Heavy Menstrual Bleeding: A Comprehensive Overview
A detailed exploration of heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) by Consultant Gynaecologist Mary Connor, highlighting its impact on women's health and well-being. The importance of early investigations, treatments, and referrals, as well as key considerations for women with obesity or estrogen imbalances. Insights from NICE guidelines and the significance of a focused medical history in assessing HMB are also discussed.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Heavy menstrual bleeding An overview Mary Connor Consultant Gynaecologist Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS FT
Disclosures Honoraria for teaching, travel expenses and consultancy fees received from: Medtronic Hologic Inc
Learning outcomes 1. Know initial investigations when a woman first presents with HMB 2. Know initial treatments when a woman first presents with HMB 3. Know when referral to secondary care is indicated
Why focus on HMB? Affects 1:5 women of reproductive age With 1:20 women contacting their GP each year Affects a woman s physical, psychological and social health and wellbeing 4% experience anxiety 67% suffer with depression
Why focus on HMB? HMB in women with obesity or condition causing unopposed estrogen excess at risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer Rates of obesity, and therefore endometrial pathology, are rising
NICE HMB 2018 Where to start
NICE Quality Standards for HMB QS47
Focused history nature of bleeding duration heaviness frequency regularity/irregularity of periods related symptoms pain tiredness
Focused history impact on quality of life soiling of clothes or bedding quantity of sanitary protection at a time disruption to daily life (unable to go out, need to leave classroom) other factors that may affect treatment comorbidities previous treatment for HMB fertility requirements
Focused history Establish symptoms that may indicate uterine cavity or histological abnormality, adenomyosis or fibroids intermenstrual bleeding postcoital bleeding pelvic pain pelvic pressure
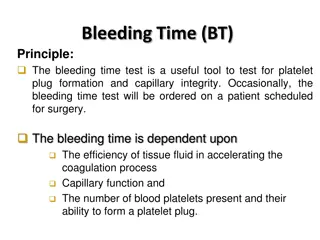
Investigations FBC test for coagulation disorders if HMB since menarche, personal/FH of coagulation disorders consider sexual health screening Cytology if due No indication for TFT, ferritin unless additional symptoms
NICE HMB 2018 No further need to examine or investigate if no additional symptoms and low risk for endometrial pathology May offer treatment at this stage
NICE HMB 2018 Pelvic ultrasound scan (preferably TVS) enlarged uterus on examination pelvic mass on examination pressure symptoms significant dysmenorrhoea unable to otherwise assess
NICE Quality Standards for HMB QS47
Role of cyclical progestogens Long course progestogens MPA (10 20 mg daily) or NET (5 mg tds) days 5 26/month reduced MBL, may be less effective than TXA, cocp, LNG-IUS No studies on satisfaction or QoL
Summary - dose regimes Long cycle regimes definitely better than short cycle for reducing MBL, so ignore the BNF! Compliance seems better with continuous treatment than cyclical NET more effective than MPA at reducing MBL
Summary - dose regimes LNG-IUS more effective at reducing overall blood loss than oral treatment IMB less troublesome with long cycles of oral progestogens than LNG-IUS
Referral to Secondary Care 1. When Hysteroscopy indicated 2. Abnormal TVS or TAS endometria polyps submucosal fibroids <3cm 3. When pain a significant factor 4. Excessive bleeding 5. Severe anaemia
NICE Quality Standards for HMB QS47
NICE HMB 2018 Hysteroscopy for women at high risk of endometrial pathology persistent IMB persistent irregular bleeding infrequent bleeding and obese PCOS Lynch syndrome unsuccessful HMB treatment
Learning outcomes 1. Know initial investigations when a woman first presents with HMB 2. Know initial treatments when a woman first presents with HMB 3. Know when referral to secondary care is indicated
Thank you! Any questions?