Examples of Measurement in Mass, Volume, and Length
Learn about the measurements of mass, volume, and length with examples and detailed explanations. Understand the concepts of accuracy, precision, units of measurement, linear measurement, area, and volume for regular and irregular objects. Explore formulas and tools used for measuring various objects.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
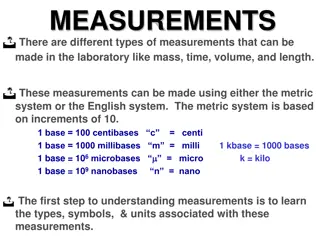
List an example of things measured by mass, volume, and length. Agenda for Wednesday Sept 24th 1. Go over test 2. Measurement notes 3. Measurement practice
Accuracy & Precision Accuracy: Freedom form mistakes or errors; Correctness Precision: The ability to repeat; Repeatability
Units of Measurement International System of Units (SI) Quantity Base Unit Abbreviation Length Meter m cm, mm, km Mass Kilogram kg g, mg Time Second s Temperature Kelvin K **Celsius (C)
Linear Measurement (straight lines) Length, Width, Height Tool: Meter stick, ruler Base unit of measurement: Meters (m)
Area How much surface an object covers Units: m2, cm2 , etc. Formula: A = L x W
Volume How much space an object takes up Two types: Regular and irregular Regular solids are box like Volume is found by measuring length, width, and height The volume of irregular objects is found by water displacement
Volume (cont.) Tool: Regular = ruler or meter stick Irregular = graduated cylinder Units of measurement: m3, cm3(for solids) L , ml (for liquids) 1cm3 = 1ml
Volume of Regular Objects Boxes: V = L x W x H Spheres Formula : V = 4/3 r3 Cylinder Formula: V = r2h * = 3.14
Measuring spheres/circles Measure end to end Use paper on edge of spheres Measured diameter we need radius Radius = diameter So: if d = 10 then r = 5
What is accuracy? Precision? Agenda for Thursday Sept 25th 1. Go over test 2. Measurement pre-lab 3. Measurement lab
Volume lab Rounding What was the smallest number of digits in any of my measurements? You would then round off your calculated value to the smallest number of digits in your measurements.
Example: If L = 2.11 cm, W = 4.3212cm and H = 7.10cm, 7.10cm has the smallest number of digits so your calculated value would be rounded to three digits. 2.11 x 4.3212 x 7.10 = 64.735897 would be rounded to 64.7
Three students reported the length of a pencil to be 12 cm, 12.0 cm, and 12.00 cm. Do all three readings contain the same information? Which one has the most? Why? Agenda for Friday Sept 26th 1. Measurement lab
How do you decide how much water is in the cylinder? How much water is there? Agenda for Monday Sept 29th 1. Volume of Irregular objects
What is the volume of a box with the following dimensions: Width = 3.45 Length = 2.56 Height = 1.89 Agenda for Tuesday Sept 30th 1. Finish Measurement notes 2. Metric Conversion Notes 3. Density
Mass Definition: The amount of matter in an object Tool: Triple beam Balance Base unit: Grams (g) A penny has the mass of about 1g 1g = 1cm3 for water only
Making a connection When you use water (this works only for water) 1 ml = 1 cm3 = 1 g
Weight Definition: The gravitational pull on an object Tool: Scale Base unit: Newton (N)
Temperature Definition: Measurement of the average kinetic energy of molecules Tool: Thermometer Base unit: Celsius (co) and Kelvin (ko)
Density Def. ratio of the mass of a substance to the volume of a substance Formula: D = m/V Density = mass/volume Units: g/cm3 Low density means atoms are not as packed together
Density Density determines whether an object will float or sink Less dense objects float Water has a density of 1 g/cm3 Use density to find substances lab
Density Problems If 12.0 cm3 has a mass of 9.17 g, what is the density? If an object has a density of 4.2 g/cm3 and a mass of 30 g, what is its volume?
Explain how you would find the volume of an irregular shaped object. Agenda for Monday Jan 13th 1. Finish notes 2. Go over worksheet 3. Mass lab
What is the difference between mass and weight? Agenda for Tuesday Jan 14th 1. QUIZ 2. Density 3. Start lab TEST TUESDAY
What is density? Agenda for Wednesday Jan 15th 1. Demo 2. Lab/worksheet