Evolution of Governance in the United States: Shays' Rebellion to the Constitutional Convention
Shays' Rebellion, led by Daniel Shays in 1786-1787, highlighted the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation, prompting the Constitutional Convention in 1787. Despite challenges and delays, key figures like James Madison and George Washington played significant roles in shaping the new governance system. The adoption of the Virginia Plan, New Jersey Plan, and the Connecticut Compromise set the foundation for the modern U.S. government.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Shays Rebellion Daniel Shays was an American soldier, revolutionary, and farmer famous for being one of the leaders of Shays' Rebellion, a populist uprising in 1786 and 1787.
The Constitutional Convention With many complaints rising about financial problems in the states, and the weakness of the Articles of Confederation, Alexander Hamilton pushed for a meeting in the summer of 1787 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania to amend the Articles. A rebellion began when Massachusetts raised taxes on farmers, and confiscated their land when farmers refused to pay. A rebellion broke out, led by Daniel Shays, a former revolutionary war soldier who had not been paid for his wartime service. Shays Rebellion was put down, and Daniel Shays was later pardoned, but this event was a warning to Hamilton and many other state delegates that something must be done about the weak national government.
The Constitutional Convention Due to the difficulty of travel in the late 18th century, very few of the selected delegates were present on the designated day of May 14, 1787, and it was not until May 25 that a quorum of seven states was secured. New Hampshire delegates would not join the Convention until more than halfway through the proceedings on July 23, and Rhode Island boycotted the entire meeting. Some delegates refused to show up, like Patrick Henry of Virginia (famous for the phrase: give me liberty or give me death & I smell a rat in Philadelphia ) Also Samuel Adams of Massachusetts refused to show up (leader of sons of liberty who led the Boston Tea Party)
The Constitutional Convention James Madison arrived first, and soon most of the Virginia delegation arrived. While waiting for the other delegates, the Virginia delegation produced the Virginia Plan, which was designed and written by James Madison. George Washington was unanimously elected president of the Convention. Thomas Jefferson could not attend because he was serving in France as the U.S. ambassador, and John Adams was in England. Despite the sweltering summer heat, the windows of the meeting hall were nailed shut to keep the proceedings a secret.
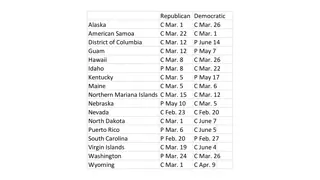
1. Articles of Confederation 2. Virginia Plan -James Madison 3. New Jersey Plan-William Patterson 4. Hamilton Plan **Connecticut Compromise Great Compromise
1 vote per state + Taxing power 1 vote per state 1 house congress 1 house congress 2-7 2-7 Articles of Confederation New Jersey Plan State Legislature State Legislature
Hamilton Plan Virginia Plan Senate Life term Assembly 3 Year term 1st House 2nd House recommendations Number based on state population electors State Legislature
The Great Compromise Connecticut Compromise The 3/5th Compromise The Fugitive Slave Clause https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mOv1Wth5ZlA
Connecticut Compromise House Since 1913 -17th Amendment House Senate Senate Number based on state population Equal Number based on state population Equal Representation Representation State Legislature
Amending the Constitution -Article 5-