Factors Affecting Transpiration in Plants
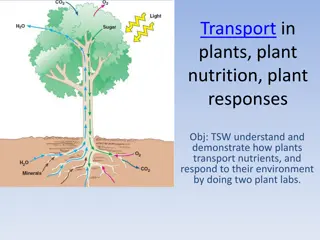
Factors influencing transpiration in plants include temperature, relative humidity, stomatal opening, and wind speed. These factors impact the rate of water loss through processes like evaporation and diffusion. Understanding how these factors affect transpiration can help in better plant care and conservation efforts.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Factors Affecting Water Loss Diffusion rate is affected by: Surface area (the higher the surface area, the greater the rate of diffusion). Difference in concentration (the greater the concentration gradient, the higher the rate of diffusion). Length of the diffusion path (the greater the length, the lower the rate of diffusion).
Preventing Excess Water Loss Cuticle (waxy layer) on leaf which is impermeable to water. Most stomata found on underside of leaf as it is cooler. Thick leaves = reduced water loss. Spines/ hairs increasing boundary layer (undisturbed layer of air). Stomata closed at certain times of the day. Stomata may be sunken and found in pits.
Study the graph in Fig. 2. It shows how four different factors affect transpiration rate. a) Which factor appears to have the greatest effect on transpiration rate? b) For each factor, briefly explain why you would expect it to affect transpiration rate as it does.
a) Which factor appears to have the greatest effect on transpiration rate? Temperature Because it: Increases the rate of evaporation Increases the rate of diffusion
b) For each factor, briefly explain why you would expect it to affect transpiration rate as it does Relative humidity: High RH more water vapour in the air outside the leaf - reduces the diffusion gradient - reduces transpiration. Low RH less water vapour steeper diffusion gradient - increases transpiration
Stomatal opening: Open more water vapour can diffuse out transpiration increase Closed less water vapour can diffuse out transpiration decreases
Wind speed: Wind blows away any water vapour which has diffused out of the leaf increases the diffusion gradient so as wind speed increases transpiration increases
An Experiment Factors affecting the rate of transpiration Collect 4 similar leaves. Add vaseline: Leaf A No vaseline Leaf B Vaseline on the top surface Leaf C Vaseline on the bottom surface Leaf D Vaseline on the top and bottom surface Weigh all the leaves then hang them up by the stem. Bring your practical book next lesson!
Factors affecting the rate of transpiration Write up the practical from last lesson into your practical book. Method Results table (including calculations of % mass lost) Analysis of the results what did you find out and why? Then collect a set of questions from the front desk and start them.
Homework Unit 2 booklet complete the sections: - Haemoglobin, starch, cellulose, glucose, glycogen - Exchange and transport Complete all sections including exam questions. Hand in Wednesday 28th January
Factors affecting the rate of transpiration We use apparatus called a potometer to measure the rate of transpiration. What is the function of each labelled part?
Factors affecting the rate of transpiration Reservoir allows the apparatus to be refilled with water to reset the experiment. Air bubble allows you to see how much water is taken up into the shoot. Capillary tube and scale if we know the diameter of the tube, we can calculate the volume of water taken up by the plant. Beaker of water allows water to be taken into the apparatus so an air bubble can be seen in the capillary tube. What other piece of equipment would we need to calculate the rate of transpiration? Why must the shoot be cut and the equipment be assembled underwater?
Set up a potometer so that you can investigate how wind speed affects the rate of transpiration. Cut a leafy shoot from a plant outside. Fill the apparatus with water. Cut the shoot underwater. Assemble the apparatus underwater, sealing the shoot into the rubber tubing with vaseline.