Global Nutrition Prevalence Rates in Children and Women
This content highlights the prevalence rates of acute malnutrition, severe acute malnutrition (SAM), moderate acute malnutrition (MAM), childhood stunting, acute malnutrition based on MUAC and edema, and acute malnutrition in pregnant and lactating women. The data is based on various criteria such as weight-for-height z-score, height-for-age z-score, MUAC measurements, and more, providing insights into the nutritional status of children and women globally.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
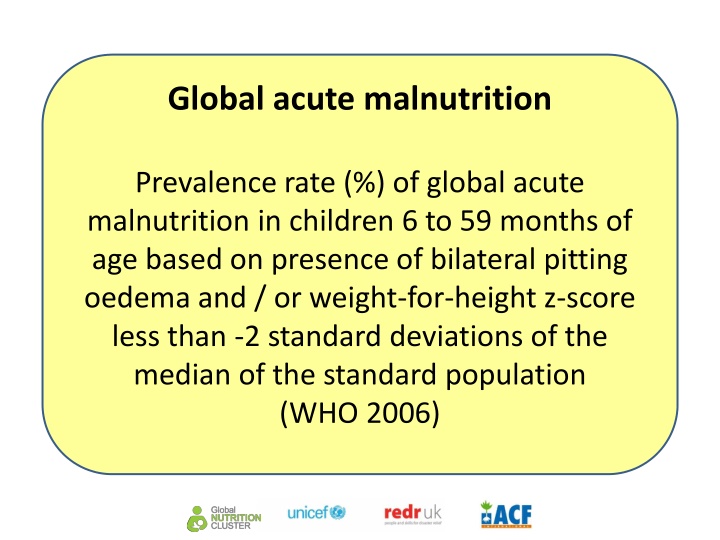
Global acute malnutrition Prevalence rate (%) of global acute malnutrition in children 6 to 59 months of age based on presence of bilateral pitting oedema and / or weight-for-height z-score less than -2 standard deviations of the median of the standard population (WHO 2006)
Severe acute malnutrition (SAM) Prevalence rate (%) of severe acute malnutrition in children 6 to 59 months of age based on presence of bilateral pitting oedema and / or weight-for-height z-score less than -3 standard deviations of the median of the standard population (WHO 2006)
Moderate acute malnutrition (MAM) Prevalence rate (%) of moderate acute malnutrition in children 6 to 59 months of age based on presence of weight-for-height z-score less than -2 and equal or greater than -3 standard deviations of the median of the standard population (WHO 2006)
Childhood stunting Prevalence rate (%) of stunting in children 0 to 59 months of age based on height-for-age z-score less than -2 standard deviations of the median of the standard population (WHO 2006)
Acute malnutrition based on MUAC and oedema Prevalence rate (%) of children 6-59 months with MUAC less than 125 mm and/or having bilateral pitting oedema
Acute malnutrition in Pregnant and Lactating Women Prevalence rate (%) PLW with MUAC less than 210-230 mm (Note: Countries use a range of different cut-offs depending on resources)
Undernutrition for 5 to 19 year olds Prevalence rate (%) of children and adolescents 5-19 years of age with Z-scores defined as BMI-for-age index less than -2 standard deviations from the median BMI of a reference population of children/adolescents of the same age and/or having bilateral pitting oedema
Acute malnutrition for older people Prevalence rate (%) of older people with a MUAC below 210mm or having bilateral pitting oedema
Minimum meal frequency for children 24-59 months Proportion of children 24-59 months who are eating 3 meals a day or more
Level of risk to common micronutrient deficiencies (high, medium, low) Qualitative assessment of nutritional risk of common micronutrient deficiencies (anaemia, iodine deficiency, vitamin A deficiency (night blindness), scurvy, beri beri, vitamin D deficiency) based on composite indicator analysis on prevalence rates, diet analysis, water quality and diarrheal disease, case finding
N-020 Vitamin A coverage in children 6--59 months Proportion of children 6 - 59 months having received vitamin A in previous 6 months
Iron supplementation coverage rate in children Proportion of children 6-59 months of age receiving micronutrient supplements that contain adequate iron
Iron-folic acid supplementation in pregnant women Proportion of pregnant women having received iron-folic acid contained supplementation daily in previous 6 months/during pregnancy
Iodized salt consumption Proportion households using adequately iodized salt in previous 6 months
Prevalence rate of vitamin A deficiency (1)Proportion of children below five years of age with sub-clinical vitamin A deficiency (2) Proportion of women of reproductive age with clinical vitamin A deficiency
Prevalence rate of anaemia Proportion of children below five years of age with Hb concentration of <11 g/dL Proportion of women in reproductive age with Hb concentration of <12 g/dL
Under-five mortality The rate of death among children below of 5 years of age in the population
Exclusive breastfeeding under 6 months Proportion of infants 0-5 months of age who are fed exclusively with breast milk
Minimum dietary diversity Proportion of children 6-23 months of age who receive foods from 4 or more food groups
Introduction of solid, semi-solid or soft food Proportion of children 6-8 months of age who received solid, semi-solid or soft foods during the previous day
Inappropriate distribution of infant formula, dried or liquid milk to children 0-<2 years Confirmed distribution of infant formula, dried or liquid milk to children 0-< 2 years
Number and percentage of displacement sites where IDP population has access to potable water supply within a safe and risk free walking distance This indicator monitors whether IDP populations in displacement sites have access to potable water
Number and percentage of displacement sites with food/nutrition needs where at least one food distribution has taken place within the past month This indicator monitors whether IDP populations in displacement sites with food needs have access to food distributions
Number and percentage of emergency affected children/youth (reported as m/f) from any social-economic background, disabled, marginalized community, leaving with HIV/AIDS (3-18 years) accessing emergency education programmes that incorporate nutrition interventions Children and youth with access to schools with nutrition programmes
Coverage of measles vaccination (%) Measles coverage refers to the percentage of children who have received at least one dose of measles-containing vaccine in a given year. This indicator is used for estimating the vaccine coverage of the total EPI strategy. To avoid overestimation, measles vaccination coverage is often used as a proxy since it is usually lower than DPT3 coverage.
Number of areas where local government across sectors use knowledge, innovation and education to build a culture of preparedness, safety and resilience. This is the be differentiated by age/sex This could include relevant information on disasters is available and accessible at all levels, to all stakeholders (through networks, development of information sharing system. ii. School curricula, education material and relevant trainings include risk reduction and recovery concepts and practices. iii. Research methods and tools for multi risk assessments and cost benefit analysis are developed and strengthened. iv. Country wide public awareness strategy exists to stimulate a culture of disaster resilience, with outreach to urban and rural communities
Number and percentage of households receiving non-food items This indicator aims to gather disaggregated data on number households supported with NFIs. Overall number of NFIs delivered should also be collected.
Proportion of households where only safe water is used for drinking and cooking Safe water is defined as water that: (1) comes from a protected and/or treated water supply and/or is treated at household or point of use; (2) is collected and stored in clean covered or narrow- necked containers; (3) is transferred safely during collection at the water point, when transferring from collection containers to storage, (4) containers and when transferring to containers used for drinking or cooking
Percentage of households with capacity to prepare food safely Proportion of households (female and male headed households) with capacity to prepare food safely (fuel, water, cooking utensils, food)
Percentage of households that have changed intra-household food distribution Assessing the impact of the crisis on food distribution patterns inside the HHs (both female and male headed households). The change can occur in several ways and have several degrees of severity: i.e. adults restrict consumption for children to eat, women do not eat to give food only to men (as they work) etc.
Number of functional basic health units/10,000 population Proxy indicator of geographical accessibility, and gender balance in staff (adequate representation of women and men) in availability of health facilities across different administrative units
Number of community health workers (F/M) per 10,000 population Indicator monitoring the availability of human resources key to delivering community-based intervention
Global acute malnutrition Prevalence rate (%) of global acute malnutrition in children 6 to 59 months of age based on presence of bilateral pitting oedema and / or weight-for-height z-score less than -2 standard deviations of the median of the standard population (WHO 2006)
Proportion of households (both female and male headed households) where food is safely stored, prepared and consumed Safe food practice involves three main precautions: (1) clean all surfaces in contact with food: wash hands before food preparation and eating, wash cooking and eating utensils, (2) use safe ingredients: use safe water and foodstuffs, wash fresh foods to be eaten raw, (3) store food safely: protect from flies, separate raw and uncooked foods, avoid storing leftovers or cooking a long time before eating.
Global acute malnutrition Prevalence rate (%) of global acute malnutrition in children 6 to 59 months of age based on presence of bilateral pitting oedema and / or weight-for-height z-score less than -2 standard deviations of the median of the standard population (WHO 2006)
Proportion of pregnant women, children under five and other vulnerable people sleeping under effective insecticide-treated mosquito nets Insecticide-treated nets are nets for hanging over sleeping places, treated with an insecticide that repels, disables and kills mosquitoes coming into contact with them. Conventionally treated nets are effective if they have been retreated correctly within the last six months (or the last yea the case of some chemicals), not washed more than three times since the last treatment and without holes or tears.
Proportion of households (Female and male headed households) with appropriate water treatment supplies and equipment Water-treatment supplies and equipment includes chemicals for flocculation and disinfection, filter systems and equipment and fuel for boiling. Equipment and supplies are appropriate where they are already known by the population concerned or where they are simple enough for the people concerned to use them safely and effectively with the instructions provided.