Environmental Impact Assessment of Frame Lake and Recommendations
The subbottom seismic profiling and stratigraphy studies reveal the sediment layers in Frame Lake and the impact of urban development on water quality. Glew coring analysis identifies layers of arsenic contamination. Recommendations include dredging to restore the lake's natural state pre-1975. The report addresses the implications of allochtonous sediment deposition and urban runoff seepage from the Trailer Park.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
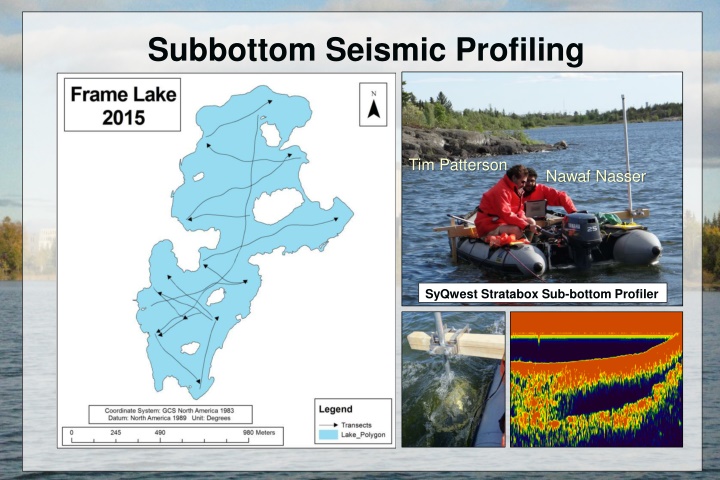
Subbottom Seismic Profiling Tim Patterson Nawaf Nasser SyQwest Stratabox Sub-bottom Profiler
Subbottom Seismic Stratigraphy 1962 to present Holocene lake sediments Proto-Great Slave Lake
Glew Coring Nawaf Nasser ~1990 ~1962
X = 23.3 cm thick Volume All Layers 206,000 m3 Drafted by: D. Monita Thickness and Volume of Arsenic Contaminated Layer
Thickness and Volume of Contaminated Layer Range As (ppm) Average As (ppm) Mean Thickness Volume (m^3) All Layers 0.233 205972.00 Layer 1 100-500 264 0.0362 32000.80 Layer 2 500-1000 787 0.0188 16619.20 Layer 3 1000-1550 1370 0.0195 17238.00 Layer 4 500-1000 482 0.0688 60819.20 Layer 5 100-500 255 0.0897 79294.80 Bins Range As (ppm) Volume (m^3) Bin 1 100-500 111295.60 Bin 2 500-1000 77438.40 Bin 3 1000-1550 17238.00 Total 205972 Land Area 884000
Thickness and Volume of Arsenic Contaminated Layers 1 2 3 1.9 cm 2.0 cm 3.6 cm 17,200 m3 16,900 m3 33,000 m3 100 to 500 ppm 500 to 1000 ppm 1000 to 1500 ppm Volume All Layers 206,000 m3 5 4 6.9 cm 9.0 cm 60,800 m3 79,300 m3 X = 23.3 cm 500 to 1000 ppm 100 to 500 ppm
Urban development has impacted water input and output from Frame Lake Causeway ~1975 Urban runoff influenced Inlet Trailer Park Seepage
Recommendation 1 Up to 40 cm of allochtonous sediment In lake deposited over relatively short time Causeway ~1975 Urban runoff influenced Inlet Dredge material to return lake to early 20th century water depth and substrate type. Trailer Park Seepage
Recommendation 2 Flow through lake too slow. Causeway ~1975 Permits build-up of nutrients in water column. Urban runoff influenced Inlet Increase flow rate at sluice gate outline by causeway. Trailer Park Seepage
Recommendation 3 Only true stream inlet in at SW corner of lake. Causeway ~1975 Permits nutrient laden water from suburban/urban area to enter lake. Urban runoff influenced Inlet Construct Storm Water Management (SWM) Pond on site. Trailer Park Seepage