Comprehensive Study Guide for Renal & Excretory System II Module in Third Year MBBS
This study guide provides in-depth information on the Renal & Excretory System II module for third-year MBBS students. It covers the objectives, learning methodologies, assessment methods, and rules and regulations of the curriculum. The guide includes details on the organization of the module, learning resources, and curriculum framework. Students will engage in integrated learning experiences through lectures, clinical rotations, practical demonstrations, and self-study, enhancing their understanding of renal and excretory system concepts.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
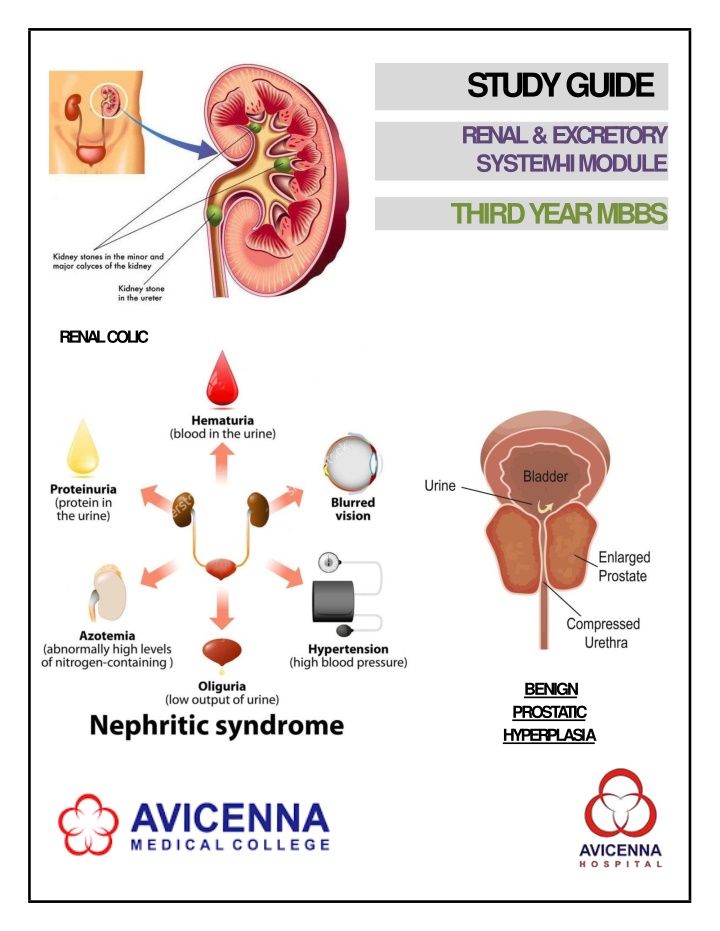
STUDYGUIDE RENAL &EXCRETORY SYSTEM-IIMODULE THIRD YEARMBBS RENALCOLIC BENIGN PROST A TIC HYPERPLASIA
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE STUDY GUIDE FOR RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM-IIMODULE Page No. 3 4 5 7 7 8 13 15 17 20 21 CONTENTS S.No 1 2 3 4 4.1 4.2 5 6 7 8 9 Overview Introduction to StudyGuide LearningMethodologies Module 2: Renal and ExcretorySystem-II Introduction Objectives and LearningStrategies LearningResources AssessmentMethods Semester Examination Rules and Regulations of UHS Modular Examination Rules and Regulations(AVMC) Schedule Page | 2
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM II MODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Year: Three Duration: 4 weeks Timetable hours: Lectures, Case-Based Integrated Learning (CBIL), Clinical Rotations, learning experience in LNH outreach centers, Laboratory, Practical, Demonstrations, Skills, Self-Study Credit hours: 3 credit hours in theory and 1.5 credit hours in practical MODULE INTEGRA TED COMMITTEE MODULECOORDINATOR: Dr. Dr. Mushtaq Ahmed CO-COORDINATOR: Dr. Fatima Arslan DEPARTMENTS & RESOURCE PERSONS FACILITATINGLEARNING CLINICAL AND ANCILLARYDEPARTMENTS Pedriatics Dr. Aneela Zareen NEUROLOGY Dr. Fatima Arslan Dr. Farhat Minhas OCCUPATIONALTHERAPY: Dr. Aneel Shafi ORTHOPEDICS: Dr. Talat Bashir PHYSIOTHERAPY Mr. Syed Hassan Abbas LNH&MC MANAGEMENT Professorr.Dr. Gulfreen Waheed, Dean & Principal, Director AVMC Dr.Brg. Gul-e-rana Controller AVMC STUDY GUIDE COMPILEDBY: Dr. Sadia Awan, Dr. Muhammad Muzzammil Sadiq ,Dr. Usama Bin Ishtiaq Page | 3
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE INTRODUCTION WHAT IS A STUDYGUIDE? It is an aidto: Inform students how student learning program of the semester-wise module has been organized Helpstudentsorganize andmanagetheirstudiesthroughoutthemodule Guide students on assessment methods, rules andregulations THE STUDYGUIDE: Communicates information on organization and management of themodule. Thiswill helpthestudentto contactthe rightpersonin caseof anydifficulty. Definestheobjectiveswhich areexpectedto beachieved at theendof themodule. Identifies the learning strategies such as lectures, small group teachings, clinical skills, demonstration, tutorial and casebasedlearning that will be implemented to achieve the module objectives. Provides a list of learning resources such as books, computer assisted learning programs, web- links,journals,forstudentsto consultin orderto maximize their learning. Highlights information on the contribution of continuous and semester examinations on the student s overallperformance. Includes information on the assessment methods that will be held to determine every student s achievement ofobjectives. Focuses on information pertaining toexamination policy, rules and regulations. CURRICULUMFRAMEWORK Studentswill experience integratedcurriculumsimilar to previousmodulesof all 5semesters. INTEGRATED CURRICULUM comprises of system-based modules such as GIT & Liver II, Renal & Excretory System II and Endocrinology II which links basic science knowledge to clinical problems. Integrated teaching means that subjects are presented as a meaningful whole. Students will be able to have better understandingof basicscienceswhentheyrepeatedlylearn in relation to clinicalexamples. LEARNING EXPERIENCES: Case based integrated discussions, skills acquisition in skills lab. computer- based assignments, learning experiences in clinics, wards, and outreach centers. Page | 4
3RD YEAR MBBS,RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE LEARNINGMETHODOLOGIES Thefollowing teaching/ learningmethodsareusedto promotebetterunderstanding: InteractiveLectures Small Group Discussion Case-Based Integrated Learning(CBIL) ClinicalExperiences o ClinicalRotations o Experience in LNH outreachcenters Practicals Skillssession Self-DirectedStudy INTERACTIVE LECTURES:In large group, the lecturer introduces a topic or common clinical conditions and explains the underlying phenomena through questions, pictures, videos of patients interviews, exercises, etc.Studentsareactively involved in the learningprocess. Page | 5
AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE SMALL GROUP SESSION: This format helps students to clarify concepts, acquire skills or desired attitudes. Sessions are structured with the help of specific exercises such as patient case, interviews or discussion topics. Students exchange opinions and apply knowledge gained from lectures, tutorials and self study. The facilitatorrole isto askprobingquestions,summarize,orrephraseto help clarify concepts. CASE- BASED INTEGRATED LEARNING (CBIL): A small group discussion format where learning is focused around aseriesof questions basedon aclinical scenario. Students discussand answer the questions applying relevant knowledge gained previously in clinical and basic health sciences during the module and construct newknowledge. TheCBILwill beprovided bythe concerndepartment. CLINICAL LEARNING EXPERIENCES:In small groups, students observe patients with signs and symptoms in hospital wards, clinics and outreach centers. This helps students to relate knowledge of basic and clinical sciencesof the module andpreparefor futurepractice. CLINICAL ROTATIONS: In small groups, students rotate in different wards like Medicine, Pediatrics, o Surgery, Obs & Gyne, ENT, Eye, Family Medicine clinics, outreach centers & Community Medicine experiences. Here students observe patients, take histories and perform supervised clinical examinations in outpatient and inpatient settings. They also get an opportunity to observe medical personnel working as a team. These rotations help students relate basic medical and clinical knowledgein diverse clinicalareas. EXPERIENCEIN LNHOUTREACHCENTERS:Learning at outreach centers of LNHhave been organized o and incorporated as part of training of third year medicinal students. The objective is to provide clinical trainingexperiencesforstudentsin primarycaresettings. PRACTICAL: Basic science practicals related to pharmacology, microbiology, pathology, forensic medicine, andcommunitymedicine havebeenschedulefor studentlearning. SKILLSSESSION: Skills relevant to respective module are observed and practiced where applicable in skills laboratory. SELF-DIRECTED STUDY: Students assume responsibilities of their own learning through individual study, sharing and discussing with peers, seeking information from Learning ResourceCenter,teachersand resource persons within and outside the college. Students can utilize the time within the college scheduled hours of self-study. Page | 6
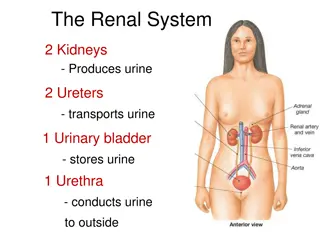
AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE SEMESTER 6 MODULE 2 : RENAL & EXCRETORYSYSTEM-II INTRODUCTION Worldwide, an estimated 200 million people have chronic kidney disease (CKD) with people in the low-to- middle income countries of Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa have the highest rates of CKD [1]. In Pakistan common causes of CKD identified in the patients included diabetic nephropathy (140, 28%), glomerulonephritis (110, 22%), hypertension (73, 14.6%), tubulo-interstitial disease (67, 13.4%) and renal stone disease (40, 8%). The cause was unknown in a significant percentage of patients (53, 10.6%). Other causes including post-partum renal failure, which constituted 2% of the cases[2]. Thismodule aimsto equipmedical undergraduateswith the essentialknowledgeandskills requiredfor dealing with prevalent renal disorders in the local context. This is the second module on renal and excretory system in MBBS course. The basics of renal and excretory system including anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, pathology and introduction to clinical presentations have been addressed in the first module. The module will focus on common diseases of the renal and excretory system, including infections, obstructive, genetics and acquired disorders and cancerous and non-cancerous renal and excretorydiseases. References: 1. Akinlolu Ojo (2014) Addressing the global burden of chronic kidney disease throughclinical and translational research. Transactions of the american clinical and climatological association, vol. 125,2014 Kifayat Ullah, Ghias Butt, Imtiaz Masroor, Kinza Kanwal, Farina Kifayat (2015) Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease in a Pakistani population. Saudi Journal of kidney diseases and transplant, 2015 Nov;26(6):1307-10. doi:10.4103/1319-2442.168694. 2. Page | 7
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE COURSE OBJECTIVES ANDSTRA TEGIES At theendof themodulethestudentswill beableto: LEARNING STRATEGY TOPICS &OBJECTIVES FACULTY OVERVIEW, CONGENITAL ANOMALIES, UTI,UROLITHIASIS Describe the gross and microscopic structure ofrenal system Correlate the anatomic basis of renal signs & symptoms Describe the development and congenital anomaliesof renalsystem Classify cystic diseases of thekidneys Discuss genetics, pathogenesis, morphology and clinical features of autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive and polycystic kidneydisease Describe cystic diseases of renalmedulla Interpret urineanalysis Demonstrate proteinuria in a given sample of urineby Lab/DipstixMethod Describe the procedure ofperforming urine C/S Explain renal functiontests Interpret renal function tests(RFT) InteractiveLectures Anatomy InteractiveLecture Pathology Practical Nephrology InteractiveLecture Small Group Discussionwith HandsOn Skills Lab Demonstrate steps of Foley scatheterization Discuss causes, pathogenesis, morphology and clinical features ofHydronephrosis Describe thefourmaintypesofrenalstones andtheir pathogenesis Identify etiologies and patho-physiology forupper and lower urinary tractinfections Identify treatments and medications used inthe management of renal calculusurolithiasis Pathology InteractiveLectures Urology InteractiveLectures Analyze clinical signs and symptoms of major renaland urinary tractdiseases Classify diuretics, mechanism of action, therapeutic uses, pharmacokinetic profile and adverse effects ofdiuretics Pharmacology InteractiveLecture Evaluate a patient with diseases of thekidneys and urinary tract Describe the effects and management ofobstructive Urology InteractiveLecture Page | 8
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE urinary tractdisease Identify common infectious etiologies for upper and lower urinary tractinfections Analyze clinical signs and symptoms of common renal diseases to construct a differentialdiagnosis Describe the approach for evaluating and treating common renaldiseases Pediatrics InteractiveLecture Describe the development of urinarysystem, normal structure, blood supply, innervations, lymphatic drainage functions and its congenitalanomalies PediatricsSurgery InteractiveLecture ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY AND GLOMERULONEPHRITIS Explain therapeutic applications ofdiuretics Explain nephrotoxic drugs Explain drugs used in renalfailure Case- Based Discussion Pharmacology Classify specific renal diseases according to threemajor components on the basis ofglomerular, vascular and tubulointerstitial types Discuss pathogenesis of glomerulardiseases Pathology InteractiveLecture Discuss the etiology and diagnosis of the commonrenal diseases in children including nephrotic andnephritic syndromes Identify the difference between upper and lowerurinary tracthematuria Explain the common causes ofproteinuria Pediatrics InteractiveLecture Discuss diseases associated with nephrotic andnephritic syndrome Pathology InteractiveLecture Describe the diagnosis and managementof o Acute kidney injury(AKI) o Nephrotic syndrome Nephrology InteractiveLecture Relate clinical signs and symptoms of renal disease to underlying pathophysiology of Tubulointerstitialdisease Nephritic & Nephroticsyndrome Pathology InteractiveLecture Discuss the mechanism of action, therapeutic uses, pharmacokinetic profile and adverse effects of various types ofdiuretics SmallGroup Discussion Pharmacology Page | 9
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Describe the pathophysiology, morphology andclinical features in Glomerular conditions associated with systemic disease CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASES (CKD) and RENAL REPLACEMENTTHERAPY(RRT) Pathology InteractiveLecture Interactive Lecture/Case-Based Discussion Describe the diagnosis and management of chronicKidney diseases Nephrology Discussthe ethical issuesinthemanagementof patients with end-stage-renal diseases including issues surrounding resource allocation such as dialysis andtransplantation Urology InteractiveLecture Describe themajorcharacteristicsof the renal replacement therapy RRTmodalities Identify indications and contraindications forRRT Compare RRT to intermittent dialysistherapy Nephrology InteractiveLecture Pediatrics InteractiveLecture Discuss Acute kidney injury and chronic kidneydiseases BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY, TUMOURS OF URINARYSYSTEM Discuss Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia andProstatic carcinoma as a cause of urinary outflowobstruction Explain the genetics, pathogenesis, morphology and clinical features of Prostaticcarcinoma Pathology InteractiveLecture Describe approaches for evaluating and treatingdiseases of prostate Urology InteractiveLecture Classify the risk factors, histology, pathophysiology& clinical features of renalcancers Classify Urothelial tumors Discuss etiology, pathogenesis, morphology and clinical features of urothelialtumors Pathology InteractiveLecture Describe the evaluation, diagnosis and managementof kidneytumors Urology InteractiveLecture Small Group Discussion Interpret imaging modalities including IVP/US/RenalCT and pyelography used in the diagnosis of renalpathologies Radiology COMMNUNITYMEDICINE Explain the concept of demography inPakistan InteractiveLectures Community Discussthe determinants of fertility in apopulationandits Page | 10
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE concept in health system ofPakistan Medicine Describe thedeterminants ofmortality anditsrole in demography ofPakistan Distinguish the various measures of morbidityand its impact onpopulation Interpretthepopulationpyramidanditsvarious applications Explain the balancing equation and its applicationin differentscenarios Explain demographictransition FORENSICMEDICINE Rape Explain Legal definition of rape and itstypes Describe procedure of medico-legal examination ofrape victim whichinclude: o Consent o Specific history related to allegedoffence o Generalexamination o Physicalexamination o Examination ofgenitalia InteractiveLectures Examination of Accused in allegedrape Describe procedure of medico-legal examinationof accused in alleged rape whichinclude: o Medicolegal Examinationof o Consent o History o Generalexamination o Physicalexamination o Examination ofgenitalia ForensicMedicine Discuss: Sexualoffences Sexual deviations/ perversions Drug-facilitated sexual assault (Daterape) SmallGroup Discussion Sodomy Describe medicolegal examination of passive andactive agents in an alleged case ofsodomy ForensicMedicine InteractiveLecture Forensic specimens collection in sex-offence Discuss the process of specimen collection whichinclude: o The purpose of forensicspecimens o Specimen collectiontechniques Page | 11
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Laboratory Diagnostictests o Discuss the types, signs & symptoms, treatment,post mortem appearance and medicolegal importanceof o Spinal poisons o Animalpoisons o Therapeutic drug poisoning/overdosage SmallGroup Discussion State medicolegal report in sexual assault case& presenting evidence incourt InteractiveLecture Discuss the types, Signs & Symptoms, treatment,post mortem appearance and medicolegalimportance o Cardiacpoisons o Irrespirablegases SmallGroup Discussion Apart from attending daily scheduled sessions, students too should engage in self-study to ensure that all the objectives arecovered. Page | 12
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE LEARNINGRESOURCES SUBJECT RESOURCES A. GROSSANATOMY 1. K.L. Moore, Clinically OrientedAnatomy B. EMBRYOLOGY 1. Keith L. Moore. The DevelopingHuman 2. Langman s Medical Embryology TEXTBOOKS 1. Community Medicine byParikh 2. Community Medicine by MIllyas 3. Basic Statistics for the Health Sciences by Jan WKuzma ANATOMY COMMUNITYMEDICINE TEXTBOOKS 1. Nasib R. Awan. Principles and practice of Forensic Medicine 1st ed.2002. 2. Parikh, C.K. Parikh s Textbook of Medical Jurisprudence,Forensic Medicine and Toxicology. 7thed.2005. REFERENCEBOOKS 3. Knight B. Simpson s Forensic Medicine. 11th ed.1993. 4. Knight and Pekka. Principles of forensic medicine. 3rd ed.2004 5. Krishan VIJ. Text book of forensic medicine and toxicology (principles and practice). 4th ed.2007 6. Dikshit P.C. Text book of forensic medicine and toxicology. 1st ed.2010 7. Polson. Polson s Essential of Forensic Medicine. 4thedition. 2010. 8. Rao. Atlas of Forensic Medicine (latestedition). 9. Rao.Practical Forensic Medicine 3rd ed,2007. 10. Knight: Jimpson s Forensic Medicine 10th 1991,11thed.1993 11. Taylor s Principles and Practice of Medical Jurisprudence.15th ed.1999 CDs: 1. Lectures on ForensicMedicine. 2. Atlas of ForensicMedicine. FORENSICMEDICINE WEBSITES: www.forensicmedicine.co.uk REFERENCEBOOKS: 1. Hutchison s Clinical Methods, 23rdEdition 2. MacLeod's clinical examination 13thedition 3. Davidson's Principles and Practice ofMedicine 4. Kumar and Clark's ClinicalMedicine 5. HCAI guidelines CDC 6. WHO TBguidelines GENERALMEDICINE Page | 13
AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE TEXTBOOKS 1. Robbins & Cotran, Pathologic Basis of Disease, 9thedition. 2. Rapid Review Pathology, 4th edition by Edward F. GoljanMD PATHOLOGY/MICROBIOLOGY WEBSITES: 1. http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/webpath.html 2. http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/ TEXTBOOK: 1. Basis of Pediatrics (8th Edition PervezAkbar) PEDIATRICS A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Lippincot IllustratedPharmacology 2. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology by Katzung PHARMACOLOGY A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Textbook Of Medical Physiology by Guyton AndHall 2. Ganong S Review of MedicalPhysiology 3. Human Physiology by LauraleeSherwood 4. Berne & LevyPhysiology 5. Best & Taylor Physiological Basis ofMedical Practice PHYSIOLOGY ADDITIONAL LEARNINGRESOURCES Hands-on Activities/PracticalStudents will be involved in Practical sessions and hands-on activitiesthat link with the Renal and Excretory module-II toenhance learning. Utilize thelabto relatetheknowledge to the specimensandmodels Labs available. Provides the simulators tolearn the basic skills and procedures. This helps SkillsLab build confidence when approaching patients inreal settings. Familiarizethestudent with theproceduresandprotocols to assist Videos patients. To increase knowledge and motivation of students through the available internet resources and CDs/DVDs. This will be an additional advantage to Computer Lab/CDs/DVDs/Internet meaningfullearning. Resources: Self Learning is when students seek information to solve cases,read through different resources and discuss among peers, and with the faculty SelfLearning to clarify theconcepts. Page | 14
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE ASSESSMENTMETHODS: Theory: o Best Choice Questions (BCQs) also known as MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions) are used to asses objectives covered in eachmodule. A BCQ has a statement or clinical scenario followed by four options (likelyanswer). Studentsafterreading t hestatement/scenariosel ect ONE,t he most appropriate response from the given list ofoptions. Correct answer carries one mark, and incorrect zero mark . There is no negative marking. Studentsmarktheirresponsesonspecifiedcomputer-based/OMRsheetdesignedforAVMC. EMQs: An EMQhas: o o Anoption list of 5-15 which maybenervesupply, functions,diagnosis,investigationsetc A Lead In Statement/Question o Two to four Stems or ClinicalScenarios Foreachstemorclinical scenario,the studentshouldchoosethemostappropriateoption fromthe o optionlist. Asingle option canbeusedonce,morethanonceornot at all. Correct answer carries one mark and incorrect zero mark . There is NO negativemarking. Student mark their responses on a specified computer-based sheet forEMQs. OSPE/OSCE: Objective Structured Practical/ClinicalExamination: Eachstudentwill beassessedonthe samecontentandhavesametimeto completethe task. Comprise of 12-25stations. Each station may assess a variety of clinical tasks, these tasks may include history taking, physical examination, skills and application of skills andknowledge Stations are observed, unobserved, interactive and reststations. Observed and Interactive Stations: o Theywill beassessedbyinternal orexternalexaminersthroughstructuredviva ortasks. Unobserved Stations: It will be static stations in which there may be an X-ray, Labs reports, pictures, clinical o scenarioswith relatedquestionsforstudentsto answerontheprovidedanswercopy. Rest station o I t is a station where there is no task given and in this time student can organize his/her thoughts. Page | 15
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE AVMC Internal Evaluation Policy Students will beassessedto determine achievement of moduleobjectivesthroughthefollowing: Module Examination: willbe scheduled on completion of each module. The method of examination comprises theory exam which includes BCQs and OSPE (Objective Structured PracticalExamination). Graded Assessment of students by Individual Department: Quiz, viva, practical, assignment, small group activities such as CBL, TBL, TOL, online assessment, ward activities, examination, and logbook. Marksof bothmodular examinationandgradedassessmentwill constitute 20%weightage. As per UHS policy, this 20% will be added by UHS to SemesterExamination. Example : Number of JSMU Marks allocated for Semester Theory and Internal Evaluation InternalEvaluation (Task Presentation + Assignments + Modular Exam 20% Semester Examination TheoryMarks Total(Theory) Semester 80% 100% FormativeAssessment Individual department may hold quiz or short answer questions to help students assess their own learning. The marks obtained are not included in the internalevaluation More than 75% attendance is needed to sit for the modular and semester examinations Page | 16
AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE MODULAR EXAMINATION RULES & REGULATIONS(AVMC) Studentmustreportto examinationhall/venue, 30 minutesbeforetheexam. Exam will begin sharp at the giventime. No student will be allowed to enter the examination hall after 15 minutes of scheduled examinationtime. Studentsmust sitaccordingto theirroll numbersmentioned ontheseats. Cell phones are strictly not allowed in examinationhall. If anystudentisfoundwith cell phonein anymode(silent, switchedoff oron)he/shewill benot be allowed to continue theirexam. No students will be allowed to sit in exam without University Admit Card, AVMC College ID Card and LabCoat Student must bring the following stationary items for the exam: Pen, Pencil, Eraser, and Sharpener. Indiscipline in the exam hall/venue is not acceptable. Students must not possess any written materialorcommunicatewith theirfellowstudents. Page | 17
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE ExaminationProtocols: In each semester , module will be assessedby theory paper com prising MCQsand EMQs. For examplesemester8 will have separate theory paper of EYE,Dermatology, PlasticSurgery& Burns,Neuro-Sciences-II& Psychiatry,GeneticsandRehabilitationmodules. There will be one OSPE (Objective Structured Practical Examination)/OSCE (Objective Structured Clinical Examinations) which will coverall threemodules of semesterseven. 1. Theory Theory paper will comprise of80 one best type MCQs and 20 EMQs. Timeduration fortheorypaperwill be120minutes. Students will mark their responses on UHS specified response sheets assessed by computer software. It will carryout 80%contributionintheoryresultsof the Semester. There is no negativemarking. 2. OSPE/OSCE: It maycomprisebetween12-25stations.Eachstationwill carry10marks. 3. UHS Grading System It will be based on GPA 4system Marks obtained in Percentagerange NumericalGrade AlphabeticalGrade 80-100 4.0 A+ 75-79 4.0 A 70-74 3.7 A- 67-69 3.3 B+ 63-66 3.0 B 60-62 2.7 B- 56-59 2.3 C+ 50-55 2.0 C <50 Un-grade-able 0 U A candidate obtaining GPA less than 2.00 (50%) is declared un-graded(fail). Cumulativetranscriptisissuedat the endof clearance of all modules. Page | 18
3RD YEAR MBBS, RENAL & EXCRETORY SYSTEM IIMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 4. RetakeExamination Retakeexaminations are for those students who fail in semester examinations and those who have passedsemester examinations with GPAlessthan 3.0 mayreappear in respective retake examination to improvegrades. The format of the retake examination is exactly the same as insemester examinations. Retakeexaminationwill beconducted3weeksafterdeclarationof results. 5. Promotion to nextclass Studentswho passbothsemesterexaminations arepromotedfromfirstyearto secondyear. Students who fail the MBBS first year semester retake examination will be promoted to second year. Students will be promoted from second year to third year and onward only if they have passed thesemesterexaminationsof thatyear. Clearance of all modules and their components of semester one to four are mandatory for promotion from second year tothird year (as per PMDC rules). As per PMDC rules any candidate failing to clear a module or its component in four (1+3) attemptsisNOTallowed to carryout furthermedicaleducation. Clearance of all modules and their components of semester/s are mandatory for promotion from third yearonward. Page | 19