EasyCFD Project Guide: Setting up and Running a CFD Analysis
Learn how to set up and run your own CFD analysis using EasyCFD software. Download the trial version, follow tutorials, create unique geometries, and submit a report detailing your experience. Explore tools, solve flow field problems, and enhance your CFD skills.
Uploaded on Aug 10, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CFD: Project Using EasyCFD to Setup and Run a CFD Analysis
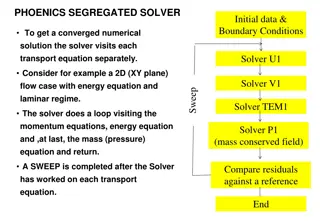
CFD Project Overview Laminar Unsteady Flow Goal: Learn how to setup and run your own CFD analysis Steps 1. Download EasyCFD (free trial version is available) 2. Follow the Video Tutorial provided as part of this Lecture Series 3. Setup a 2ndanalysis using a geometry you create 4. Write up a Report Note: review this entire PPT before starting on the project
EasyCFD Download Navigate to: http://www.easycfd.net/index_files/Page551.htm Download the Trial Version of EasyCFD Install EasyCFD Only compatible with Windows Operating Systems
EasyCFD Example Simulation On the USMAthematics CFD Lecture website you will find a tutorial video which will provide step by step instructions to complete an analysis of the flow field around an obstacle. http://usmathematics.com/wp/cfd-lecture/ Be aware that the Trial Version does not allow you to save your project. So make notes and take screenshots when appropriate
EasyCFD Create your own Simulation Once you have completed the example problem, explore the software a bit more to become familiar with the various tools and options, specifically the geometry creation tools. Once familiarized, follow the example analysis again, but create your own unique geometry. Point Scale: 80 Points: Completing the example analysis 85 Points: Completing the example analysis and an additional analysis using a simple geometry (ex. triangle, square, etc.) 100 Points: Completing the example analysis and an additional analysis using a complex/unique geometry
Write and Submit your Report Write up a short report detailing your experience. Discuss the following: The workflow, including any issues following the tutorial What steps you took to better learn about EasyCFD capabilities The geometry you selected and why Any challenges creating or meshing the geometry Any issues with solving the CFD analysis with your geometry Please include images from both the example problem and your own geometry, including images of the mesh and images of the CFD solution. Please submit reports to Dr. Hromadka ted@phdphdphd.com
Sample Geometry for 100 Points (Do Not Duplicate)
Potential Issues with Complex Geometry Complex geometries can create issues during the meshing step. These issues can manifest as warnings during the meshing or in a lack of solution convergence when solving. Below are some warnings and automatic correction messages you may see when meshing the geometry you created. If offered an automatic correction, click Yes to All or Yes . The specifics of these errors are beyond the scope of this lesson but take note of the importance of meshing to ensuring a successful CFD simulation. A warning may or may not need correction. Try running the solver first. If convergence is an issue, you may want to try refining the mesh per the instructions in the following slides.
Solution Convergence Complex geometries and geometries leading to unsteady flow (like the example) can lead to errors when trying to find a solution to the CFD analysis. A common cause is divergence of the residuals. If this happens, you will see the following warning message. An example of diverging residuals is also shown. There are a couple reasons this error could occur. The flow regime could be unsteady, thus there is no single answer so the residuals will not converge. However, even unsteady flow problems may not lead to residual divergence if the mesh is refined or if the time step of the simulation is reduced. The probable solution to this issue is to refine the mesh (refer back to the Video for how to refine the mesh) or decrease the size of the timestep. If the solver executes, you may also see a warning that the convergence criteria has not been reached , this is especially true if the geometry is creating unsteady flow conditions. For the purpose of this exercise this warning may be ignored.
Boundary Condition Issues After successfully conducting a CFD analysis, you may see the below warning. This means that the model domain is not large enough to capture all the flow field effects and that the boundaries of the model are influencing the results. The fix in this case would be to increase the size of the domain and move the boundaries away from the created geometry. However, for this exercise it is enough to make note of the issue.
Note: In industrial applications of computational engineering mathematics (CEM) related software packages, such as demonstrated by our example problem, one typically encounters limitations of the CEM software, usually from high levels of discretization and computational matrix solution difficulties and the like. Be aware of the software underpinnings and be cautious in assuming that you have a "correct" solution simply because the software "ran" and you have a computational solution in hand. This particular topic is beyond the scope of the current class, but this type of assessment can be found in the current literature as well as in graduate courses. The course web page includes assessment topics of CEM modeling accuracy issues under the general topic of RESEARCH.