Infection Prevention in Point of Care Testing: Equipment and Hygiene Guidelines
This information focuses on infection prevention measures related to point-of-care testing (POCT), particularly concerning shared devices like lancing equipment and glucometers. It highlights the importance of evaluating equipment design, proper hand hygiene practices, and guidelines for using fingerstick and lancing devices. The content stresses the risks of blood-borne pathogen transmission and provides recommendations to minimize these risks when utilizing POCT in healthcare settings.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
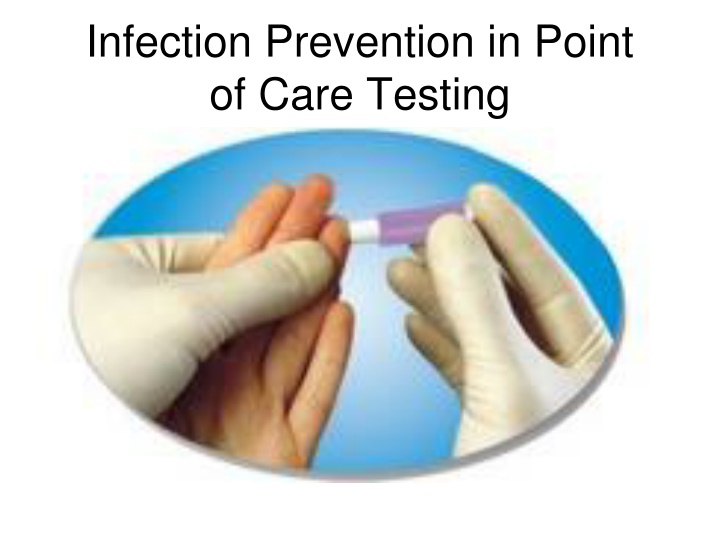
Infection Prevention in Point of Care Testing
Point of Care Testing (POCT) Diagnostic testing at or near the site of patient care Uses portable handheld devices Glucose testing most common
Infection Control Concerns Shared POCT devices are a potential vehicle for transmission of blood-borne pathogens, such as Hepatitis B Some outbreaks of Hepatitis B in healthcare settings tied to lapses in standard precautions when glucometers and lancing devices were used for multiple patients
Evaluate Equipment Review POCT equipment such as lancing devices and glucometers to determine if equipment is designed for: Single-use (disposable) Health care professional use, and intended for multiple use per the manufacturer Patient self-testing, intended for use by one patient Equipment designed for patient self-testing should NOT be employed for facility POCT
Hand Hygiene and Gloves: CDC Wear gloves during blood glucose monitoring Remove and discard gloves after every patient Change gloves that have touched potentially blood-contaminated objects or fingerstick wounds before touching clean surfaces Perform hand hygiene immediately after the removal of gloves and before touching other medical supplies intended for use on other persons
Fingerstick / Lancing Devices CDC: Single-use, auto-disabling disposable fingerstick devices prevent reuse For use in settings where assisted monitoring of blood glucose is performed Discard entire device after one and only one use CDC: Multiple use-capable lancing devices: Should ONLY be used by INDIVIDUAL persons for self-monitoring, not for assisted monitoring
Glucometer Shared glucometer is a potential vehicle for blood borne pathogen transmission Whenever possible, glucometers should NOT be shared CDC: If a glucometer must be shared, the device MUST be cleaned and disinfected after every use per the manufacturer s instructions. CDC: If the manufacturer does not specify how the device should be cleaned and disinfected, then it should NOT be shared.
Insulin Pens Risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens from shared use CDC: insulin pens are for single-patient use only and should NEVER be used for more than one person Even if needles are changed between patients, contamination of the pen reservoir could result in transmission of blood-borne pathogens from a previous user