Comprehensive Guide to Body Movements and Special Movements
Explore different types of ordinary body movements such as flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and circumduction, along with special movements like dorsiflexion, plantar flexion, inversion, eversion, supination, and pronation. Engage with detailed descriptions and visual representations of each movement to enhance your understanding of human anatomy and physiology.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
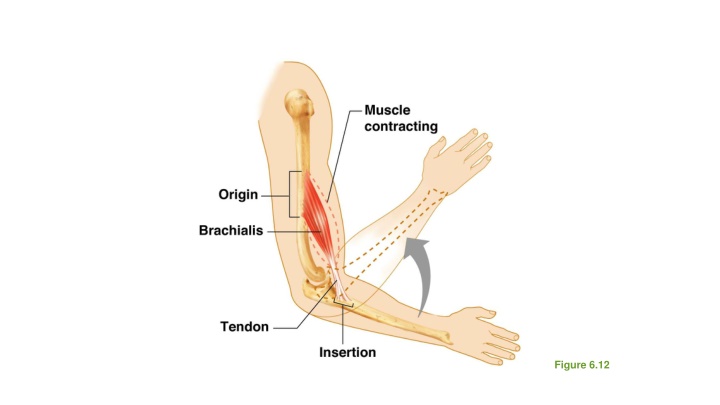
Types of Ordinary Body Movements Flexion Decreases the angle of the joint Brings two bones closer together Typical of hinge joints like knee and elbow Extension Opposite of flexion Increases angle between two bones
Types of Ordinary Body Movements Abduction Movement of a limb away from the midline Adduction Opposite of abduction Movement of a limb toward the midline
Types of Ordinary Body Movements Figure 6.13d
Types of Ordinary Body Movements Circumduction Combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction Common in ball-and-socket joints
Types of Ordinary Body Movements Figure 6.13d
Special Movements Dorsiflexion Lifting the foot so that the superior surface approaches the shin Plantar flexion Depressing the foot (pointing the toes)
Special Movements Figure 6.13e
Special Movements Inversion Turn sole of foot medially Eversion Turn sole of foot laterally
Special Movements Figure 6.13f
Special Movements Supination Forearm rotates laterally so palm faces anteriorly Pronation Forearm rotates medially so palm faces posteriorly
Special Movements Figure 6.13g