Poisonous Plants and Their Effects on Humans
Poisonous plants can have deleterious effects on individuals, leading to severe consequences and even death if not managed properly. These plants produce toxins that interfere with the body's essential functions, ultimately causing impairment and potential fatality. Recognizing the grades of poisoning, from mild symptoms like itching to severe conditions such as respiratory distress and seizures, is crucial for prompt intervention and treatment. Understanding phytotoxicology and the defensive mechanisms of plants against various threats helps in preventing toxic plant exposures.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Poisonous Plants Poisonous Plants Tanvir Ahmed Fahim
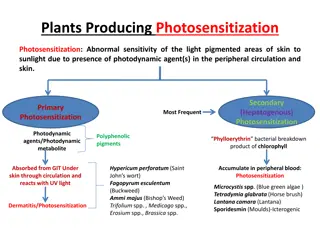
Poison Poison :: A A poison under underappropriate appropriate conditions, Poisonous Poisonous plant plant :: Poisonous affect affect very very deleteriously deleteriously and poisons poisonsis is known knownas as phytotoxicology Poisonous Poisonousplants plantsproduce producepoison Phytotoxin Phytotoxin.. Thus Thus poisonous organisms, organisms, and and damage damage the easily easily tolerable tolerable and and manageable treated treatedproperly properly.. Plant Plant toxins toxins are are generally generally the insects, insects, predators predators and methods methodswhich whichenhance enhancedefensive poison is is a a natural conditions,whether natural or or synthethic whether it itis isingested, synthethic substance ingested,inhaled, substance that inhaled,or orabsorbed that is is capable capable of of producing absorbedor orinjected producing adverse injectedthrough throughthe adverse effects theskin effects on on an an individual skin.. individual Poisonous plants and may phytotoxicology.. poisonor ortoxin poisonous plants plants produce the basic basic life manageable;; or or it it may plants are may cause cause impairment impairment of of the are the the plants plants possessing possessing toxic the body toxic principles principles which body function, function, even which when even leading leading to to death when introduced introduced into death.. The into the The study study of of plant the body body will will plant toxinthat produce these life principle, principle, ii..e e.. protoplasm may be be severe severe enough, thatis isa aprotein these poisonous protoplasm of of the enough, that proteinin innature poisonous compounds nature..The compounds that the cells cells.. Poisoning that may may lead lead to to drastic The Poison Poison is isproduced that interfere Poisoning may producedby byposinous interfere in in the may be be mild drastic consequences consequences even posinousplants the metabolism metabolism of of living mild to to moderate moderate that even death, plantsis iscalled called living that is is not death, if if not the metabolites metabolites produce and microorganisms microorganisms .. These defensivemechanism mechanism.. produce through These toxins toxins found through plants found in in food plants to to protect food plants protect themselves themselves against plants is is due due to to natural against different different threats natural or or new new reproduction threats like reproduction like
Grades Grades of of poisoning poisoning Following Followingare Mild Mild poisoning poisoning :: poisoning are are like like itching itching (on dizziness, dizziness,dryness drynessof ofmouth Moderate Moderatepoisoning poisoning:: poisoning become becomedistressing distressing and Common Commonsymptoms symptomsincluding of ofmouth mouthand andthroat, throat,blisters Severe Severepoisoning poisoning:: If If the patient patient.. In In many many cases, symptoms symptoms- -appearance appearance indicating Common Common symptoms symptoms including seizure, seizure, narrowing narrowing of of air air passages digital digitalleaves, leaves, aconitum aconitumetc etc are the thegrades gradesof ofpoisoning poisoning may (on the the palm palm of of hands, mouth etc etc..e e..g g..poisoning poisoningIf If the andaggravated aggravatedif if left including- - diarrhea, blisters thepoisoning poisoningproduced cases, if if patient patient is is left indicating involvement including - - Excessive, passages etc etc.. Severe poisoning produced may be be called called as as mild hands, soles poisoningdue thesymptoms left untreated diarrhea,abdominal produced by bypoisonous mild poisoning soles of of feet, feet, body dueto toAsparagus, symptomsare arenot untreated abdominalpain, poisonous plants poisoning if if the body etc etc) ) sneezing, Asparagus,daffodils notsevere, severe, ii..e e..may plants the symptoms symptoms produced sneezing, lacrimation, lacrimation, redness daffodilsetc etc.. maybearable bearableby bythe produced by by the redness of of skin the poisonous poisonous plants skin ,shivering, plants ,shivering, thepatient patientfor forsometimes, sometimes,or or pain,severe severevomiting, vomiting,gas gas- -enteritis, enteritis,colitis, colitis,burning burningsensation sensation producedby by poisonous left untreated, untreated, drastic involvementof of vital Excessive, uncontrolled uncontrolled diarrhea Severe poisoning poisoning may poisonous plants drastic consequences vitalsystem systemof of the diarrhea or or vomiting, may be be observed plantsare consequences may thebody bodylike vomiting, hypotension, observed by by following aresevere severeenough enoughand may occur, likecs cs,,cns cnsor orrs rs.. hypotension, hypertension, following plants plants :: e e..g g.. Nux andcant occur, even cantbe betolerated tolerated by bythe even leading leading to to death the death.. hypertension, spasm, Nux- -vomica, spasm, vomica,
Types of poisonous plants Types of poisonous plants 1. 1. Cyanogenic Cyanogenic plants plants 2. 2. Gastro Gastro entric entric plants plants 3. 3. Atropine containing plants Atropine containing plants 4. 4. CNS toxic plants CNS toxic plants 5. 5. Cardio toxic plants Cardio toxic plants 6. 6. Hepatotoxic plants Hepatotoxic plants
CYANOGENETIC CYANOGENETIC PLANTS PLANTS Toxic ToxicPrinciple Principle::Cyanogenetic Plants Plants:: apple apple( (Malus Damage Damage to to the the plant together togethercausing causing HCN Mechanism Mechanismof oftoxic vacuole vacuoleprevents preventsthem become becomeactivated activatedby byenzymes Toxicity Toxicityresides residesin inthe Once Once free free cyanide cyanide is is released halts haltscellular cellularrespiration respiration.. Oxyhemoglobin cyanide cyanide- -cytochrome cytochromeoxidase Cyanogenetic glycosides Malusdomestica domestica) ) apricot plant from from wilting, wilting, trampling, HCNto tobe beformed formed..Beta toxicaction action:: Cyanogenic Cyanogenicglycosides themfrom fromdamaging damagingthe enzymesin inthe thecytoplasm therelease releaseof ofCyanide Cyanideion, released from from the Oxyhemoglobin cannot oxidase will will not glycosidesor orcyanogens apricot( (Prunus trampling, frost, Beta- -glycosideases glycosideasesare glycosidesin inplants theplant plantunder cytoplasm..These ion,CN CN- -.. the plant plant tissue cannot release not function functionin inelectron cyanogens Prunusarmeniaca armeniaca) ) bamboo frost, drought, drought, bruising arealso plants are undernormal normalconditions Theseremove removethe bamboo( (Bambusa bruising etc etc.. results alsoproduced producedby bymicroorganisms arestored storedin inthe thevacuole conditions.. But, But,if ifthe thesugar sugarpart partof ofthe Bambusabamboo) results in in the microorganisms.. vacuole.. Storing theplant themolecule molecule and bamboo) Prunus the enzymes enzymes and Prunusdomestica domestica( (Plum and glycosides glycosides coming Plum) ).. coming Storingthem plantis isattacked, attacked,they andrelease releasetoxic themin ininactive theyare toxic HCN inactiveforms arereleased released and HCN.. formsin inthe the and tissue and and is is absorbed absorbed it it reacts releaseoxygen oxygenfor for electron electrontransport transport.. reacts with electrontransport transportin inthe with ferric ferric iron iron in in cytochrome cytochrome oxidase thecytochrome cytochromesystem oxidase which systemsince since the which the
Diagnosis Diagnosis:: Clinical Clinical signs diarrhoea diarrhoea,, convulsion Laboratory Laboratorydiagnosis Lesions Lesions- - Bright Bright red signs- - Signs convulsion diagnosis- - Measurement redcolor colorto toblood Signs may may include include excitement, excitement, general general muscle muscle tremors, tremors, dyspnea, dyspnea, salivation, salivation, defecation, defecation, severe severe Measurementof ofcyanide bloodand cyanidein inGI GIcontents andmucous mucous membranes, contents.. membranes,detection detectionof ofplant plantmaterial materialin inGI GItract tract..
Gastro Gastro- -enteric Plants enteric Plants Mouth and throat irritants Mouth and throat irritants This group includes plants that cause irritation in mouth and throat upon chewing. This group includes plants that cause irritation in mouth and throat upon chewing. Plants : Plants : Colocasia Colocasiaesculanta esculanta( (Colocasia Colocasia) ) Symptoms of toxicity: Burning sensation , Increased salivation , Blisters on tongue Symptoms of toxicity: Burning sensation , Increased salivation , Blisters on tongue Gastric mucosa irritants Gastric mucosa irritants This group includes plants that produce spontaneous emesis upon ingestion This group includes plants that produce spontaneous emesis upon ingestion Plants : Crinum Plants : Crinum asiaticum asiaticum (lily) (lily) Symptoms of toxicity: Emesis , Convulsions Symptoms of toxicity: Emesis , Convulsions
Intestinal mucosa irritants Intestinal mucosa irritants This group includes plants that produce emesis, colic (abdominal pain) and diarrhea within one hour of This group includes plants that produce emesis, colic (abdominal pain) and diarrhea within one hour of ingestion. Plants : ingestion. Plants : Aesculus Aesculusindica indica(horse chestnut) (horse chestnut) Symptoms: Abdominal pain , Emesis , Diarrhea , Muscular weakness , Hypotension , Dermatitis , Symptoms: Abdominal pain , Emesis , Diarrhea , Muscular weakness , Hypotension , Dermatitis , Blisteron Blisteron tongue & throat tongue & throat Plants producing delayed gastroenteritis Plants producing delayed gastroenteritis This group includes plants that produce gastroenteritis after these are ingested and swallowed. This group includes plants that produce gastroenteritis after these are ingested and swallowed. Plants : Plants : Ricinus Ricinus Communis Communis( (Arand Arand) ) Symptoms: Burning sensation , Gastroenteritis , Diarrhea , Emesis , Respiratory disturbances , Cardiac arrest. Symptoms: Burning sensation , Gastroenteritis , Diarrhea , Emesis , Respiratory disturbances , Cardiac arrest.
Atropine Atropine containing Plants Plants include include:: Atropa Symptoms Symptoms of of toxicity Convulsions, Convulsions,Dizziness, containing plants Atropa belladonna, toxicity :: Intense Intense thirst, Dizziness,Blurred Blurredvision, plants belladonna, Datura thirst, Flushed vision, Coma Daturastramonium stramonium,,Hyoscyamus Flushed skin, skin, CNS CNS hyperirritability Comaand anddeath death.. Hyoscyamusniger hyperirritability ,, Delirium, niger Delirium, Arythmias Arythmias,, Hallucination, Hallucination, CNS CNS toxic There There are are many Convulsants Convulsants This This group Plants Plants include Symptoms Symptoms:: Seizure, toxic plants plants many plants plants containing containing neurotoxin neurotoxin that thathave have toxic toxic effects effectson onthe thenervous nervoussystem system.. groupof of plants include:: Cicuta Seizure,Hallucination plants causes Cicutavirosa Hallucination,,Confusion, causes convulsions convulsions or orseizure virosa( (Hemlock Hemlock) )Azadirachta Confusion,Cerebral seizure Azadirachtaindica Cerebraldamage indica( (Neem damage,,Unconciousness Unconciousness,,Block Neem), ), Strychnos Strychnosnux nux- -vomica vomica( (Kuchla Blocknerve nerveimpulse Kuchla) ) impulse
Plants Plants that Thisgroup Plantsinclude Signsof oftoxicity that alter groupof of plants include:: Cannabis toxicity:: Depression alter awareness awareness plants contains Cannabissativa Depression,,Blurred This contains substances substances that sativa( (Marijuana Marijuana) ) Opium Blurredvision thatcan Opiumpoppy vision,Unconsciousness, ,Unconsciousness,Delerium cancause cause an an altered poppy( (Papaver alteredmental Papaversomniferum somniferum) ) Delerium,,Dementia, mentalor or behavioural behaviouralstate statein in animals animals.. Plants Signs Dementia,Cardiac Cardiac and andrespiratory respiratorydistress distress.. Plants Plants having These plants Plants:: Nicotiana Signs of of toxicity Hypertesion Hypertesion,, Cough, having nicotine nicotinelike plants contain contain either Nicotianatobaccum toxicity include Cough, Chest likeaction action either nicotine nicotine or or similar tobaccum( (Tobacco Tobacco) ) include :: Nausea, Nausea, Vomitting Chestpain pain These similar substances substances.. Plants Signs Vomitting,, Salivation, Salivation, Diarrhoea Diarrhoea,, Convulsions, Convulsions, Muscle Muscle twitching, twitching, Weakness, Weakness,
Cardiotoxi Cardiotoxic Plants Plants that cause cardiovascular changes . Several plants contain chemicals that rapidly and significantly affect the Plants that cause cardiovascular changes . Several plants contain chemicals that rapidly and significantly affect the heart. heart. Plants that effect heart are : Digitalis purpurea purpurea, Digitalis , Digitalis lanata Signs and symptoms of toxicity: Nausea, Vomiting, Signs and symptoms of toxicity: Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhoea Diarrhoea, Respiratory distress , Cardiac arrest, c Plants Plants that effect heart are : Digitalis lanata , Respiratory distress , Cardiac arrest, Arrythmias Arrythmias Hepatotoxic plants Hepatotoxic plants This group of plants contains This group of plants contains Hepatoxin Plants that produce hepatotoxicity are : Plants that produce hepatotoxicity are : Terminalia Signs and symptoms of toxicity: Rash, fever, fatigue, edema, itching, yellowing of skin, loss of appetite , Signs and symptoms of toxicity: Rash, fever, fatigue, edema, itching, yellowing of skin, loss of appetite , abdominal pain abdominal pain Hepatoxin that can cause damage or inflammation of liver. that can cause damage or inflammation of liver. Terminaliachebula chebula, , Trifolium Trifoliumspp. spp.