Exploring the Electromagnetic Spectrum with Wavelengths Foldable
Explore the Electromagnetic Spectrum through a guided foldable activity that involves researching and labeling different wavelengths, comparing sizes, identifying longest and shortest waves, understanding frequencies, and providing examples of wavelengths from various sources such as radio broadcasting, cosmic rays, and more. Get hands-on with this interactive educational tool to learn about the vast range of electromagnetic waves.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
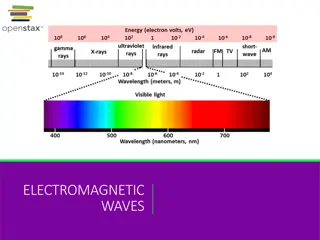
2A Electromagnetic Spectrum What s the Wavelength? Foldable guided instructions key 100
Directions: Create your Electromagnetic (EM) Spectrum Foldable 1. Cut along the dashed lines up to the solid mid-line. 2. Fold hotdog style along the solid mid-line. 3. Write the missing wavelength labels on the flaps. 4. Research the EM Spectrum to find out each EM wavelengths : wavelength size comparisons and identify longest and shortest EM waves wavelength frequency (highest and lowest only) example of the wavelength (source, use, etc.) 5. Use the clues from EM Spectrum printed on the foldable to assist you. 101
102 Wavelength size: Wavelength size: Wavelength size: Wavelength size: Wavelength size: Wavelength size: Wavelength size: ______________ Wavelength ______________ Wavelength ______________ Frequency Wavelength example: Wavelength example: Wavelength example: Wavelength example: Wavelength example: ______________ Frequency Wavelength example: Radio Broadcasting Wavelength example: Cosmic Rays from Space
103 Names: Note: Use the clues on the EM Spectrum foldable to assist you. and an example of the wavelength. )source, use) wavelength frequency (highest and lowest only) longest & shortest EM waves. Sketch (label crest , trough , wavelength distance ) wavelength size comparisons and identify the wavelengths : Parts of a Wave Research the EM Spectrum to find out each EM 5. Write the missing wavelength labels on the flaps. 4. Frequency: Fold hotdog style along the solid mid-line. 3. Cut along the dashed lines up to the solid mid-line. 2. Wavelength: Create your Electromagnetic (EM) Spectrum Foldable 1. Define: Directions: Visible Light X-Rays
104 Key: Double-sided copy (inside side 1) (top edge) Cut along the dashed lines. Fold on the solid line. Wavelength size: Height of Buildings Wavelength size: Wavelength size: Wavelength size: Wavelength size: Wavelength size: Shortest Wavelength size: (nucleus of atom) Size of Honey Bee Size of Pinpoint Size of Protozoans (single cell micro- organisms) Size of Molecules Size of Atoms Longest Wavelength Shortest Wavelength Lower Frequency Wavelength example: Wavelength example: Wavelength example Wavelength example: Highest Frequency Wavelength example: Wavelength example: Radio Broadcasting Night Vision Goggles Rainbow UV Light from the Sun Airport Security Scanner Wavelength example: Cosmic Rays from Space Microwave Oven
105 Key: Double-sided copy (outside side 2) Names: Note: Use the clues on the EM Spectrum foldable to assist you. and an example of the wavelength. )source, use) wavelength frequency (highest and lowest only) longest & shortest EM waves. Sketch (label crest , wavelength distance , trough ) wavelength size comparisons and identify the wavelengths : Parts of a Wave Research the EM Spectrum to find out each EM 5. Write the missing wavelength labels on the flaps. 4. Frequency: Fold hotdog style along the solid mid-line. 3. Cut along the dashed lines up to the solid mid-line. 2. Wavelength: Create your Electromagnetic (EM) Spectrum Foldable 1. Define: Directions: Ultraviolet Rays Infrared Rays Gamma Rays Radio Waves Visible Light Microwaves X-Rays (top edge)
Radio Waves Longest electromagnetic (EM) wavelengths Lowest EM frequencies Not harmful to living organisms 106
Microwaves A type of radio wave Not dangerous to living organisms Speed guns, and of course microwave ovens, use microwave EM waves 107
Infrared Rays IR wavelengths are shorter than radio waves and microwaves IR waves can be felt as heat Heat lamps and infrared cameras use IR electromagnetic waves 108
Visible Light Wavelengths that are longer than UV, X-ray, and Gamma Ray waves Humans can see this form of electromagnetic radiation White light can be separated into red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet 109
Ultraviolet Rays UV electromagnetic radiation can damage or kill living cells UV waves cause sunburns and skin cancer in humans Used as a disinfectant 110
X-Rays X-rays penetrate most matter Dangerous to living organisms Too much exposure to X-rays can cause cancer in humans 111
Gamma Rays Shortest electromagnetic (EM) wavelengths Highest EM frequencies Most penetrating and dangerous of all electromagnetic waves to living things, including humans 112