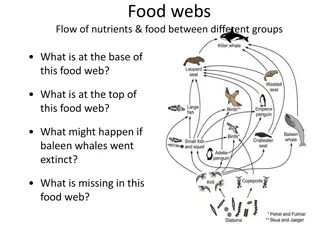
Food Webs in Nature
Food webs represent the interconnected relationships among organisms in nature, starting with the sun as the primary energy source. Plants act as producers by converting sunlight into sugars, which are consumed by herbivores like insects. Secondary consumers, such as carnivores, then prey on these herbivores. Decomposers play a crucial role in breaking down dead organisms. Overall, combined food chains form intricate food webs that sustain diverse ecosystems, showcasing the balance of nature's energy flow.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Food Webs Food Webs are Food Chains that intersect each other. Food webs are what really happens in nature.
All Food Chains and Webs start with the sun. The sun is the source of all the energy on the earth.
Plants are producers. They turn energy from the sun into sugars that animals can use.
Insects and other animals eat plants for energy. They are primary consumers. They are herbivores.
Secondary consumers are animals that eat other animals for energy. They are called carnivores.
Decomposers are organisms that eat dead things for energy.
Summary Combined food chains make food webs. Food webs start with the sun Food webs contain producers, consumers, and decomposers. We are part of the food web, too!
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com Is home to well over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This a free site. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching