Government Revenue and Spending
Federal government spending is divided into two main categories: mandatory and discretionary spending. Mandatory spending includes entitlement programs like Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid, while discretionary spending covers areas such as transportation, education, and national defense. Explore the breakdown of federal expenditures and learn about key spending programs in this comprehensive overview.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 14: Government Revenue and Spending Section 3: Federal Government Spending pgs. 428-433
Federal Expenditures https://media.nationalpriorities.org/uploads/total_spending_pie,__2015_enacted.png The programs & services the federal government funds are divided into two categories. 1. Mandatory spending or spending that is required by current law 2. Discretionary spending or spending that the government must authorize each year.
Mandatory Spending This makes up well over half of all federal spending and most of it is in the form of entitlements which are social welfare programs. Social Security is a one of these programs. As we saw in the last section it aids older citizens who have retired, children who have lost a parent or both parents, and people with disabilities. Social Security takes the largest amount of federal spending. https://www.ssa.gov/framework/images/icons/png/logo-fb-share.png
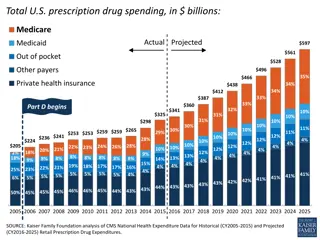
More Mandatory Spending Programs The Medicare program was introduced in 1966, to provide people over 65 with medical coverage. Employers and employees each pay 1.45% of employee income. In 2006, means testing was added, so the most wealthy would not received Medicare. Medicaid was started at the same time as Medicare, to give medical coverage to poor people. 63% of Medicaid is paid for by the federal government and the rest is paid for by the state. http://teststripz.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/Medicaid-Medicare-and-Dual.jpg
Other Mandatory Spending Programs http://sustainfloyd.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/07/SNAP.jpg The Food Stamp program provides funds for about 26 million low-income people. Veterans benefits include health care coverage & disability payments for injured vets. Vets also receive educational benefits. Vet benefits total $50 billion a year. Unemployment insurance is also part of mandatory spending. Border protection and enforcement of some immigration laws.
Discretionary Spending More than a third of federal revenue goes to discretionary spending, and it includes: Interstate highway system & transportation programs, like Amtrak Natural resources & the environment, including conservation programs, pollution clean-up, and national parks education, like college tuition assistance http://www.in.gov/dva/images/amtrak-train1.jpg
More Discretionary Spending Science, space, technology, and other research programs Justice administration, including enforcement agencies, such as the FBI, and the federal court system. The largest discretionary expenditure is national defense and it takes up 50% of the discretionary budget. http://3ynk0w1orym5czc542xmo55k.wpengine.netdna-cdn.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/FBI.jpg
The Federal Budget & Spending https://media.nationalpriorities.org/uploads/total_spending_pie,__2015_enacted.png Each year the President and Congress work together to establish the federal budget, a plan for spending federal tax money. The budget is prepared for a fiscal year, a 12-month period for which an organization plans its expenditures. The federal government s fiscal year runs from October 1stto September 30th. The President s budget is prepared by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and takes into account estimated tax receipts and requests by all federal departments & agencies.
Congress Acts on the Budget The Congressional Budget Office helps the House and Senate develop guidelines for different appropriations, which are set amounts of money set aside for specific purposes. Members of Congress often make deals to gain votes for appropriations that they support. Congress votes on the final budget and sends it to the president for approval. If the budget is not approved by the beginning of the new fiscal year, the Congress passes resolutions to keep the government running on a day-to- day basis. https://fcw.com/Blogs/FCW-Insider/2013/09/~/media/D95692762FF04E0D8EB331F8021855C1.ashx
Methods of Federal Spending http://coe.sdsu.edu/doc/Current/Grants-bagofmoney.png After budget approval, the funds are spent in several ways. One way is direct spending, by which the government buys goods and services that it needs. A 2ndway is through transfer payments money distributed to individuals who do not provide goods or services in return. Example: Social Security The 3rdway is grant-in-aid transfer payment from the federal government to state of local government. Example: grants to states, local governments, or regions
The Impact of Federal Spending B/c the federal gov. sends trillions of dollars, it is a big factor in the economy. It influences the economy in three ways: 1. Resource Allocation-the federal gov. decides where it is going to spend its money 2. Income Redistribution-for example: transfer payments for health care, retirement, Food Stamp benefits, or how the gov. awards contracts 3. Competition with the Private Sector- for example veterans hospitals, federal housing, even education http://images.slideplayer.com/15/4728754/slides/slide_13.jpg