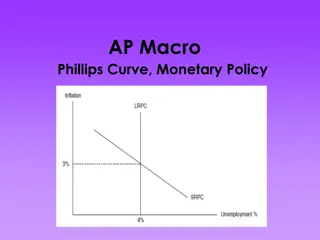
Inflation, Deflation, and Stagflation in Economics
Inflation is the continuous increase in the general price level, leading to a loss of the money's value. This chapter explores the causes of inflation, including demand-pull and cost-push factors. Remedies such as monetary and fiscal policies are discussed to control inflation. Additionally, the concept of deflation, the opposite of inflation, is explained.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 5 Inflation, Deflation, and stagflation Course instructor: Folad khan Contact: foladkhan650@yahoo.com
Inflation Inflation is situation in which there is continuous increase in the general price level and the money is continuously losing its value. In inflation it is not necessary that the prices of all commodities will be rising. The prices of some goods may remain constant and a few other actually falling. Inflation also does not mean that prices of goods rise proportionally. Inflation is continuous upward movement in the general level of price
Causes of Inflation 1. Demand pull inflation Demand pull inflation occurs from excess demand for output When aggregate demand increase faster then aggregate supply of goods and services, the price of goods tend to rise Sources of Demand pull inflation I. Continuous increase in money supply II. Continuous increase in aggregate demand III. Increasing the government expenditures
Causes of Inflation 2. Cost push inflation The cost push inflation describe a situation where the process of rising prices is initiated and sustained by rising costs which push up general prices level Increase in the cost of factor of production create cost push inflation Sources of cost push inflation I. Increase in money wage rate II. Profit push inflation III. Material push inflation IV. Higher taxes V. Rise in the import prices
Remedies of inflation 1. Monetary policy Monetary policy is policy that influences , the economy through changes in the money supply and available credit Monetary policy is adapted by the central bank of the country Measures of central bank to control inflation through monetary policy I. Open market operation II. Variation in the bank rate III. Credit rationing IV. Changing reserve requirement
Remedies of inflation 2. Fiscal policy Policy that control the inflation through government revenues and government expenditures Measures of central bank to control inflation through Fiscal policy I. Changes in Taxation II. Changes in government expenditure III. Government borrowing
Deflation Deflation is completely opposite situation of inflation in the economy When the general level of price continuously fall, the value of money increases, such a situation in the country is called deflation Causes of Deflation I. Increase in unemployment II. Reduction in the income of people III. Fall in the private investment IV. Sudden increase in the total output V. Central bank increase the discount rate VI. Or combination of them
Effect of deflation on different sector in the economy 1. Trader lose: they purchase it higher price and sell at lower price due to deflation 2. Producer lose: purchase raw material at higher price and sell finished goods at lower price 3. Investing class: Equity holder lose, debt holders gain 4. Fixed income group gain 5. Consumer gain 6. Creditor gain, debtors lose 7. Tax payers lose
Reflation Reflation is the situation in the country, where economy is started to get out of depression It is phenomenon of rising prices due to increase in aggregate demand Reflation may be defined as inflation deliberately undertaken to relieve a depression Reflation is similar with inflation in two respects 1. In inflation and reflation both, the money supply increase 2. Both result in upward movement of general price level
Difference between Inflation and Reflation I. Inflation poses a serious problem of rising prices without any increase in output and employment II. In Reflation there is moderate continuous rise in the price level leading to more production and employment III. Reflation is adopted by government as deliberate policy IV. Reflation take place below the level of full employment V. Price rise very slowly during reflation, whereas there is rapid increase in the general level of prices under inflation
Disinflation When an economy start to recover from the ill situation of inflation, the situation is known as disinflation It is desire of every government that the prices should remain at a reasonable level The process through which the prices are brought down without causing unemployment and reducing output is called disinflation Like reflation this policy is also undertaken by government deliberately
Stagflation The phenomenon of rising prices and unemployment at the same time In the words of Samuelsson, stagflation involves inflationary rise in prices and wages at the same time people are unable to find jobs and firms are unable to find customers for what their plants can produce Stagflation is more serious problem then inflation as the economy is hit by the declining output and rising unemployment. It redistribute the income in favor of rich and create unrest in the community with growing unemployment.
Causes of Stagflation Reduction of aggregate supply According to the modern economists, one of the main factor causing stagflation is the reduction of aggregate supply of goods When there is decline in the aggregate supply of goods, the prices level rises and the output and employment falls The reduction in supply occur due to three factors 1. Resource cost: rise the price of raw material, wages, imported material 2. Reduction in the labor supply: if the wages rise due to labor union the output and employment level will fall and prices will go up 3. Increase in taxes:
As your mid term is plan to begin at 31 August 2019, you can contact for any query regarding the course till this level Contact: foladkhan650@yhoo.com 0730157561