Comparative Studies on Carpal Bones of Ox
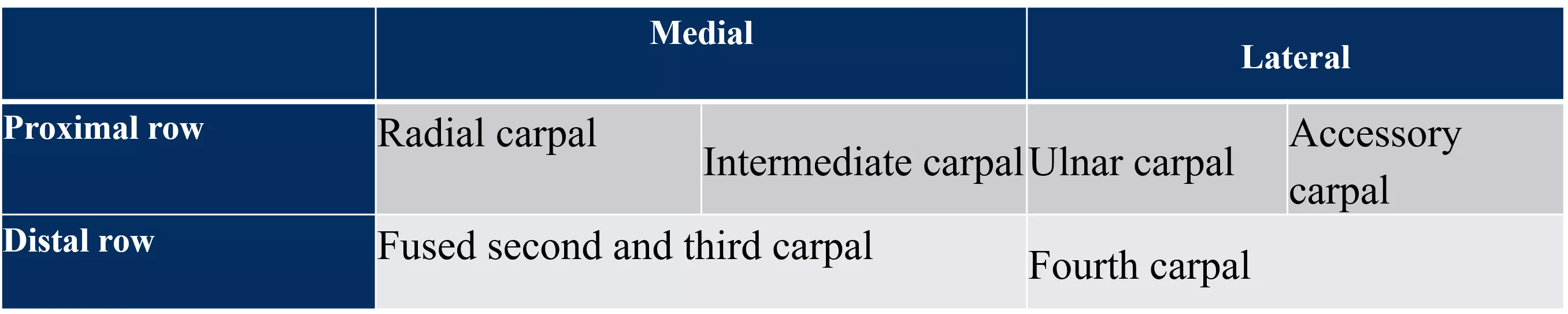
The carpus of ox consists of six bones arranged in two rows - four in the proximal and two in the distal rows. These bones include the radial carpal, intermediate carpal, ulnar carpal, accessory carpal, and fused second and third carpal bones. Each bone has specific features and articulations contributing to the overall structure and function of the carpal region in oxen.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
VAN-601 UNIT-II COMPARATIVE STUDIES ON CARPAL BONES OF OX By: Dr Manoj Kumar Singh Assistant Professor Department of Veterinary Anatomy
Ox The carpus consists of six bones arranged in two rows -four in the proximal and two in the distal rows. They are short bones arranged as noted below. Medial Lateral Proximal row Radial carpal Accessory carpal Intermediate carpalUlnar carpal Distal row Fused second and third carpal Fourth carpal
Radial carpal (scaphoid) It is the largest bone of the upper row. The proximal surface is convexo-concave from before backward and articulates with the radius. The distal surface articulates with the fused second and third carpal. The lateral face bears facets for the intermediate carpal. The dorsal, medial and volar surfaces are continuous and rough.
Intermediate carpal (lunar) It is wedge-shaped. The dorsal surface is rough and forms the base. The apex is posterior, is prolonged medially. The proximal surface is convexo- concave from before backward and articulates with the radius. The distal surface is divided by a sagittal ridge into two facets for the second and third and the fourth carpals. The medial surface has facets for the radial carpal. The lateral surface articulates with the ulnar carpal.
Ulnar carpal (cuneiform) It is very irregular. The proximal surface is oblique directed backward and downward, encroaches on the distal surface and articulates with the fourth carpal. The medial surface has facets for the intermediate carpal. The dorsal surface is rough and convex The volar surface has a facet for the accessory carpal.
Accessory carpal (pisiform) It is short, thick and rounded. It is a sesamoid bone situated behind the ulnar carpal. The proximal surface is narrow and rough for flexor ulnaris and ulnaris lateralis. The distal surface is broad and rough. The dorsal surface has facet for the ulnar carpal.
Fused second and third carpal (os magnum) It is the largest of the carpals the medial one of the two bones of the distal row. The proximal surface has two facets, medial larger for the radial carpal and the lateral smaller for the intermediate carpal. The distal surface articulates with the large metacarpal. The lateral surface has facets for the fourth carpal. The medial and dorsal surfaces are continuous rough and convex.
Fourth carpal (unciform) The intermediate and the ulnar carpals. proximal surface has two facets for the The distal surface articulates with the large metacarpal. The medial surface has facets for the fused second and third carpal. The dorsal and the lateral surfaces are continuous and rough.
Horse Has seven or eight bones. They are: Radial carpal: Resembles that of the ox. Intermediate carpal: The lateral angle of its proximal face is more pointed. Ulnar carpal: The smallest bone of the proximal row. The proximal face articulates only with the radius. Accessory carpal: It is discoid. The medial face is concave and the lateral is convex and rough. A smooth groove for the long tendon of ulnaris lateralis crosses its anterior part obliquely downward and slightly forward. The anterior border has two facets -the upper concave for the radius and the lower convex for the ulnar carpal.
First carpal (trapezium): It is inconstant; when present it is situated behind the second. Second carpal (trapezoid): It is the smallest bone of the distal row. The proximal face has a convex facet for the radial carpal. The distal face is flat and articulates with the medial small and large metacarpals. The lateral face has two facets for the third carpal. The dorsal and the medial faces are continuous and rough. Third carpal (os magnum): It is the largest carpal. It is irregularly triangular with the base anterior. The proximal face articulates with the radial and the Intermediate carpals and distal with the large and medial small metacarpals. The medial border is more concave than the lateral. Fourth carpal (unciform) - It the proximal face is convex and articular and encroaches on the lateral face. The distal face articulates with the large and the lateral small metacarpals. The medial face has two facets for the third carpal
PIG It has eight bones four in each row. Medial Lateral Proximal row Radial carpal Intermediate carpal Ulnar Carpal Accessory carpal Distal row First carpal Second carpal Third carpal Fourth Carpal The bones of the proximal row resembles that of an ox with the exception that accessory carpal is similar to that of horse but has no lateral groove. The first carpal is small, elongated from before backward, rounded and articulates in front with the second carpal.
DOG It has seven bones -Three in the proximal and four in the distal row. The radial and the intermediate are fused. Medial Lateral Proximal row Radial -Intermediate carpal Ulnar carpal Accessory carpal Fourth carpal Distal row First carpal Second carpal Third carpal
Fowl There are only two free bones in the adult. The radial carpal is quadrilateral while the ulnar carpal is forked. The bones of the lower row fuse with those of the carpus during the development forming the carpometacarpal bone. Medial Radial carpal Lateral Ulnar carpal Proximal row Intermediate carpal Accessory carpal Fourth carpal Distal row First carpal Second carpal Third carpal

 undefined
undefined



 undefined
undefined