Aeolian Processes and Erosional Landforms
Aeolian processes, driven by wind, shape landscapes through erosion and deposition. This presentation by Pranati Manna explores wind erosion methods like deflation, corrasion, and attrition, as well as transportation and deposition mechanisms. Aeolian landforms, including deflation basins, mushroom tables, and pedestal rocks, are formed through the interaction of wind-blown sediments with various environments. Understanding these processes enriches our knowledge of geological formations influenced by wind.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Aeolian Process And Erosional Landform Presented by: Pranati Manna Dept. of Geography Bajkul Milani Mahavidyalaya Date: 15.03.2023
WIND Moving air mass is known as the wind. Produces Varieties of landforms by erosion and deposition. It cannot develop any landscapes by itself: requirs some materials as tools ( Particles of sand, silt etc.)
Wind Erosion Chiefly three methods: Deflation : The lifting and removal of loose sand, dust particles from the Earth s surface. Forms shallow basins called deflation basins. Corration or Abrasion: The wearing down of solid rocks by the impact of wind borne particles. Attrition : Wind blown particles collide each other and get worn.
Transportation By Wind Three methods: Saltation : results from impact and elastic bounce. Suspension : particles are lifted high into atmosphere and are carried great distances before they settle. Rolling or Traction: the movenment of particles on ground. The coarser fragments are carried in this way
Deposition By Wind Causes : Any obstruction to wind Reduction in velocity Increased load Rain
Aeolian Landforms Are formed by the erosion and deposition of windblown sediments. The sediments are generally sourced from deserts, glacial deposits, rivers or coastal shorelines. Aeolian sediments are often composed of well- rounded, sand- to- silt- sized particles, that are weathered by wind abrasion during transport. Sediments are deposited when the velocity of the wind falls and there is not enough energy avaliable to entertain and transport the sediments . Sands will begin to accumulate wherever they are deposited and often continue to move along the ground
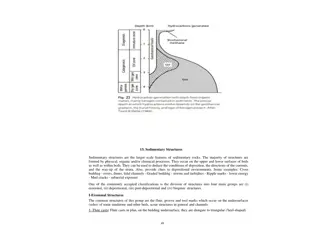
Erosional Landforms Deflation Basins Depressions formed from barren unconsolidated material. Formed by eddy air currents. Also known as deflation hollows or blow outs. Measure from few centimetres to several kilometres across Depth up to 10 km
MUSHROOM TABLE AND PEDESTAL ROCKS Isolated rocks from which the base has been partially cut by the undercutting of the wind. A common mushroom- shaped landform created by wind erosion .
YARDUNG A yardung is an elongate ridge or remnant rock feature sculpted by abrasive action . Oriented parallel to the prevailing wind.
ZEUGEN A zeugen is a conspicuous , tabular pile of durable rock in the desert. Typically , layers of both hard and soft rocks alternate.
VENTIFACT Formed by abrasion effect. Stones with flat surfaces. Commonly distinguished by two or more flat faces meeting at sharp ridges generally well polished. The windward face of the rock is flattend and smoothened. If has one smooth surface then known as EINKANTER and if three DREINKANTERS.
DESERT PAVEMENTS OR LAG DEPOSITS Formed when wind carries finer, more lightweight particles such as sand away. Large particles are left behind and protected from further erosion desert pavements. Also called as desert armor. The areas covered with large sized rocks are called Hamadas.