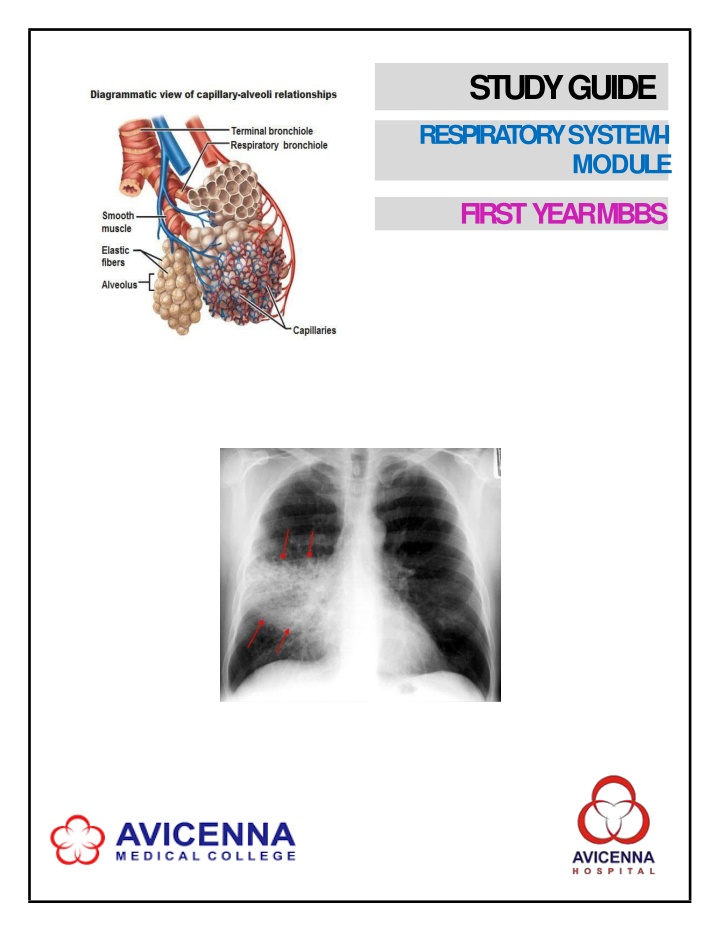
Respiratory System Study Guide for First Year MBBS Students
Introduction to the study guide for the Respiratory System module in the first year of MBBS at Avicenna Medical College. It includes details on curriculum framework, learning methodologies, assessment methods, and key personnel involved in the module. The guide aims to assist students in organizing their studies, understanding module objectives, and navigating assessment procedures effectively.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
STUDYGUIDE RESPIRA TORYSYSTEM-I MODULE FIRST YEARMBBS
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE STUDY GUIDE FOR RESPIRA TORY SYSTEM-IMODULE Credit hours: 3 credit hours in theory 1.5 credit hours inpractical Page No 03 04 06 08 08 09 19 21 24 25 26 S.No 1 2 3 4 5 6 6.1 6.2 7 8 9 CONTENT List of Integrated Modular Committeemembers Introduction to StudyGuide Learning Methodologies Module 2: RespiratorySystem-I Importance Objectives andStrategies Learning Resources AssessmentMethods Semester Examination Rules and Regulations of UHS Modular Examination Rules and Regulations(AVMC) Schedule Page | 2
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Year:One Duration: 4 weeks Timetable hours: Lectures, Case-Based Learning (CBL), Team based Learning (TBL), Self-Study, Practical, Skills, Demonstrations, Field Visits, Visit to Wards& Laboratory MODULE INTEGRA TEDCOMMITTEE MODULECOORDINATOR: CO-COORDINATORS: Professor Dr. Zubair Ahmad(Biochemistry) Professor Dr. Rubina Hafeez (Pathology) Professor Dr.Rehana Shahid(Anatomy) DEPARTMENTS & RESOURCE PERSONS FACILITA TINGLEARNING BASIC HEALTHSCIENCES CLINICAL AND ANCILLARYDEPARTMENTS FAMILYMEDICINE Professor Dr. Muhammad Luqman ANATOMY Professor Dr.Rehana Shahid BIOCHEMISTRY Professor Dr. Zubair Ahmad MEDICALEDUCATION Professor Dr. Waheed Ahmad COMMUNITYMEDICINE Professor Dr. Rana Muhammad Akhtar Khan INTERNALMEDICINE Dr. Muhammad Usman Amir PATHOLOGY HEMATOOGY Dr. Syeda Ijlal Zehra Zaidi Professor Dr. Rubina Hafeez PHYSIOLOGY Professor Dr. Binyamin Ahmad PHARMACOLOGY Professor Dr. Rana Tariq Mehmood AVMCMANAGEMENT Professor Dr. Gulfreen Waheed, PrincipalAVMC Brig.Dr. Gul e Rana , Director AVMC Dr. Sadia Awan Dr. Muhammad Muzzammil Sadiq Dr. Usama Bin Ishtiaq STUDY GUIDE COMPILEDBY: Department of Health CareEducation Page | 3
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE INTRODUCTION WHAT IS A STUDYGUIDE? It is an aidto: Inform students how student learning program of the semester-wise module has been organized Helpstudentsorganize andmanagetheirstudiesthroughoutthemodule Guide students on assessment methods, rules andregulations THE STUDYGUIDE: Communicates information on organization and management of themodule Thiswill helpthestudentto contacttherightpersonin caseof anydifficulty Definestheobjectiveswhich are expectedto beachieved at theendof themodule Identifies the learning strategies such as lectures, small group teachings, clinical skills, demonstration, tutorial and casebasedlearning that will be implemented to achieve the module objectives Provides a list of learning resources such as books, computer assisted learning programs, web- links,journals,forstudentsto consultin orderto maximize their learning Highlights information on the contribution of continuous and semester examinations on the student s overallperformance Includes information on the assessment methods that will be held to determine every student s achievement ofobjectives Focuses on information pertaining toexamination policy, rules and regulations CURRICULUMFRAMEWORK Students will experience integrated curriculum of 1st &2nd semesters. INTEGRATED CURRICULUM comprises of system-based modules such as Locomotor system, Respiratory System and Cardiovascular system which links basic science knowledge to clinical problems. Integrated teaching means that subjects are presented as a meaningful whole. Students will be able to have betterunderstandingof basicscienceswhentheyrepeatedlylearn in relation to clinical examples. Case-based discussions, computer-based assignments, early exposure to clinics, wards, and skills acquisition in skills lab and physiotherapy department are characteristics of integrated teachingprogram. Page | 4
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Page | 5
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE LEARNINGMETHODOLOGIES The following teaching/ learningmethodsareusedto promotebetterunderstanding: Teaching/LearningTechnique Icons InteractiveLectures Hospital / Clinic visits Small Group Sessions Case-BasedLearning Practicals / Skills session SelfStudy Page | 6
1ST YEAR MBBS, SEMESTER 2 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE INTERACTIVELECTURES In large group, the lecturer introduces a topic or common clinical conditions and explains the underlying phenomena through questions, pictures, videos of patients interviews, exercises, etc. Students are actively involved in the learningprocess. HOSPITAL VISITS: In small groups, students observe patients with signs and symptoms in hospital or clinical settings. This helps students to relate knowledge of basic and clinical sciences of the relevant module. SMALL GROUP SESSION(SGS): This format helps students to clarify concepts acquire skills or attitudes. Sessions are structured with the help of specific exercises such as patient case, interviews or discussion topics. Studentsexchangeopinions andapplyknowledgegainedfrom lectures, tutorials and self study. The facilitator role isto askprobing questions,summarize,or rephrasetohelp clarify concepts. CASE-BASEDLEARNING: A small group discussion format where learning is focused around a series of questions based on a clinical scenario. Students discuss and answer the questions applying relevant knowledge gainedin clinical andbasichealth sciencesduring themodule. PRACTICAL: Basic science practicals related to anatomy, biochemistry, pathology, pharmacology and physiologyarescheduledfor studentlearning. SKILLSSESSION:Skillsrelevant to respectivemodule areobservedandpracticed where applicablein skills laboratory or DepartmentofPhysiotherapy. SELFSTUDY:Students assumeresponsibilities of their own learning through individual study, sharing and discussing with peers, seeking information from Learning Resource Center, teachers and resource persons within and outside the college. Students can utilize the time within the college scheduled hours ofself-study. Page | 7
1 1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE SEMESTER 2 MODULE 2: RESPIRA TORYSYSTEM-I IMPORTANCE OF RESPIRATORYSYSTEM Themodule focuses on integrating basic health sciencesto clinical medicine. It will be taught in acombination of lectures, tutorials, small group learning sessions, practical and skills classes and possibly visits to clinics / wards. The module will explore the normal as well as the abnormal physiology of the respiratory system. Students will be introduced to a variety of pathologies to facilitate a better understanding of how the respiratory system is impacted by disease. It will give the broad overview of the system. The module will also address respiratory adaptations to exercise as well as examining its responses to different environments like high altitudes and deep sea diving. This will extend students integrative abilities. Video and hands on sessionsoncopingwith medical emergencieswill beausefulintroductionto clinical skill development. AIMS OF THISMODULE: The module aims toprovide: Knowledge and understanding of the structures andfunctions of the respiratory system and how it responds to changing metabolic needs of the body, organs and tissues, revealing the relevance of such knowledge to clinicalpractice Knowledge andunderstandingof the origin andassociatedrisk factorsof commondiseasesof the respiratorysystem Knowledge andpreventionof commoninfectious diseasesassociatedwith therespiratory diseases Practiceof basicskillsusedin testingthe functionof thissystemin asimulatedclinical setting Knowledge of drugsusedto treatrespiratorydiseases Page | 8
1 1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE COURSE OBJECTIVES AND TEACHINGSTRA TEGIES At theendof themodulethestudentswill beable to: ANATOMY TOPIC TEACHINGSTRATEGY STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THORAX, RIBS,THROACIC VERTEBRA, STERNUM, THORACIC CAGE (MUSCLES, JOINTS) &DIAPHRAGM Definediaphragm Describe the thoracic cage and itsboundaries, thoracic Inlet andoutlet Discuss intercostals muscles and their neurovasculature Describe suprapleural membrane and endothoracic fascia. Describe the attachments ofdiaphragm Describe the blood supply and nerve supplyof diaphragm Describe the openings present in thediaphragm and their respectivelevels List the structures passing through the openingsand piercing thediaphragm List the functions ofdiaphragm List diseases caused by phrenic nerveinjury Describe the location, shape, parts and clinical significance ofSternum Describe general feature of vertebralcolumn Describe Spinal Curvature in children andadults Describe general features of thoracicvertebrae Differentiate typical and atypicalvertebrae Desribe the diseases related tovertebral column (scoliosis, disc prolapse) Classifyribs Discuss the features ofribs Describe the joints and attachments (musclesand ligaments)ribs Describe theclinical featuresin conditions of cervical rib and ribfracture INTRODUCTION TO RESPIRATORY TRACT AND GROSS ANATOMY OF PLEURA ANDLUNG List the parts ofrespiratory tract Describe the clinical (upper and lower respiratory tract) and anatomical (conducting andrespiratory) divisions of respiratorytracts Page | 9
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Describe parietal and visceral pleura andits innervation Describe arrangement of pleura according tolines of orientation (mid sternal, mid clavicular and axillary etc) Describe apex , base surfaces and borders of lungs Describe hilum of thelungs Discuss fissures and lobes of thelungs Describe the divisions of bronchialtree. Describe the bronchopulmonary segmentationand theirimportance Name the diseases related topleura Outline thefeaturesof diseasesrelatedto pleura Describe the surface anatomy oflungs VASCULATURE OF LUNGS,BRONCHIAL AND PULMONARY VESSELS AND LYMPHATICS OFTHORAX Describe the origin, course and termination of bronchial vesselsandtheir territory of supply/ drainage Discuss the origin, course and terminationof pulmonary vessels and theirfunctions Describe the nerve supply oflung Describe the different groups oflymph nodes in thorax Discuss the deep as well as the superficiallymphatics of thorax Discuss the significance of lymphatics drainageof thorax MEDIASTINUM, ITS DIVISIONS AND CONTENTS OFSUPERIOR AND ANTERIORMEDIASTINUM Definemediastinum Describe the divisions ofmediastinum Definetheextentandboundaries ofmediastinum Describe the boundaries of superiormediastinum List the contents of superiormediastinum Describe origin, extent and termination ofaorta Describe intrathoracic part of aorta, its branches and relations within in thesuperiormediastinum Describe the tributaries of superiorvena cava within superiormediastinum Discuss the nerves within superiormediastinum Describe the major viscera present insuperior mediastinum Describe the contents of anterior mediastinum POSTERIOR MEDIASTINUM AND ITS CONTENTS (THORACIC AORTA ANDESOPHAGUS) Describe the boundaries of posteriormediastinum Page | 10
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE A VICENNA MEDICA L COLLEGE List the contents of posteriormediastinum Describetheextent andpositionof thoracicaortain posteriormediastinum Name the branches of thoracicaorta Describe the length, extent and relationsof esophagus Describe the blood supply, nerve supply,venous drainage and lymphatics ofesophagus Discuss the clinical significance ofanatomical constrictions ofesophagus POSTERIOR MEDIASTINUM THORACIC SYMPATHETIC TRUNK, THORACIC DUCT, PHRENIC AND VAGUSNERVE Discussthethoracicpartof symphatheticchain, ganglia, and branches Describe the origin, intrathoracic course andbranches of vagus & phrenicnerves Describe origin, extent, tributaries, territoryof drainage and termination of thoracicduct AZYGOS SYSTEM OFVEINS Define Azygos system of veins Describe the formation, course, relations and tributaries of azygos, hemi-azygos &accessory hemi- azygosveins Discuss variations in the origin ofazygos vein Discuss the clinical importance ofazygos system of veins CROSS SECTIONAL ANATOMY OFTHORAX Identify mediastinal great vessels, organs andlymph nodes on cross sectional images at differentlevels Identify the structural change at T4 vertebral levelor angle of Louis HISTOLOGY OF RESPIRATORY EPITHELIUM ANDITS VARIATIONS IN DIFFERENT PARTS OF CONDUCTINGSYSTEM Identify the respiratory epithelium onmicroscope Describe respiratory epithelium Discuss the component cells of respiratoryepithelium Discussthevariationsof epithelium in differentparts of conducting system of respiratorytracts HISTOLOGY OF TRACHEA ANDLUNG Describe the histological features ofdifferent layers of trachea Describe divisions of bronchialtree Discuss the structural variation in differentparts of bronchial tree Describe the structure of alveoliand inter-alveolar Page | 11
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE A VICENNA MEDICA L COLLEGE septum. Discussthe functionsof differenttypeof cells, forming the alveolarwall Describe the structure and function ofblood -air barrier DEVELOPMENT OF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM(EMBRYO) Review the intraembryonic mesoderm and its parts Discuss the divisions of lateral platemesoderm Describe the Cephalocaudal and transverse foldings of embryonicdisc Discuss the formation of Pleuropericardialand Pleuroperitonealmembranes Discuss the steps of development ofdiaphragm from its composite embryonicderivatives Discuss the formation of Laryngo-trachealgroove and respiratory diverticulum or LungBud Describe the branching of primitivebronchi Discussthe stagesof development/ maturation of Lungs Name the congenital anomalies of respiratorysystem (Tracheoesophagal fistulaetc) BIOCHEMISTRY TOPIC TEACHINGSTRATEGY Explain chemical structure of phospholipidsand their biochemical role inARDS Discuss the normal regulation ofpH, normal ABGs ranges , anion gap and theirbiochemical significance Explain the mechanism of respiratorypH disturbances and their ABGscorrelation Explain the mechanism of metabolic pH disturbances and their ABGscorrelation COMMUNITYMEDICINE TOPIC TEACHINGSTRATEGY INTRODUCTION TO RESPIRATORYDISEASES List the respiratory diseases / droplet infections Page | 12
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE prevalent inPakistan Discuss the prevention and control ofrespiratory diseases PNEUMOCONIOSIS AND ITSPREVENTION Describe the various types of pneumoconiosis diseases and theirprevention Describe the epidemiology of silicosis andits prevalence inPakistan TUBERCULOSIS AND ITSPREVENTION Explain tuberculosis as a public health problem in Pakistan andworldwide ASTHMA AND ITSPREVENTION Describe the signs and symptoms, diagnosis and prevention ofasthma CHICKEN POX ANDPREVENTION Describe the signs and symptoms, diagnosis and prevention of chickenpox INFLUENZA ANDPREVENTION Describe briefly the signs and symptoms, diagnosis and prevention ofinfluenza TRAVELMEDICINE List the diseases occurring in travelers andtheir pathogenicorganisms Discuss the control measures for preventionof diseases among travelers and role ofinternational healthregulations P A THOLOGY TOPIC STRATEGY COPD1 Define emphysema and chronicbronchitis Classify emphysema Discuss etiology, pathogenesis and morphology of emphysema and chronicbronchitis Define Asthma andBronchiectasis ClassifyAsthma Discuss etiology, pathogenesis and morphologyof 2018 Page | 13
1 1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNJA MEDICAL COLLEGE Asthma & Bronchiectasis Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)/ Atelectasis Define atelectasis andARDS Classifyatelectasis Discuss the pathogenesis of types ofatelectasis Discuss its etiology pathogenesis associated factors andmorphology Common pathogens of community acquired pneumonias Definepneumonia List the common bacteria and virusescausing pneumonia along with their general and characteristicfeatures Pneumonia Classify various types ofpneumonia Explain etiology and pathogenesis ofpneumonia Describe the morphological aspects ofpneumonia (including stages) List the complications ofpneumonia Explain the morphological features associatedwith viral pneumonia Define aspiration pneumonia and lungabscess Describe the pathogenesis and morphologyof aspiration pneumonia and lungabscess Describe chronic pneumonia with respect toeach etiological factor andmorphology Pulmonary vasculardiseases Define pulmonary embolism, pulmonary hypertension & diffuse pulmonaryhemorrhage syndrome Discuss the etiology, pathogenesis, morphology and clinical course of pulmonaryembolism Discuss causes, pathogenesis, morphology and clinical course of pulmonaryhypertension Explain the pathogenesis and clinical featuresof diffuse pulmonary hemorrhagesyndrome Describe the etiology, pathogenesis, morphologyof: 1. Goodpasture ssyndrome 2. Idiopathic Hemosiderosis 3. Polyangitis with Granulomatosis Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Discuss the general characteristics, virulentfactors and pathogenesis related to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Explain acid faststaining Explain laboratory diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, culture and other techniques usefulin diagnosis. Explain breifly gene experttechniques Tuberculosis Page | 14
1 1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Definetuberculosis Discuss its pathogenesis with respect to theimmune mechanism Explain the formation and morphology ofgranuloma Explain radiological features of tuberculosis supported by laboratory data (including geneexpert technique, PCRetc.) Explain the principle of Montouxtest PHARMACOLOGY TOPIC TEACHINGSTRATEGY Drugs used in Asthma & COPD Classify drugs used for the management ofasthma Explain mechanism of action,pharmacokinetic properties, & side effects of agonists. Mention pharmacologyofanticholinergicand methylxanthines and their role inasthma. Explainmechanism ofaction & sideeffectsof leukotrienemodifiers Discuss role of mast cell stabilizers andcorticosteroids in asthma Demonstratemethodsof application of aerosolinhalers andnebulizers Drugs used for community acquired pneumonia(Penicillins) List drugs used forthe management of community acquiredpneumonia Classifypenicillins Explain pharmacokinetics & dynamics ofpenicillins Drugs used for community acquiredpneumonia Describe role of otherdruggroupsin themanagement of community acquiredPneumonia. Anti-TuberculosisDrugs Classify anti-tuberculosisdrugs, Explain dynamics of anti-tuberrculousdrugs Explain rationale ofATT Describe role ofother druggroupsin themanagement of Tuberculosis Page | 15
1 1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Anti-Tussives Explainrole ofmucolyticsin treatmentof cough PHYSIOLOGY TOPIC TEACHINGSTRATEGY Mechanics ofrespiration Briefly describe the function of respiratorypassages Explain mechanism of pulmonary ventilation with reference to thoracic cage &muscles of respiration Define alveolar pressure &pleural pressure, alveolar ventilation Discuss transpulmonary pressure and its changes during respiration Define deadspace Lungcompliance Define lung compliance &list factors affecting lung compliance Describetherole of surfactantinmaintainlung compliance Differentiate compliance work, tissueresistance work & airway resistancework Pulmonary volumes andcapacities Listthe pul.vol& capacitywith theirnormalvalues& significance in pulmonary functiontest Determine functional residual capacity, residual volume & total lung capacity, helium dilution method Pulmonary circulation V/Q relationship Describe pressure in pulmonary circulation &blood flow three various zones oflung (1,2,3) Explain pulmonary capillarydynamics Explain mechanism of development ofpulmonary edema and importance of ventilation/perfusion Ratio& effectsof mismatchingof thisratio Diffusion ofgases Define respiration unit &respiration membrane Describe mechanics of diffusion acrossrespiration membrane & factors effectingdiffusion List partial pressure of respiration gases in atmosphere, humidified, alveolar &expired air Briefly described the diffusing capacity ofO2 and Page | 16
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE CO2 O2 transport O2Hbcurve Explain transport of O2 from lungs to bodytissues Briefly describe the role of Hb inO2 transport Explain oxy-Hb dissociation curve and factors that shift thiscurve Define Bohreffect Transport of Co2 in relation tophysiology. Describe the carriage in blood (chlorideshift) Relate effect of CO2 and O2 transport (Haldane effect) Define respiratory exchangeratio Respiratory adjustment to exercise, high altitude & deep sea Describe resp. adjustments duringexercise Explain physiology of acclimatization Explain physiology of deep seadiving Hypoxia and itstype Define hypoxia and itstypes Describe coughing & sneezingreflex Regulation ofrespiration List the respiratory centers &their effect on regulation ofrespiration Describe thechemicalcontrolof respiration(chemo receptors) Perform the experimentsonpowerlabwith respect to respiration MICROBIOLOGY TOPIC TEACHINGSTRATEGY Identify the microscopic stages ofpneumonia Enumerate the common pathogens causingCAP (typical andatypical) Identify the microscopic and pathogenic featuresof MycobacteriumTB Page | 17
1 1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE PULMONOLOGY (CHESTMEDICINE) TOPIC TEACHINGSTRATEGY GASEOUSTRANSPORT Correlate ABG results with respiratorydiseases Correlate pulmonary function tests with respiratory diseases RADIOLOGY TOPIC TEACHINGSTRATEGY Identifythenormal radiologyof chestonX-ray RESEARCH AND SKILLSLAB TOPIC TEACHINGSTRATEGY RESPIRATORYEXAMINATION Demonstrate the steps of respiratoryexamination BIOCHEMISTRY DIAGNOSTICLABORA TORY TOPIC TEACHINGSTRATEGY Describe ABG analysis and discuss theinterpretation Page | 18
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE LEARNINGRESOURCES SUBJECT RESOURCES A. GROSSANATOMY 1. K.L. Moore, Clinically OrientedAnatomy 2. Neuro Anatomy by RichardSnell B. HISTOLOGY 1. B. Young J. W. Health Wheather s FunctionalHistology C. EMBRYOLOGY 1. Keith L. Moore. The DevelopingHuman 2. Langman s Medical Embryology ANATOMY A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Harper s IllustratedBiochemistry 2. Lehninger Principle ofBiochemistry 3. Biochemistry byDevlin BIOCHEMISTRY A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Community Medicine byParikh 2. Community Medicine by MIllyas 3. Basic Statistics for the Health Sciences by Jan WKuzma COMMUNITYMEDICINE A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Robbins & Cotran, Pathologic Basis of Disease, 9thedition. 2. Rapid Review Pathology, 4th edition by Edward F. GoljanMD PATHOLOGY/MICROBIOLOGY 1. http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/webpath.html 2. http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/ A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Lippincot IllustratedPharmacology 2. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology by Katzung PHARMACOLOGY A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Textbook Of Medical Physiology by Guyton AndHall 2. Ganong S Review of MedicalPhysiology 3. Human Physiology by LauraleeSherwood 4. Berne & LevyPhysiology 5. Best & Taylor Physiological Basis of MedicalPractice B. REFERENCEBOOKS 1. Guyton & Hall PhysiologicalReview 2. Essentials Of Medical Physiology byJaypee 3. Textbook Of Medical Physiology byInduKhurana 4. Short Textbook Of Physiology byMrthur 5. NMSPhysiology PHYSIOLOGY Page | 19
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE ADDITIONAL LEARNINGRESOURCES Hands-on Activities/PracticalStudents will be involved in Practical sessions and hands-on activitiesthat link with the respiratory module toenhance learning with understanding. Utilize thelabto relatethe knowledge to thespecimensandmodels Labs available. A skills lab provides the simulators tolearn the basic skills and SkillLab procedures. This helps build the confidence to approach thepatients. Video familiarize the student with the proceduresandprotocols to assist Videos patients. It increases the knowledge. Students should utilize the available internet resources and CDs/DVDs. This will be an additional advantage to increase Computer Lab/CDs/DVDs/Internet learning. Resources: Self learning is scheduled to search for information to solve cases,read through different resources and discuss among the peers and with the SelfLearning faculty to clarify theconcepts. Page | 20
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE ASSESSMENTMETHODS: Theory: Best Choice Questions (BCQs) also known as MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions) are used to asses objectives covered in eachmodule. A BCQ has a statement or clinical scenario followed by four options (likelyanswer). Studentsafterreadingt hestatement/scenarioselect ONE,t he most appropriate response from the given list ofoptions. Correct answer carries one mark, and incorrect zero mark . There is no negative marking. Studentsmarktheirresponsesonspecifiedcomputer-based/OMRsheetdesigned forAVMC EMQs: An EMQhas: o Anoption list of 5-15 which maybenervesupply, functions,diagnosis,investigationsetc A Lead In Statement/Question o Two to four Stems or ClinicalScenarios Foreachstemorclinical scenario,the studentshouldchoosethemostappropriateoption fromthe o option list. Asingle option canbeusedonce,morethanonceornot at all. Correct answer carries one mark and incorrect zero mark . There is NO negativemarking. Student mark their responses on a specified computer-based sheet forEMQs. OSPE/OSCE: Objective Structured Practical/ClinicalExamination: Eachstudentwill beassessedonthe samecontentandhavesametimeto completethe task. Comprise of 12-25stations. Each station may assess a variety of clinical tasks, these tasks may include history taking, physical examination, skills and application of skills andknowledge Stations are observed, unobserved, interactive and reststations. Observed and Interactive Stations: o Theywill beassessedbyinternal orexternalexaminers throughstructuredviva ortasks. Unobserved Stations: It will be static stations in which there may be an X-ray, Labs reports, pictures, clinical o scenarioswith relatedquestionsforstudentsto answerontheprovidedanswercopy. Rest station o I t is a station where there is no task given and in this time student can organize his/her thoughts. Page | 21
AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVMC Internal Evaluation Policy Students will beassessedto determine achievement of moduleobjectivesthroughthefollowing: Module Examination: willbe scheduled on completion of each module. The method of examination comprises theory exam which includes BCQs and OSPE (Objective Structured PracticalExamination). Graded Assessment of students by Individual Department: Quiz, viva, practical, assignment, small group activities such as CBL, TBL, TOL, online assessment, ward activities, examination, and logbook. Marksof bothmodular examinationandgradedassessmentwill constitute 20%weightage. As per UHS policy, this 20% will be added by JUHS to SemesterExamination. Example : Number of JSMU Marks allocated for Semester Theory and Internal Evaluation InternalEvaluation (Task Presentation + Assignments + Modular Exam 20% Semester Examination TheoryMarks Total(Theory) Semester 80% 100% FormativeAssessment Individual department may hold quiz or short answer questions to help students assess their own learning. The marks obtained are not included in the internalevaluation More than 75% attendance is needed to sit for the modular and semester examinations Page | 22
1 1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE MODULAR EXAMINATION RULES & REGULATIONS( AVMC Studentmustreportto examinationhall/venue, 30 minutesbeforetheexam. Exam will begin sharp at the giventime. No student will be allowed to enter the examination hall after 15 minutes of scheduled examinationtime. Studentsmust sitaccordingto theirroll numbersmentioned ontheseats. Cell phones are strictly not allowed in examinationhall. If anystudentisfoundwith cell phonein anymode(silent, switchedoff oron)he/shewill benot be allowed to continue theirexam. No students will be allowed to sit in exam without University Admit Card, AVMCCollege ID Card and LabCoat Student must bring the following stationary items for the exam: Pen, Pencil, Eraser, and Sharpener. Indiscipline in the exam hall/venue is not acceptable. Students must not possess any written materialorcommunicatewith theirfellowstudents. Page | 23
AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 1ST YEAR MBBS, SEMESTER 2 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE ExaminationProtocols: In each semester , module will be assessedby theory paper com prising MCQsand EMQs. For examplesemester8 will have separate theory paper of EYE,Dermatology, PlasticSurgery& Burns,Neuro-Sciences-II& Psychiatry,GeneticsandRehabilitationmodules. There will be one OSPE (Objective Structured Practical Examination)/OSCE (Objective Structured Clinical Examinations) which will coverall threemodules of semesterseven. 1. Theory Theory paper will comprise of80 one best type MCQs and 20 EMQs. Timeduration fortheorypaperwill be120minutes. Students will mark their responses on UHS pecified response sheets assessed by computer software. It will carryout 80%contributionintheoryresultsof the Semester. There is no negativemarking. 2. OSPE/OSCE: It maycomprisebetween12-25stations.Eachstationwill carry10marks. 3. UHSGradingSystem It will be based on GPA 4system Marks obtained in Percentagerange NumericalGrade AlphabeticalGrade 80-100 4.0 A+ 75-79 4.0 A 70-74 3.7 A- 67-69 3.3 B+ 63-66 3.0 B 60-62 2.7 B- 56-59 2.3 C+ 50-55 2.0 C <50 Un-grade-able 0 U A candidate obtaining GPA less than 2.00 (50%) is declared un-graded(fail). Cumulativetranscriptisissuedat the endof clearance of all modules. Page | 24
1ST YEAR MBBS, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM-IMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 4. RetakeExamination Retakeexaminations are for those students who fail in semester examinations and those who have passedsemester examinations with GPAlessthan 3.0 mayreappear in respective retake examination to improvegrades. The format of the retake examination is exactly the same as insemester examinations. Retakeexaminationwill beconducted3weeksafterdeclarationof results. 5. Promotion to nextclass Studentswho passbothsemesterexaminations arepromotedfromfirstyearto secondyear. Students who fail the MBBS first year semester retake examination will be promoted to second year. Students will be promoted from second year to third year and onward only if they have passed thesemesterexaminationsof thatyear. Clearance of all modules and their components of semester one to four are mandatory for promotion from second year tothird year (as per PMDC rules). As per PMDC rules any candidate failing to clear a module or its component in four (1+3) attemptsisNOTallowed to carryout furthermedicaleducation. Clearance of all modules and their components of semester/s are mandatory for promotion from third yearonward. Page | 25