Exploring the Planets of Our Solar System
Discover the fascinating characteristics of the planets in our solar system, from the rocky surfaces of Mercury and Mars to the thick atmospheres of Venus and Earth, and the gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn. Learn about their sizes, temperatures, moons, and unique features that make each planet distinct in the vast cosmos.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
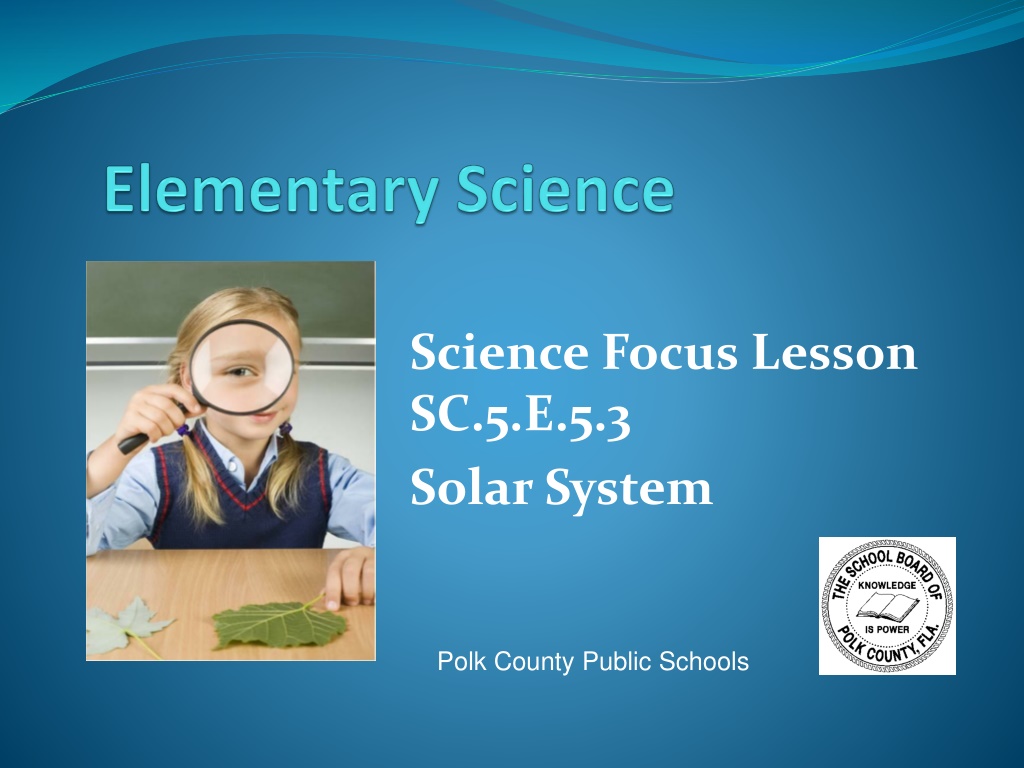
Science Focus Lesson SC.5.E.5.3 Solar System Polk County Public Schools
Planets Planets have mass, rotate on an axis and revolve around the sun in a flattened circle called an ellipse. The planets are much smaller than the sun. Inner planets are much smaller than the outer planets. The inner planets are mostly solid and the outer planets are mostly gas.
Order and Description of the Planets Mercury (inner planet) Mercury is the closest planet to the sun. Surface is rocky Almost no atmosphere Diameter 4,878 km 0 moons Temperature-180 OC at night to 450 OC during the day (HOT) Length of Mercury s year (orbit) is 88 Earth days. Venus (inner planet) Venus is the 2nd planet from the sun. Surface is rocky Very thick atmosphere made mostly of carbon dioxide Diameter 12,104 km 0 moons Temperature on the surface is about 470 OC (HOT) Length of Venus s year (orbit) is 225 Earth days.
Order and Description of the Planets (cont.) Earth (inner planet) Earth is the 3rd planet from the sun. Surface is rocky; 70% is covered by water Atmosphere consists of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% other gases Diameter 12,756 km 1 moon Length of Earth s year is 365.25 Earth days. Mars (inner planet) Mars is the 4th planet from the sun. Surface is rocky with mountains and canyons. Thin atmosphere made mostly of carbon dioxide Diameter 6,786 km 2 moons Temperature on the surface is about 20 OC to -123OC (WARM and COLD) Length of Mar s year is 687 Earth days.
Order and Description of the Planets (cont.) Jupiter (outer planet) Jupiter is the 5th planet to the sun. Surface is liquid hydrogen gas Atmosphere of very thick hydrogen gas. Diameter 142,984 km; Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system. 38 moons Temperatures fall to about -160OC (VERY COLD) Length of Jupiter s year(orbit) is 11.86 Earth years. Jupiter has a storm in its atmosphere called the Great Red Spot . Saturn (outer planet) Saturn is the 6th planet from the sun. Surface is entirely gas, its surface IS its atmosphere! Thin atmosphere made mostly of hydrogen and helium Diameter 120,536 km; it is the second largest planet of the solar system. 30 moons Temperature on the surface is about -190OC (VERY COLD) Length of Saturn s year is(orbit) 29.46 Earth years.
Order and Description of the Planets (cont.) Uranus (outer planet) Uranus is the 7th planet to the sun. Surface is thought to be mostly gaseous Atmosphere of very thick hydrogen, helium, & methane gas. Diameter 51,108 km 24 moons Temperatures are as low as -220OC (VERY COLD) Length of Uranus year (obit) is 84 Earth years. Neptune (outer planet) Neptune is the 8th planet from the sun. Surface is made of gaseous elements Thick atmosphere made of hydrogen, helium, &methane gases Diameter 49,538 km 8 moons Temperature on the surface is the coldest at a little below -220OC (VERY COLD) Length of Neptune s year (orbit) is 165 Earth years.
Guided Practice Talk to your shoulder partner about the answer to each question. Check your work. A star named Sirius appears as the brightest star in the nighttime sky, even though a star named Pollux actually gives off more light. Which of the following best explains why Sirius appears brighter than Pollux in our nighttime sky? 1. Sirius has a different color than Pollux does. Sirius has different gases than Pollux does. Sirius is closer to Earth than Pollux is. Sirius is larger than Pollux is. a. b. c. d.
The answer isC Stars that are closer appear to be brighter. Pollux Sirius
Guided Practice 2. What is the shape of the orbit of a planet around the sun? a. elliptical b. circular c. Semi-circular d. identical
The answer isA The planets travel in an elliptical path around the sun. An ellipse is described as a flattened circle that is longer than it is wide.
Guided Practice 3. Jacob started creating a diagram to show some of the common characteristics of the planets in our solar system. Which characteristic should Jacob write in the empty circle of the diagram? a. made mostly of gas b. has a rocky surface c. revolves around a star d. is a satellite of another planet
The answer isC Planets revolve around a star. The length of time that one revolution takes is called a year. Our planet, Earth, revolves around our star, The Sun, in approximately 365 days.
Guided Practice 4. Keisha wants to show Amy what happens during one Earth day. Keisha holds a small globe representing Earth, and Amy holds a large ball representing the Sun. What should Keisha do to show Amy what happens during one Earth day? a. Keisha should move the globe in one complete circle around Amy. Keisha should move the globe toward Amy and then away from her. Keisha should slowly lift the globe above her head and then lower it. Keisha should slowly spin the globe one complete time about its axis. b. c. d.
The answer isD Planets rotate on their axis. The length of time it takes for a planet to rotate is called a day. The Earth takes approximately 24 hours to rotate on its axis, this is the length of one Earth day.
Summarizing Pass a piece of paper around the table. Each group member adds a detail that answers the question. Keep the paper moving until time is called- see how many ideas your group can generate! Essential Question: Describe the planets, moons, asteroids, comets and identify Earth s position related to them.
Check Your Understanding 2. Life on Earth is possible because of the Sun. The Sun provides energy for all living things to grow. Plants need the Sun to make their own food. The water cycle would not be possible without the Sun. Which statement best describes the Sun? a. The Sun is a large planet that provides heat and light to Earth. b. The Sun is the largest star in the universe and provides heat and light to Earth. c. The Sun is a comet that provides heat and light to Earth. d. The Sun is a medium-sized star that provides heat and light to Earth.
Check Your Understanding 3. Constellations are patterns of stars in the sky. Which statement best describes these stars? The stars in a constellation are equal distances from Earth. The stars in a constellation are the same size. The stars in a constellation pattern never move. The stars in a constellation are different distances from Earth. a. b. c. d.
Check Your Understanding 4. Why does the Sun seem larger and brighter than other stars? The Sun can be seen from Earth during daylight hours. The Sun is closer to Earth than other stars in the universe. The Sun reflects light from all the moons in the solar system. The Sun can make its own light. a. b. c. d.
Check Your Answers 1. c 2. d 3. d 4. b