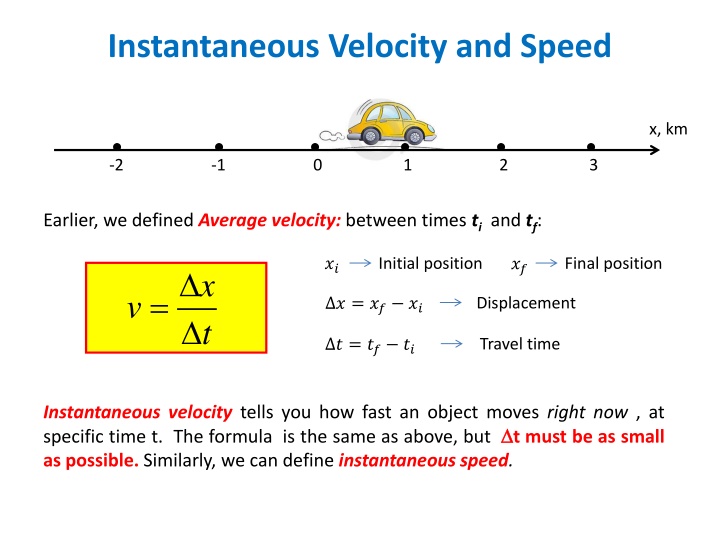
Instantaneous Velocity and Speed x, km -2 -1 0 1 2 3 Earlier, we defined Average velocity: between times ti and tf: ?? ?? Initial position Final position x t = v ? = ?? ?? Displacement ? = ?? ?? Travel time Instantaneous velocity tells you how fast an object moves right now , at specific time t. The formula is the same as above, but t must be as small as possible. Similarly, we can define instantaneous speed.
Homework Problem 1. The picture shows the path of an ant that it covered in 1 minute. Find its average speed. You will need to come up with a creative way to measure the distance travelled. Please describe it. Use anything you want. . 1 m Can you think of a way to find its average velocity?
Problem 2. The figure below shows the position of a sloth crawling back and forth along a straight line. Find its instantaneous speed and velocity at each time interval and fill the table on the right. Also, find the average speed and velocity of the robot (you ll need to figure out the total distance travelled for this). Time interval ,s Speed, m/s Velocity, m/s 0-2 2-5 5-7 7-12 12-14 14-16 16-19 19-20 20-21 Average (0-21)
Bonus problem. Two speed climbers are racing an Audi car to the top of a mountain. The climbers can go in a straight line from the bottom to the top of the mountain, which has a height of 1,200ft. The climbers average a speed of 0.17ft/s. The car has to go through narrow sinuous roads, so its average speed in the race is 29.3mph. The road to the top of the mountain is 60 miles long. Who will win the race, the climbers or the car? By how much? Once you have made your prediction, you can watch the race take place at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xKLsBk5CijQ