Study Guide for Locomotor System Module in First Year MBBS at Avicenna Medical College
The study guide for the Locomotor System Module in the first year MBBS at Avicenna Medical College provides an overview, learning methodologies, objectives, learning resources, assessment methods, and examination rules. It includes information on the curriculum framework, integrated teaching approach, and various departments involved in facilitating learning. The guide helps students organize their studies, understand assessment methods, and navigate through the module effectively.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
STUDYGUIDE LOCOMOTORSYSTEM MODULE FIRST YEARMBBS
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE STUDY GUIDE FOR LOCOMOTORMODULE Page No 03 04 05 07 07 08 25 27 29 30 S.No CONTENTS 1 2 3 4 5 6 6.1 6.2 7 8 Overview Introduction to StudyGuide LearningMethodologies Module 3: LocomotorSystem Importance Objectives andstrategies LearningResources AssessmentMethods Modular Examination Rules And Regulations(AVMC) Schedule Page | 2
AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE Year:One Duration: 4 weeks Timetable hours: Lectures, Case-Based Learning (CBL), Team based Learning (TBL), Self-Study, Practical, Skills, Demonstrations, Field Visits, Visit to Wards& Laboratory MODULE INTEGRA TEDCOMMITTEE MODULECOORDINATOR: CO-COORDINATORS: Professor Dr. Zubair Ahmad(Biochemistry) Professor Dr. Rubina Hafeez (Pathology) Professor Dr.Rehana Shahid(Anatomy) DEPARTMENTS & RESOURCE PERSONS FACILITA TINGLEARNING BASIC HEALTHSCIENCES CLINICAL AND ANCILLARYDEPARTMENTS FAMILYMEDICINE Professor Dr. Muhammad Luqman ANATOMY Professor Dr.Rehana Shahid BIOCHEMISTRY Professor Dr. Zubair Ahmad MEDICALEDUCATION Professor Dr. Waheed Ahmad COMMUNITYMEDICINE Professor Dr. Rana Muhammad Akhtar Khan INTERNALMEDICINE Dr. Muhammad Usman Amir PATHOLOGY HEMATOOGY Dr. Syeda Ijlal Zehra Zaidi Professor Dr. Rubina Hafeez PHYSIOLOGY Professor Dr. Binyamin Ahmad PHARMACOLOGY Professor Dr. Rana Tariq Mehmood AVMCMANAGEMENT Professor Dr. Gulfreen Waheed, PrincipalAVMC Brig.Dr. Gul e Rana , Director AVMC Dr. Sadia Awan Dr. Muhammad Muzzammil Sadiq Dr. Usama Bin Ishtiaq STUDY GUIDE COMPILEDBY: Department of Health CareEducation Page | 3
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEHE INTRODUCTION WHAT IS A STUDYGUIDE? It is an aidto: Inform students how student learning program of the module has been organized Helpstudentsorganize andmanagetheirstudiesthroughoutthe module Guide students on assessment methods, rules andregulations THE STUDYGUIDE: Communicates information on organization and management of themodule. Thiswill helpthe studentto contacttherightpersonin caseof anydifficulty. Definestheobjectiveswhich areexpectedto beachieved at theendof themodule. Identifies the learning strategies such as Interactive Lectures, small group teachings, clinical skills, demonstration, tutorial and case based learning that will be implemented to achieve the module objectives. Provides a list of learning resources such as books, computer assisted learning programs, web- links, journals,forstudentsto consultinorderto maximize their learning. Highlights information on the contribution of continuous examinations on the student s overallperformance. Includes information on the assessment methods that will be held to determine every student s achievement ofobjectives. Focuses on information pertaining toexamination policy, rules and regulations. CURRICULUMFRAMEWORK Students will experience integratedcurriculum. INTEGRATED CURRICULUM comprises of system-based modules such as Locomotor, Respiratory and CVS modules which links basic science knowledge to clinical problems. Integrated teaching means that subjects are presented as a meaningful whole. Students will be able to have better understanding of basicscienceswhen theyrepeatedlylearnin relationto clinical examples. Case-based discussions, computer-based assignments, early exposure to clinics, wards, and skills acquisition in skills lab and physiotherapy department are characteristics of integrated teachingprogram. Page | 4
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE LEARNINGMETHODOLOGIES Thefollowing teaching/ learningmethodsareusedto promotebetterunderstanding: InteractiveLectures Hospital / Clinic visits Small Group Discussion Case-BasedLearning Practicals Skillssession E-Learning Self-DirectedLearning TBL INTERACTIVELECTURES In large group, the Interactive Lecturer introduces a topic or common clinical conditions and explains the underlying phenomena through questions, pictures, videos of patients interviews, exercises, etc. Students areactivelyinvolved in the learning process. HOSPITALVISITS: In small groups, students observe patients with signsand symptoms in hospital or clinical settings.Thishelpsstudentsto relate knowledge of basicandclinical sciencesof the relevant module. Page | 5
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE SMALLGROUP DISCUSSION (SGD): This format helps students to clarify concepts acquire skills or attitudes. Sessions are structured with the help of specific exercises such as patient case, interviews or discussion topics. Students exchange opinions and apply knowledge gained from Interactive Lectures, tutorials and self study.Thefacilitator role isto askprobing questions, summarize,or rephraseto help clarify concepts. CASE- BASED LEARNING: A small group discussion format where learning is focused around a series of questionsbasedon aclinical scenario.Students discussandanswerthe questionsapplying relevant knowledge gainedin clinical andbasichealth sciencesduring themodule. PRACTICAL: Basic science practicals related to anatomy, biochemistry, pathology, pharmacology and physiologyarescheduledfor studentlearning. SKILLS SESSION: Skills relevant to respective module are observed and practiced where applicable in skills laboratory or DepartmentofPhysiotherapy. SELFDIRECTED LEARNING: Students assume responsibilities of their own learning through individual study, sharing and discussing with peers, seeking information from Learning Resource Center, teachers and resource persons within and outside the college. Students can utilize the time within the college scheduled hours of self-study. TEAM BASED LEARNING: Team-based learning (TBL) is a structured form of small-group learning that emphasizes student preparation out of class and application of knowledge in class. Students are organized strategically into diverse teams of 5-7 students that work together throughout the class. Before each session/class, students prepare by reading prior to class. In class students are given different tasks or test where they work asteam. Page | 6
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE LOCOMOTORMODULE IMPORTANCE OF LOCOMOTORSYSTEM It is likely that individuals at some time suffer from a problem related to the musculoskeletal system, ranging from a very common problem such as osteoarthritis or back pain to severely disabling limb trauma or rheumatoid arthritis. Many musculoskeletal problems are chronic conditions as well. Themost common symptoms arepain and disability, with an impact not only on individuals quality of life but also, importantly, on people s ability to earn a living and be independent. It has been estimated that one in four consultations in primary care is causedby problems of the musculoskeletal system.Healthy lifestyle suchasexerciseanddiet recommendedfor maintaining goodhealth. Throughout this module, students will have the opportunity to link basic science knowledge to clinical problems.Teaching relevantbasicscienceswith clinical exampleswill helpyoumakeconnectionsamong conceptsandretaintheinformationforlaterclinical education. Page | 7
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE A VICENNA MEDICA L COLLEGE TOPICS, OBJECTIVES ANDSTRA TEGIES Bytheendof themodule studentswill beableto: ANATOMY LEARNING STRATEGY TOPICS &OBJECTIVES (1) Introduction to the Musculoskeletalsystem: Discuss the division and functions of skeletalsystem Enumerate the parts of axial and appendicularskeleton Define pectoral and pelvicgirdle Describe thedivision andcurvature of vertebralcolumn Discussthe typesandnumberof vertebraefoundin adults (2) Clavicle Osteology MuscleAttachment: Identify the features of bone likeborders, surfaces and land marks used for side determination Discuss the attachments ofmuscles (3) Histology ofCartilage: Enumerate the general properties ofcartilage Discussthe differenttypesof cartilage,theirproperties andlocations Describe the process of growth ofcartilage (4) Sternoclavicular and AcromioclavicularJoints: Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion/ Demonstration Classify types ofjoint Describe the structure ofjoints List the muscles acting on thejoint Explain the movements at thejoint Explain clinical aspects of thejoint (5) Scapula Osteology & Attachment: Identify thebone Identify the sites ofbone Identify the bony landmarks of bone likeborders, surfaces and land mark used for sidedetermination Discuss the attachment of muscles onscapula Page | 8
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE (6) Embryology Development of Paraxial Mesoderm &muscles: Define epiblast andhypoblast Describe chorionic cavity Discuss the formation ofmesoderm and paraxial mesoderm Explain the differentiation of trilaminargerm disc Explain myogenesis Discuss the development of skeletomuscularsystem (7) Osteology of Humerus & Attachment: Identify thebone Identify the site ofbone Identify the bony landmarks ofbone like borders, surfaces and land mark used for sidedetermination Discussthe attachmentof attachmentsof muscles (08) PectoralRegion: Enumerate the muscles of pectoralgirdle Describetheattachmentsof muscleof pectoral girdle andits neurovascularsupply Explaintherole of musclesof pectoral regionin stabilizingthepectoral girdle Discuss the clavi-pectoralfascia Describe the triangle ofauscultation List the nerves and blood vessels of thisregion Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion/ Demonstration (09) Development of Joints & Muscles of Shoulder: Describe the development of Bones ofshoulder joint Describe the development of jointsand cartilage Describe the muscles ofshoulder Describe the nerve supply of thesemuscles Explain actions of the muscles ofshoulder Describe the clinical correlates of shouldermuscles (10) Anatomy Shoulder joint & itsMovements: Classify the types of shoulderjoint Describe the structure of shoulderjoint Listthemuscles actingon thejoint/rotatorcuffmuscles Explain the range ofmobility Describe the movements of shoulderjoint Explain clinical aspects of thejoint Page | 9
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE (11) Histology, Bone: Identifythedifferenttypesof bonesinmicroscope Discuss histogenesis of Bone Describe the process of Endochondral and IntramembranousOssification Describe ossification of limbbones (12) Axilla, boundaries and contents along with axillary artery and vein: Describe the position, shape ofaxilla Name the boundaries and muscle forming the boundaries ofaxilla Discuss the formation, course and relations ofaxillary vessels Describe arrangement and groups axillary lymphnodes (13) Development of limbs & congenitalanomalies: Discussthe siteandtimeof appearanceof upperandlower limb bud Define apical ectodermal ridge(AER) Describe the mesenchymal proliferation under the influence ofAER and differentiationinto cartilaginousmodelsof futurelimb bones Definethe sourceof mesodermformingthelimbmuscles Discussthe handplate andformationof digital raysresultinginto digits Describe themusclesinvolved in andprocessof rotationof limb Discus the congenital anomalies of thelimbs Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion/ Demonstration (14) Brachial Plexus / Brachial plexus injuries: Describetheformationof brachialplexus,with itsroot valueanddivisions (roots, trunk, division, andcords) Discussthe relation of brachialplexusalsoin connectionto clavicle (Supra, retro, infra clavicularparts Enumerate the branches arising from thecords Illustrate the brachialplexus Listthemuscles andskinsuppliedbythe branchesof brachialplexus Discussinjuries to the plexus and the resultantdeformitiesof upperlimb (15) Anterior compartment of arm, muscles & neurovascularsupply: Enumeratethemuscles ofanteriorcompartmentof arm Discussthe attachmentof muscles,theirnervessupplyandtheiractions Explain the course of musculocutaneous nerve, its branchesand distribution Discuss the large nerves ofarm Relatetheimpactof lesions of mainnervesof the compartment Page | 10
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE (16) Posterior compartment of arm, muscles & neurovascularsupply: Identifythecompartmentsof armandhow theyareformed Listthemuscles presentintheposteriorcompartmentof arm Describe the actions performed by the muscles ofposterior compartment of arm Listthenervesupply ofthemusclesof thiscompartment Explainthecourseof vesselspresentin thiscompartment alongwith the supply tothe structures in this compartment Discuss the clinical correlation ofthe compartment (17) Breast Development, Histology & Gross: Discuss the anatomy ofbreast Explaintherelation of breastwithin pectoral region Describe the blood supply and lymphatic drainage ofbreast Discuss the relation of breast disease withaxilla Explain the development ofbreast Discuss the histological features ofbreast (18) Histology of Muscles: Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion/ Demonstration Distinguish thethreetypesof muscleat the lightandelectronmicroscope levels based on distinctive features of each musclefiber Describe the structural basis of musclestriations Discuss the structural elements involved inmuscle contraction Explainthefunctions andorganizationof theconnectivetissuein muscles (19) Osteology of Radius & attachments ofMuscle: Identify the bones of forearmand hand Determine side ofbones Identify the features ofbones Identify the muscles attached tobones Identify clinical significance ofbones (20) Osteology of Ulna & Muscles & AttachmentMuscles: Identify thebone Determine the side ofbone Describe the surfaces, borders and ends of thebone Identify the bony landmarks ofbone Identify the muscles attached tobone Discuss clinical significance ofbone Page | 11
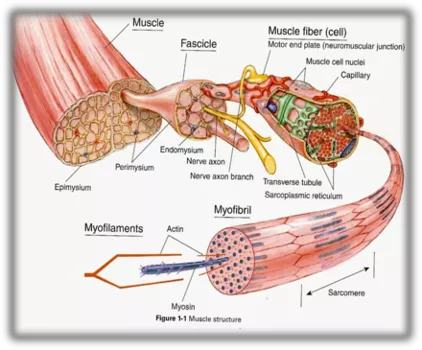
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE (21) Anterior Compartment of forearm, muscles and neurovascularsupply: Enumerate the compartments of forearm and howthese compartments areformed Discussthe musclespresentin theanteriorcompartment of forearm Explainthedivision of musclelayerin the anteriorcompartment Discussthe actionsperformedbythemuscles of anteriorcompartment Explainthenervesupplyof themusclesof thiscompartment Discussthe courseof vesselspresentin thiscompartment alongwith the supply tothe structures in this compartment Describe attachment and functions of flexorretinaculum Discuss the clinical correlation of thecompartment (22) ElbowJoint: Identifythemorphologyof the joint Discuss the muscles acting on the elbowjoint Explain the neurovascular supply of thejoint Describe thecarryingangleandapplied aspectof thejoint (23) Cubital fossa & Anastomosis aroundelbow: Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion/ Demonstration Describe the boundaries, contents and relationship among structures of cubitalfossa Identify the surface anatomy of thefossa Discuss the clinical importance ofthe fossa Describe the anastomosis and collateralcirculation Describe formation of anastomosis around elbowjoint (24) Posterior compartment of forearm, muscles & neurovascularsupply: Enlist the muscles present in the posterior compartment offorearm Explain the division ofmuscle layer in the compartment Explainactionsof themusclesof posteriorcompartment of forearm Discussthe nervesupplyof themusclesof thiscompartment Describethecourseofvesselsalongwith the supplyto thestructuresin thiscompartment Discuss the clinical correlation ofthe compartment (25) Lymphatic of upperlimb: Describegroupsandareaof drainageof eachgroupof lymphnodes Discuss the commencement, course and termination ofsuperficial lymphatic vessels Discusstheclinical conditions relatedto lymphatic channels of upperlimb Page | 12
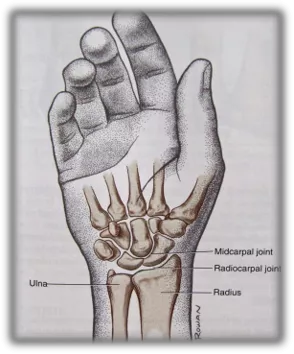
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE (26) Superficial veins of upperlimb: Discuss the normal anatomy ofveins Differentiate between superficial and deepveins Explain the course of majorsuperficial veins Discuss the applied anatomy of superficialveins (27) Osteology of thehand: Describe the bony arrangement ofthe hand (28) Muscles & Spaces ofHand: Locatethedifferentspacesof the handonbothpalmaranddorsalaspects Describe the spaces ofhand Discuss the clinical importance of thesespaces (29) Blood vessels and nerves ofhand: Enumerate the arterial supply of thehand Discuss the course and relations of radial and ulnar arteries Explainthecourseof branchesof radial and ulnar arteriesof thehand Discussthe formationof superficialanddeeppalmararch,veinsof hand and theirtributaries Describe the nervesof thehandandtheirinjuries Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion/ Demonstration (30) Wrist joint, Radioulnar & Small joints ofhand: Describe wrist joint Discuss the neurovascular supply of wristjoint Describe radioulnar joints and discuss its neurovascularsupply Discuss the movements occurring at thejoints Explain clinical correlations ofjoints Classify the intercarpal, metacarpal and interphalangealjoint (31) Surface Anatomy of Upperlimb: Perform surface markings of anterior and posterior axillary folds, brachial artery, cubital fossa , median cubital vein, flexor retinaculum, radial and ulnar pulse ,anatomical snuffbox , cephalic and Basilic veins, dorsal venous arch and superficial and deep palmar arches. (32) Cutaneous supply of upperlimb: Describein detail thecutaneoussupplyanddermatomesof upperlimb Page | 13
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE (33) Hip Bone Osteology & MuscleAttachment: Enumerate the parts of hipbone Discuss sidedetermination Describein detail theosteologyof eachpartof hipbone Discuss muscle attachments of hipbone Discuss ligamentous attachments Discuss the clinical correlation of thebones (34) Femur Osteology and MuscleAttachment: Identify thebone Determine the side of thebone Describe the anatomical position ofthe bone Identify the bonylandmarks Discuss the muscles attached to thebone Discuss the ligaments attached to thebone Discussthe fracturesandother clinical conditions associatedwith thebone Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion/ Demonstration (35) Deep fascia of thigh, its modification and Inguinalligament: Explain the arrangement and attachment of deep fascia ofthigh Discuss the location ofsaphenous opening and its relations Describe the inguinalligament Discussthe clinical conditions associatedwith deep fasciaof thigh and inguinal ligament (36) Muscles of Anterior compartment of thigh femoral triangle,femoral sheath & Neuro vascularsupply: Discussthe arrangementof thighinto compartments Explainthemusclesof anterior compartment of thigh andtheir respective actions Describe the innervation and blood supply of muscles ofanterior compartment ofthigh Explain thefollowing: o Femoral triangle, its boundaries andcontents o Femoral sheath and itscontents Discussthe clinical conditions associatedwith anteriorcompartmentof thigh, femoral triangle and femoralsheath Page | 14
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE (37) Formation & Injuries lumbosacralplexus: Discuss the formation of lumbarplexus Listthe branchesof lumberplexus with theirroot values Discuss relation of the nerves with psoas majormuscles Describe the structures supplied by lumbarplexus Explain the formation of sacralplexus Describe the composition and relationship ofsacral plexus Enumerate branches of thisplexus Discuss the cutaneous supply of lowerlimb Discuss the injuries of lumbosacralplexus (38) Muscles, nerves and vessels of medial compartment of thigh: Discussthe arrangementof thighinto compartments Explainthemusclesof medialcompartmentof thigh andtheir respective actions Describetheinnervationand blood supplyof muscles of medial compartment ofthigh Discussthe clinical conditions associatedwith themedial compartmentof thigh Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion/ Demonstration (39) GlutealRegion: Describe the location ofregion Discuss bones andligaments Discussthe muscles of theregionandtheir respectiveactions Discuss the nerves and bloodvessels Enumerate different structures entering and leaving theregion Discuss the clinical conditions associated withthe region (40) Muscles of Posterior compartment of thigh and neurovascularsupply: Discussthe arrangementof thighinto compartments Explain the muscles of compartment and their respectiveactions Describe the innervations and blood supply of muscles ofposterior compartment ofthigh Discuss the greater and cruciate anastomosis at the back ofthigh Discuss the clinical conditions associated with thecompartment Page | 15
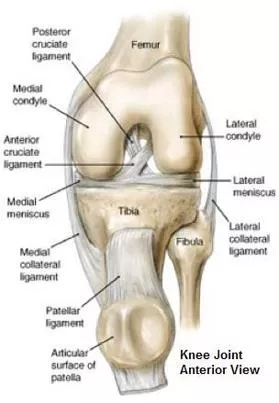
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE A VICENNA MEDICA L COLLEGE (41) Hip joints & movements, anastomosis around hipjoint: Describe the formation ofhip joint Discuss the characteristics features of synovialjoint Describe the articular surfaces of hipjoint Discuss the attachment of jointcapsule Explain the ligaments stabilizing thejoint Discussthemusclesactingonthejoint anddifferentmovements performed at thejoint Describetheinnervationsand bloodsupplyof thejoint Describe the arterial anastomosis around the hipjoint Discuss the clinical conditions associated withthe joint (42) Tibia Osteology & attachment: Identify thebone Determine the side of thebone Describe the anatomical position ofthe bone Identify the bonylandmarks Discuss the muscles attached to thebone Discuss the ligaments attached to thebone Describetheossificationof tibia andits primary andsecondary ossification centers Discussthe fracturesandother clinical conditions associatedwith thebone Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion/ Demonstration (43) Knee joint, genicular anastomosis, locking andunlocking: Classify the joint Discuss articular surfaces of joint, the synovialcapsule Explain types of movement performed and themuscles responsible for thatmovement Describe the locking and unlockingmechanism Discuss the neurovascular of kneejoint (44) Popliteal Fossa & itscontent: Discuss the boundaries offossa Enumerate the contents offossa Describe the relationship of thecontents Explain how popliteal artery can bepalpated Discuss clinical aspects related to popliteal fossa like theBaker s cyst Page | 16
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE (45) Fibula Osteology andattachment: Identify the bone and its sidedetermination Mark the attachment ofmuscles and ligaments Elaborate the joints formed byit Describe the nerve injuries related toit (46) Superficial veins of lower limb (Small & great Saphenousvein): Enumerate the superficialveins Identifythecourseof greatandsmallsaphenousveins Discusstheirconnectionswith thedeepveinsof the leg Explain related clinical conditions like venousthrombosis (47) Osteology offoot: Discussthe bonesformingthe architectureof foot Identify joints formed by thesebones Describerelatedclinical conditions likeflat foot andclubfoot (48) Anterior & Lateral compartment of leg (Muscles, nerves and vessels): Discuss the fascial compartments ofleg Explain muscles of anterior and lateral compartment withits neurovascularsupply Describe clinical conditions like the compartmentsyndrome Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion/ Demonstration (49) Posterior compartment of leg: Enumerate the muscles of thecompartment Discuss nerve supply of thesemuscles Discussthe actionsof musclesof thecompartment (50) Sole of foot & nerves and vessels of foot: Describe thearchitecture Enumerate thelayers Discuss the musclepresent Discuss the blood supply and nervesupply (51) Arches offoot: Describethearchitectureof arches of foot and the factorsresponsible for theirmaintenance Elaboratethebones which areresponsible forformingthesearches Describe the ligaments which hold thesearches Describethefunctions of thearchesof foot Describe Plantar Fasciitis and other relevantinjuries List the advices regarding the rehabilitation forplantar fasciitis Page | 17
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE (52) Ankle joint, superior & Interior tibiofibularjoint: Describe the ankle Joint, the type, articular surface and thesynovial capsule Discuss the Superior and Inferior Tibio-Fibular Joints, Sub-talar Joint, transverse tarsal joint or mid-tarsaljoint Describethemovementsperformedandthemusclesresponsible forthat movements Discuss the neurovascular supply of thejoints (53) Nerve injuries of lowerlimb: Explainthedifferentnervesof lower limb andtheirroot value Discuss the causes of injuries Enumerate the commonsites Discuss the symptoms caused by theseinjuries Discussthe fractureof bonesof lower limb Explain Injuries of lower leg andankle Discuss Pott s fracture Explain Sprain ankle Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion/ Demonstration (54) Vertebral column and muscles of back: Describe the distinguishing characteristics ofvertebrae in different vertebralregions Explain the curves of the vertebral column and howthese change after birth Describetheattachmentof theligamentsthat providesupportforthe vertebralcolumn Enlistthemusclesof backwith theirnervesupplyandactions (55) Surface anatomy of lowerlimb: Markinguinal ligament,femoraltriangle,patellartendonandpopliteal fossa. Markthe courseblood vesselsof lower limbe.g.(Great saphenous) Palpatepulsation of the blood vessels(Femoral,popliteal, posteriortibial and dorsalis pedis arteries) Markthe courseof important nervesof lower limb(e.g.Sciaticnerve, common peroneal at fibularhead) (56) X-Rays of Upper and lowerlimbs: Identify bones of both thelimbs Differentiate between hands and feet on Xrays Identifynormalappearanceof all limb joints and joint space. Identify the epiphysealplate Demonstration Page | 18
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE BIOCHEMISTRY LEARNING STRATEGY TOPICS &OBJECTIVES (1) Extracellularmatrix Discussthe structureandchemicalcompositionof extracellular matrixe.g. Glycosaminoglycans, Collagen andElastin (2) VitaminC Describethebiochemical role of vitamin Cwith respectto Collagenand ECM Interactive Lecture/Small GroupDiscussion (3) Vitamin D & Parathyroid Hormone: Role In Calcium & PO4-Metabolism Discuss the basic relationship between vitamin D, PTH, calcium and Phosphate in relation to bonemetabolism Discuss signs and symptoms due to deficiency or excess of Calcium Discuss causes and investigations of hypocalcemia andhypercalcemia Practical Estimate serum Calcium andPhosphate Practical Estimate serum AlkalinePhosphatase (4) Reaction Of AminoAcid Describe the Deamination, Transamination and all theother reactions of AminoAcid (5) AmmoniaMetabolism Explain Ammonia metabolism and itsdetoxification (6) UreaCycle Describethemetabolic pathwayof Ureaalongwith itsabnormalities Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion (7) Metabolism & Disorders OfPhenylalanine,Tyrosin Discussthe metabolismof PhenylalanineandTyrosinealongwith their disorders (8) Metabolism & Disorder OfTryptophan (9) Metabolism Of Sulphur Containing Amino Acids Discussthe metabolismof tryptophan alongwith itsdisorders Discuss the metabolism of Sulphur containing amino acids along withtheir disorders Page | 19
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE (10) Metabolism Of Branched Chain AminoAcids Discussthe metabolismof branchedchainaminoacidsalongwith their disorders Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion (11) Catabolism Of Carbon Skeleton Of Amino Acids Explainthecatabolism of carbonskeletonof aminoacids Practicals: Describe different types of chromatography andHPLC Demonstration Perform paperchromatography Practical COMMUNITYMEDICINE LEARNING STRATEGY TOPICS &OBJECTIVES (1) Discuss road accidents/ injuriesprevention Discussthe global,regionalandlocalstatisticsof Roadtrafficaccidents Discuss the common causes of roadaccidents Discuss the prevention of road trafficinjuries Explain Hayden matrix ofprevention Discuss Legislations of roadsafety InteractiveLecture ORTHOPEDICS LEARNING STRATEGY TOPICS &OBJECTIVES (1) Fractures Discussthe clinical presentation of commonfracturesanddislocationsof upper and lowerlimb InteractiveLectures Page | 20
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE A VICENNA MEDICA L COLLEGE PATHOLOGY LEARNING STRATEGY TOPICS &OBJECTIVES (2) Osteoporosis Describe clinical features and pathogenesis ofOsteoporosis InteractiveLectures (3) BoneRepair Discuss mechanism of bone repair afterfractures PHARMACOLOGY LEARNING STRATEGY TOPICS &OBJECTIVES (1) Drugs Used To TreatOsteoporosis Explain osteoporosis Discuss the etiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinicalmanifestations and diagnosis ofosteoporosis Classifythe drugsusedin treatmentof osteoporosis alongwith the their basic pharmacology Case- Based Discussion (2) Pain management of jointpain: (3) MuscleRelaxant Discuss the etiology of jointpain Classify the drugs used in the jointpain management Discuss the basics of NSAIDS along with theirpharmacology Explaintherole of Opioidanalgesicsin painmanagement Discuss the basic pharmacology ofOpioids Case- Based Discussion Practical Describe the drugs acting on skeletalmuscles. Page | 21
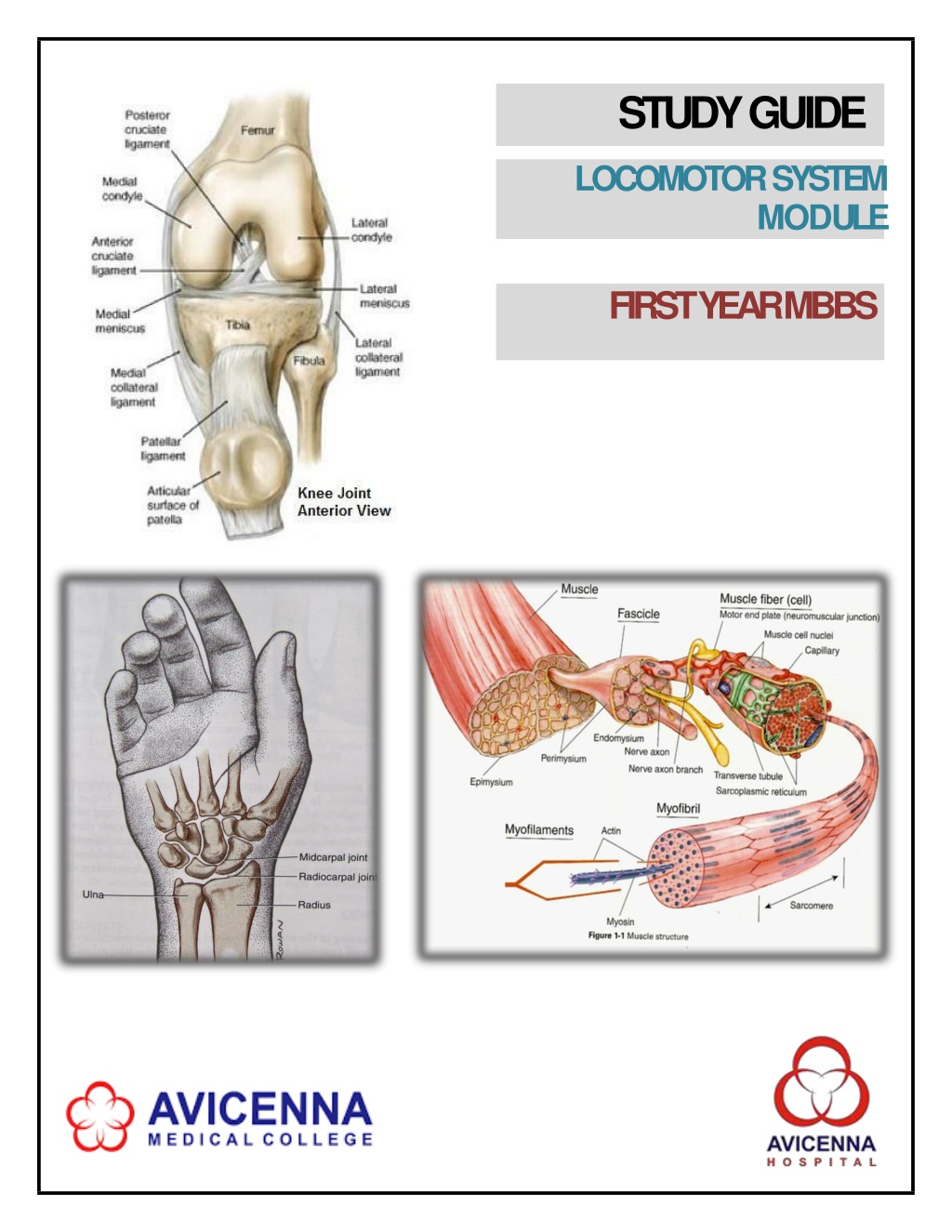
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE PHYSIOLOGY LEARNING STRATEGY TOPICS &OBJECTIVES (1) MembranePotential Define Nernst Potential, Nernstequation Explain the significance of Nernstpotential Describe the origin ofresting membrane potential Interactive Lecture/Small GroupDiscussion (2) Introduction to powerlab Describe different parts of power lab and theirapplication in differentexperiments Demonstration (3) Action Potential (phases, generation &propagation) Describe the different phases of actionpotential Given a graph, identify different phases of actionpotential Define the following: generation and propagation of actionpotential, threshold potentials and all ornone law Interactive Lecture/Small GroupDiscussion (4) Nerve ConductionVelocity Practical Determine nerve conduction velocity inhuman (5) Physiological properties of SkeletalMuscle Define contractility (isometric and isotonic) and excitability, fatigue, summation (spatial and temporal) and motorunit Differentiate among tetanization, tetanus andtetany Describe briefly the staircase phenomenon(treppe) Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion (6) Mechanism of skeletal musclecontraction Describe briefly the structure ofSarcomere Explain sliding filament mechanism and powerstroke Define troponin tropomyosincomplex (7) Electromyogram(EMG) Explain the recording physiology of muscle contraction and changes during EMG Practical Page | 22
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE (8) Simple muscle twitch(SMT) &summation Define simple muscle twitch andsummation Identify the graphs of SMT andsummation Practical (9) Neuromuscularjunction List the components of neuromuscularjunction Explain the sequence of events duringtransmission Define end platepotential Describe excitation contractioncoupling Describe briefly the role ofSarcoplasmic reticulum (10) Disorders of neuromuscularjunction Define disorders of neuromuscular junction (Myasthenia Gravis, Lambert-Eatonsyndrome) Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion (11) Muscle adaptation to exercise Describe the types ofmuscle fibers (type I and II) Determinetheeffectof exerciseonmuscularblood flow Briefly statetheeffectof training,enduranceand resistanceonmuscle fibers (12) Tetanization & Fatigue Define tetanization andfatigue Identify the graphs of tetanizationand fatigue Practical (13) Parathyroid & Calcitoninhormones Discuss secretion, action, functions of parathyroidhormones Discuss calcitonin hormone and role of vitamin D and Calcium Bone physiology and remodelling (14) Differentiatebetweenthemodelingandremodelingof bone Discuss the steps of boneremodeling Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion MuscleMemory (15) Define musclememory Discuss the role of myonuclei during encoding , storage and retrieval of musclememory Energy Expenditure during exercise (16) Explain aerobic and anaerobic exercise along with the energysystem Page | 23
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Deep tendon reflexes(DTR) (17) Discuss the root values ofDTR ElicitDTR Interactive Lecture/Small GroupDiscussion RADIOLOGY LEARNING STRATEGY TOPICS &OBJECTIVES 1. X-Rays of upperlimb 2. X-Rays of Lowerlimb Differentiate between hands and feet on Xrays On plain X-ray, identify thefollowing: i. Bones of both thelimbs ii. Joints and theirtypes SmallGroup Discussion SKILLSLAB LEARNING STRATEGY TOPICS &OBJECTIVES (1) FirstAid Perform bandaging of openwounds Give first aid in case ofan amputated digit Perform splinting infractures Demonstrationand Hands-On practice GENERALSURGEY LEARNING STRATEGY TOPICS &OBJECTIVES (2) BreastDiseases InteractiveLecture Discuss the clinical presentation ofcommon breast diseases Page | 24
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE LEARNINGRESOURCES SUBJECT RESOURCES A. GROSSANATOMY 1. K.L. Moore, Clinically OrientedAnatomy 2. Neuro Anatomy by RichardSnell B. HISTOLOGY 1. B. Young J. W. Health Wheather s FunctionalHistology C. EMBRYOLOGY 1. Keith L. Moore. The DevelopingHuman 2. Langman s Medical Embryology ANATOMY A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Harper s IllustratedBiochemistry 2. Lehninger Principle ofBiochemistry 3. Biochemistry byDevlin BIOCHEMISTRY A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Community Medicine byParikh 2. Community Medicine by MIllyas 3. Basic Statistics for the Health Sciences by Jan WKuzma COMMUNITYMEDICINE A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Robbins & Cotran, Pathologic Basis of Disease, 9thedition. 2. Rapid Review Pathology, 4th edition by Edward F. GoljanMD PATHOLOGY/MICROBIOLOGY 1. http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/webpath.html 2. http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/ A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Lippincot IllustratedPharmacology 2. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology by Katzung PHARMACOLOGY A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Textbook Of Medical Physiology by Guyton AndHall 2. Ganong S Review of MedicalPhysiology 3. Human Physiology by LauraleeSherwood 4. Berne & LevyPhysiology 5. Best & Taylor Physiological Basis of MedicalPractice B. REFERENCEBOOKS 1. Guyton & Hall PhysiologicalReview 2. Essentials Of Medical Physiology byJaypee 3. Textbook Of Medical Physiology byInduKhurana 4. Short Textbook Of Physiology byMrthur 5. NMSPhysiology PHYSIOLOGY Page | 25
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE OTHER LEARNINGRESOURCES Hands-on Activities/PracticalStudents will be involved in Practical sessions and hands-on activitiesthat link with the locomotor moduleto enhancethe learning. Utilize thelabto relatetheknowledge to the specimensandmodels Labs available. A skills lab provides the simulated learning experience tolearn the basic skills and procedures. This helps build the confidence to approachthe SkillsLab patients. Video familiarize the student with the proceduresandprotocols to assist Videos patients. To increase the knowledge, students should utilize the available internet resources and CDs/DVDs. This will be an additional advantage to increase Computer Lab/CDs/DVDs/Internet learning. Resources: Self Learning is scheduled to search for information to solve cases,read through different resources and discuss among the peers and with the SelfLearning faculty to clarify theconcepts. Page | 26
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE ASSESSMENTMETHODS: Theory: Best Choice Questions (BCQs) also known as MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions) are used to assess objectives covered in eachmodule. A BCQ has a statement or clinical scenario followed by four options (likelyanswer). Students after reading the statement/scenario select ONE, the most appropriate response from the given list ofoptions. Correct answer carries one mark, and incorrect zero mark . There is no negative marking. Studentsmarktheirresponsesonspecifiedcomputer-based/OMRsheetdesigned for AVMC OSPE/OSCE: Objective Structured Practical/ClinicalExamination: Eachstudentwill beassessedonthe samecontentandhavesametimeto completethe task. Comprise of 12-25stations. Each station may assess a variety of clinical tasks, these tasks may include history taking, physical examination, skills and application of skills andknowledge Stations are observed, unobserved, interactive and reststations. Observed and interactive stations will be assessed by internal orexternal examiners. Unobserved will be static stations in which there may be an X-ray, Labs reports, pictures, clinical scenarioswith relatedquestionsforstudentstoanswer. Rest station is a station where there is no task given and in this time student can organize his/her thoughts. InternalEvaluation Students will beassessedto determine achievement of moduleobjectivesthroughthefollowing: Module Examination: will be scheduled on completion of each module. The method of o examination comprises theory exam which includes BCQs and OSPE (Objective Structured Practical Examination). Graded Assessment of students by Individual Department: Quiz, viva, practical, assignment, small o group activities such as CBL, TBL, TOL, online assessment, ward activities, examination, and log book. Marksof bothmodular examinationandgradedassessmentwill constitute 20%weightage. As per UHS policy, this 20% will be added by tUHS o AnnualExamination. Page | 27
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Example : Number of Marks allocated for Final Theory and Internal Evaluation InternalEvaluation (Class test +Assignments + Modular Exam) 20% Final Examination TheoryMarks Total(Theory) Final TheoryExam 80% 100% FormativeAssessment Individual department may hold quiz or short answer questions to help students assess their own learning. The marks obtained are not included in the internalevaluation More than 75% attendance is needed to sit for the modular and final examinations Page | 28
1st YEAR MBBS, LOCOMOTORMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE MODULAR EXAMINATION RULES & REGULATIONS(AVMC) Studentmustreportto examinationhall/venue, 30 minutesbeforetheexam. Exam will begin sharp at the giventime. No student will be allowed to enter the examination hall after 15 minutes of scheduled examinationtime. Studentsmust sitaccordingto theirroll numbersmentioned ontheseats. Cell phones are strictly not allowed in examinationhall. If anystudentisfoundwith cell phonein anymode(silent, switchedoff oron)he/shewill benot be allowed to continue theirexam. No students will be allowed to sit in exam without University Admit Card, AVMC ollege ID Card and LabCoat Student must bring the following stationary items for the exam: Pen, Pencil, Eraser, and Sharpener. Indiscipline in the exam hall/venue is not acceptable. Students must not possess any written materialorcommunicatewith theirfellowstudents. UHS GradingSystem It will be based on GPA 4system Marks obtained in Percentagerange NumericalGrade AlphabeticalGrade 80-100 4.0 A+ 75-79 4.0 A 70-74 3.7 A- 67-69 3.3 B+ 63-66 3.0 B 60-62 2.7 B- 56-59 2.3 C+ 50-55 2.0 C <50 Un-grade-able 0 U A candidate obtaining GPA less than 2.00 (50%) is declared un-graded(fail). Cumulativetranscriptisissuedat the endof clearance of all modules. Page | 29
 undefined
undefined