Indian Public Finance- Module-IV Fiscal Federalism
The concept of fiscal federalism in India involves the sharing of financial resources among the Centre, States, and Local Governments. This includes issues of vertical and horizontal imbalances, the role of the Finance Commission, and the financial resources available to Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs).
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Indian Public Finance- Module-IV Fiscal Federalism Topic: Financial Resources of PRIs (M.A Economics 4thSemester) By Dr. Icy K John
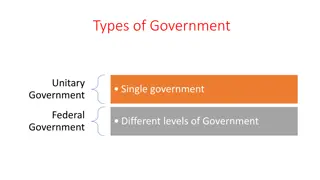
Fiscal Federalism Meaning The process of sharing financial resources among the forms of Government in a federal set up. The main forms of Government in the Indian Federal setup Centre, State and Local Governments Constitutional functions and privileges of centre, state and local Governments. The main sources of revenue for centre and states. Union list, State list and Concurrence list
The main issues in the Centre State financial relationships Problems of fiscal federalism Vertical imbalances Horizontal imbalances The expanding role of the centre The widening resource base of the centre Resource constrains of the State.
Finance Commission and Fiscal Federalism Appointment of Finance Commission Terms and conditions Major recommendations of Finance Commission Gadgil Formula for sharing of financial resources between the Centre and the States Weightages for Population, Tax mobilisation, Social and Economic backwardness, Special problems, etc. Modified Gadgil Formula
Finance of Panchayati Raj Institutions Evolution of PRIs Panchayat system under Mughals and British Grama Swaraj The vision of Mahatma Gandhi Balwantrai Mehta Committee in 1957 Report of the Committee in 1959 Establishment of community development blocks Asok Mehta Committee in 1979, Recommendations to setup three-tier panchayat District Panchayat at the top, Block Panchayat in the middle and Village Panchayat at the bottom. 73rdand 74thconstitutional amendments in 1995 institutionalisation of Panchayati Raj Transfering 29 functions to village panchayat Village Panchayat the agent and agency of Rural development Grama Sabha The basic unit for formation of development plan implementation of development plan by PRIs
Main sources of Financial Resources for PRIs Plan Fund The assistance provided by the State Government Own fund Resources generated by the Village Panchayat Fund for Centrally sponsored schemes Fund for State sponsored schemes Beneficiary contribution Voluntary Contribution Institutional Finance The role of State Finance Commission