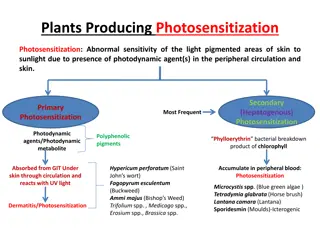
Evolution and Classification of Plants
Exploring the evolutionary history of plants, from cyanobacteria to modern-day magnolias. Learn about endosymbiosis, plant classification, major plant lineages, and examples of different plant types such as nonvascular and vascular plants. Delve into the intricate features that define various plant categories.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Evolutionary Past Cyanobacteria Blue- green algae Photosynthetic Responsible for the marked increase in Oxygen 2000 million years ago
Cyanobacteria Evidence DNA shows the first green plants evolved from prokaryotes between 2500 and 1000 million years ago. Same chlorophyll in algae and land plants.
Endosymbiosis a symbiotic relationship between two organisms in which one of the two organisms (the endosymbiont) lives inside the body of the other one (the host).
Classification of Plants Kingdom - Plantae Division (-phyta) Class (-opsida) Subclass (-idae) Order (-ales) Family (-aceae) Genus Species (Genus + specific epithet)
Magnolia grandiflora Plantae--includes all plants Magnoliophyta--flowering plants Magnoliopsida--dicots Magnoliidae--subclass for Magnolia-like plants Magnoliales--order for Magnolia-like plants Magnoliaceae--family for Magnolia-like plants Magnolia--genus that includes all Magnolias grandiflora--specific epithet
Circumscription of Features A new condition is added at each step to set up a category that is MOST specific. Example: Things with wheels = buses, cars, bicycles, skates, airplanes, trains, etc. And is ground transport = buses, cars, bicycles, trains And can carry more than one person = buses, cars, trains And runs on rails = trains http://www.csdl.tamu.edu/FLORA/tfplab/lab1a.htm#taxonomy
Four major lineages Nonvascular lack xylem & phloem & seeds Seedless vascular have xylem & phloem, lack seeds Gymnosperms - have seeds, but not enclosed Angiosperms - enclosed seeds
Examples Seedless Vascular Nonvascular Dicot Angiosperm Gymnosperm Monocot
Classes of Angiosperms Monocotyledonae (Monocots) Very few are annuals Lilies, grasses, cattails, palms, yuccas, orchids, irises Dicotyledonae (Dicots) More primative, 1/6 are annuals Almost all kinds of trees and shrubs Snapdragons, mints, peas, sunflowers
Parts of the flower PISTIL Stigma Style Ovary STAMEN Anther Filament becomes the fruit becomes the seed
Reproductive Organs Close up of stigma, style and anthers in a tulip
Works Cited retrieved 5/16/06 http://www.personal.psu.edu http://www.biology.iastate.edu http://www.emc.maricopa.edu http://fybio.bio.usyd.edu.au http://scitec.uwichill.edu http://images.google.com/images http://www.cas.vanderbilt.edu
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.