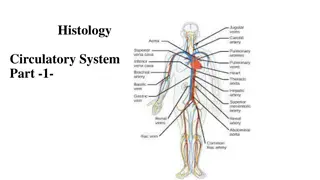
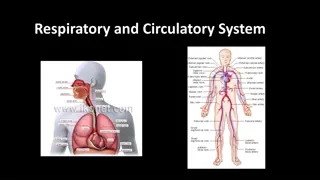
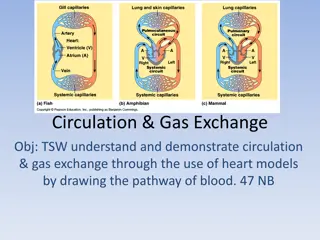
Exploring the Components of the Circulatory System
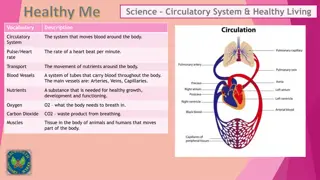
The circulatory system, comprising the heart, blood vessels, and various components like arteries, veins, and capillaries, plays a crucial role in distributing oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. The heart pumps blood through a double circulatory system, ensuring oxygenation of blood in the lungs and distribution to all body tissues. Components such as red and white blood cells, platelets, plasma, and the alveoli in the lungs contribute to vital functions like gas exchange and immune responses.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
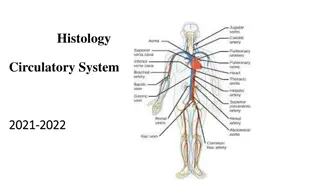
Blood vessels The heart is an organ that pumps blood around the body in a double circulatory system aorta pulmonary?artery vena? cava Pumps blood to the lungs where gas exchange takes place. Right ventricle Different structure in the heart have different functions pulmonary? veins Left ventricle Pumps blood around the rest of the body. Artery Vein Capillary left? atrium Carry blood away from the heart Carry blood to the heart Connects arteries and veins right? atrium Controls the natural resting heart rate. Artificial electrical pacemakers can be fitted to correct irregularities. left? ventricle Pacemaker (in the right atrium) Thin walls, large lumen, carry blood under low pressure, have valves to stop flow in the wrong direction, carry deoxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary vein). Thick muscular walls, small lumen, carry blood under high pressure, carry oxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary artery). One cell thick to allow diffusion, Carry blood under very low pressure. right? ventricle Heart Coronary arteries Carry oxygenated blood to the cardiac muscle. coronary? arteries Prevent blood in the heart from flowing in the wrong direction. Heart valves Blood AQA GCSE ORGANISATION part 2 Blood is a tissue consisting of plasma, in which blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are suspended The heart pumps low oxygen/high carbon dioxide blood to the lungs alveolus Pale yellow fluid Transports CO2, hormones and waste. Plasma (55%) Carries air to/from the lungs Rings of cartilage protect the airway. Trachea Red blood cells (45%) Large surface area, no nucleus, full of haemoglobin. Carries oxygen CO2 O2 bronchioles (air? sacs? at? the?end) Carries air to/from the air sacs (alveoli) Splits into multiple pathways to reach all the air sacs. alveolar? wall Bronchioles trachea Some produce antibodies, others surround and engulf pathogens. White blood cells (<1%) red? blood?cells Site of gas exchange in the lungs Maximises surface area for efficient gas exchange. Part of the immune system capillary Alveoli lung CO2out bronchus O2in Allows gas exchange between into/out of blood Oxygen diffuses into the blood and carbon dioxide diffuses out. gas? exchange? in? an? alveolus Clump together to form blood clots. diaphragm Capillaries Platelets (<1%) Fragments of cells better hope brighter future
Blood vessels The heart is an organ that pumps blood around the body in a double circulatory system aorta pulmonary?artery vena? cava Pumps blood to the lungs where gas exchange takes place. Right ventricle pulmonary? veins Left ventricle Pumps blood around the rest of the body. left? atrium Carry blood away from the heart Carry blood to the heart Connects arteries and veins right? atrium Controls the natural resting heart rate. Artificial electrical pacemakers can be fitted to correct irregularities. left? ventricle Pacemaker (in the right atrium) Thin walls, large lumen, carry blood under low pressure, have valves to stop flow in the wrong direction, carry deoxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary vein). Thick muscular walls, small lumen, carry blood under high pressure, carry oxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary artery). One cell thick to allow diffusion, Carry blood under very low pressure. right? ventricle Heart Coronary arteries Carry oxygenated blood to the cardiac muscle. coronary? arteries Prevent blood in the heart from flowing in the wrong direction. Heart valves Blood AQA GCSE ORGANISATION part 2 Blood is a tissue consisting of plasma, in which blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are suspended The heart pumps low oxygen/high carbon dioxide blood to the lungs alveolus Pale yellow fluid Transports CO2, hormones and waste. Carries air to/from the lungs Rings of cartilage protect the airway. Large surface area, no nucleus, full of haemoglobin. Carries oxygen CO2 O2 bronchioles (air? sacs? at? the?end) Carries air to/from the air sacs (alveoli) Splits into multiple pathways to reach all the air sacs. alveolar? wall trachea Some produce antibodies, others surround and engulf pathogens. red? blood?cells Site of gas exchange in the lungs Maximises surface area for efficient gas exchange. Part of the immune system capillary lung CO2out bronchus O2in Allows gas exchange between into/out of blood Oxygen diffuses into the blood and carbon dioxide diffuses out. gas? exchange? in? an? alveolus Clump together to form blood clots. diaphragm Fragments of cells better hope brighter future
Blood vessels The heart is an organ that pumps blood around the body in a double circulatory system aorta pulmonary?artery vena? cava Pumps blood to the lungs where gas exchange takes place. pulmonary? veins Pumps blood around the rest of the body. left? atrium right? atrium Controls the natural resting heart rate. Artificial electrical pacemakers can be fitted to correct irregularities. left? ventricle Thin walls, large lumen, carry blood under low pressure, have valves to stop flow in the wrong direction, carry deoxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary vein). Thick muscular walls, small lumen, carry blood under high pressure, carry oxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary artery). One cell thick to allow diffusion, Carry blood under very low pressure. right? ventricle Heart Carry oxygenated blood to the cardiac muscle. coronary? arteries Prevent blood in the heart from flowing in the wrong direction. Blood AQA GCSE ORGANISATION part 2 Blood is a tissue consisting of plasma, in which blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are suspended The heart pumps low oxygen/high carbon dioxide blood to the lungs alveolus Transports CO2, hormones and waste. Rings of cartilage protect the airway. Large surface area, no nucleus, full of haemoglobin. CO2 O2 bronchioles (air? sacs? at? the?end) Splits into multiple pathways to reach all the air sacs. alveolar? wall trachea Some produce antibodies, others surround and engulf pathogens. red? blood?cells capillary Maximises surface area for efficient gas exchange. lung CO2out bronchus O2in gas? exchange? in? an? alveolus Oxygen diffuses into the blood and carbon dioxide diffuses out. Clump together to form blood clots. diaphragm better hope brighter future
Blood vessels The heart is an organ that pumps blood around the body in a double circulatory system aorta pulmonary?artery vena? cava pulmonary? veins left? atrium right? atrium left? ventricle right? ventricle Heart coronary? arteries Blood AQA GCSE ORGANISATION part 2 Blood is a tissue consisting of plasma, in which blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are suspended The heart pumps low oxygen/high carbon dioxide blood to the lungs alveolus CO2 O2 bronchioles (air? sacs? at? the?end) alveolar? wall trachea red? blood?cells capillary lung CO2out bronchus O2in gas? exchange? in? an? alveolus diaphragm better hope brighter future