History of China: Opium War to Boxer Rebellion
Tumultuous period in China with the Opium War, Taiping Rebellion, and Boxer Rebellion. From economic exploitation to internal uprisings, witness China's struggle against Western imperialism and internal turmoil. Discover the impact of unequal treaties, peasant revolts, and attempts at modernization amid foreign interference and resistance.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
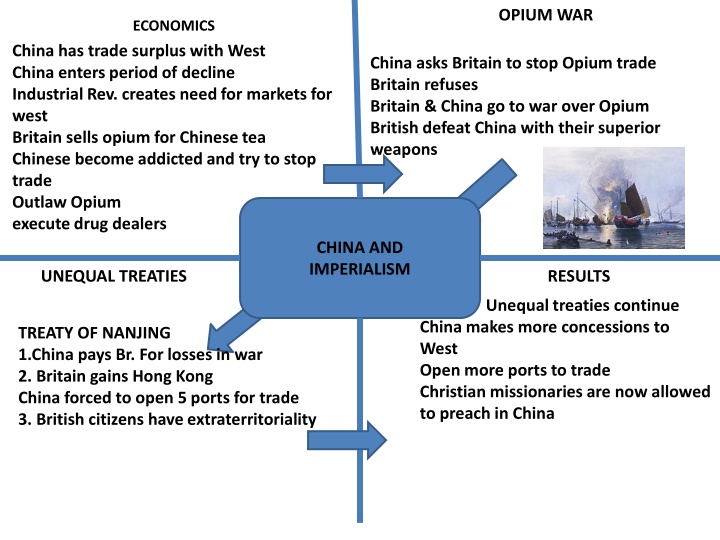
OPIUM WAR ECONOMICS China has trade surplus with West China enters period of decline Industrial Rev. creates need for markets for west Britain sells opium for Chinese tea Chinese become addicted and try to stop trade Outlaw Opium execute drug dealers China asks Britain to stop Opium trade Britain refuses Britain & China go to war over Opium British defeat China with their superior weapons CHINA AND IMPERIALISM UNEQUAL TREATIES RESULTS Unequal treaties continue China makes more concessions to West Open more ports to trade Christian missionaries are now allowed to preach in China TREATY OF NANJING 1.China pays Br. For losses in war 2. Britain gains Hong Kong China forced to open 5 ports for trade 3. British citizens have extraterritoriality
ECONOMICS CHINA Extravagant Imperial Court Leaves country in bad shape Tax evasion by the rich Peasants taxed crops taken for the rich Massive poverty Starvation Lack of food and $$ to buy food and crops Qing Dynasty in decline Infrastructure in poorly maintained Canals, dams, etc. causes flooding, ruins crops, people starving Population explosion creates many hardships TAIPING REBELLION RESULTS PEASANTS REVOLT 1850-1864 Peasants call for end of Qing Dynasty Taiping Rebels control parts of Chins for 14 yrs Regional governors, generals & gov. defeat the peasant rebellion Qing Dynasty almost toppled by rebellion 20 to 30 million deaths Qing Dynasty survives but had to share power with regional commanders Europeans keep up pressure Russia seized lands in the north
CHINA TRIES TO RESTORE ORDER China tries to adopt Western technology Gov. does not support any change Sino-Japanese War-China looses Taiwan to Japan Spheres of Influence Carving up of China by West Trade Open Door Policy-instituted by West MODERNIZATION Hundred Days of Reform 1.Civil Service updated 2. Streamline Government 3. New Industries encouraged 4. Education for all 5. Build up of military BOXER REBELLION QING FALLS UPRISING OF THE BOXERS Righteous Harmonious Fists Goal-drive out foreigners who are polluting China s land Boxers attack foreigners Western powers & Japan join forces and defeat the Boxers China has to support Westernization China expands economically Nationalism spreads Turmoil continues Christian Missionaries seen as threat to traditional Chinese Confucianism Presence of foreign troops protected by extraterritoriality
BRITISH COLONIAL RULE CAUSES OF DISCONTENT East India Co. required Sepoy to serve anywhere in British empire Hindus Travel against their religion East Ind. Co. passes law allowing Hindu widows to remarry Sepoy required to bit off tips of cartridges for rifles greased in cow fat sacred to Hindus or pig fat pork forbidden for Muslims Troops refused & were Imprisoned East Ind. Co. goal was to make money East Ind. Co. improved roads, preserved peace, reduced banditry British introduced: Western Education Converted Indians to Christianity Pressed for Social Change End to slavery, Caste, Saiti Improved status of women SEPOY REBELLION INDIAN NATIONALISM DIFFERENT VIEWS ON CULTURE Sepoys rise up against British Officers Rebellion moves across Northern & Central India Sepys Massacre British British crush rebellion & do away with East India Co. India comes under control of British Empire Western education is spearheaded National Movement begins demand democracy and equality learned from Western Education British exploit diversity of India Mughal power weakened-India becomes fragmented Indians with different traditions & languages do not unite against British Br. Encourages competition & disunity among local princes British use superior weapons to overpower