Charge, Coulomb's Law, and Electric Fields
Charge is a fundamental quantity in nature, with electrons and protons having positive and negative charges. Coulomb's Law explains how charges interact, while electric field diagrams illustrate the concept of electric fields. The force between charges can be calculated using the formula, F = qE.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Physics 4 Nov 19, 2019 Agenda: About Charge Coulomb s Law Electric Field Diagrams Do Now Review of vector addition: Add 50 N @ 35 and 60 N @ 110 Objective: 5.1 Electrostatics Assignment: p205 #1-9
About Charge Charge is a fundamental quantity of nature and is a feature of all matter because matter consists of electrons and protons. 1) Charge comes in two varieties: positive and negative (arbitrary names) Electrons are negative, protons are positive. Neutral matter has approximately equal numbers of electrons and protons Pos rod Neg rod https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NsxhbgCrrSQ
About Charge 2) Charge is quantized. The charge of one electron is the smallest amount of charge you can have. All charges are some multiple of 1.6 x 10-19 C. Charge is measured in Coulombs and given the symbol Q or q. 3) Charge is conserved. Charge is neither created nor destroyed Touching two objects together instantly equilibrates and evenly distributes their charges. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NsxhbgCrrSQ Explain what is happening
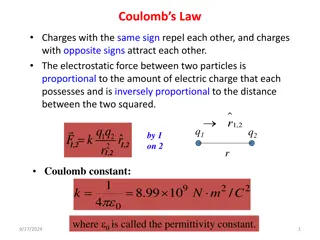
Coulombs Law Two charges will exert an electrical force on one another. Opposite charges attract Same charges repel Force is proportional to both charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two charges. Proportionality constant is k = 9.0 x 109 N m2/C2 (To make the units work) k = 1/4??o O = permittivity of vacuum = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2 ? = ????? ?? A force just like any other. Added just like any other.
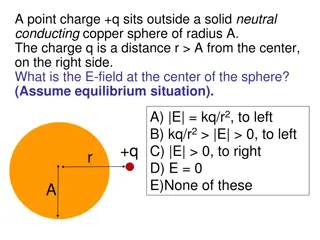
Electric Field Diagrams Mechanism for how charges act over a distance: Electric field. Direction of electric field is in the same direction as the force on a small positive test charge q+ Strength indicated by arrow length Direction: tail of field lines begin at + and radiate outward. Direction: Arrow heads point toward a charge and radiate inward. Similar to gravitational field
Electric field formulas F = qE As a result, there is a formula of electric field based on Coulomb s Law. ? = ?? ?? Can calculate electric field knowing the force and test charge or the magnitude of the electric field present at a given distance from an isolated charge.
Exit slip and homework Exit Slip What is the electrostatic force (magnitude and direction) between a positive charge of 1.3 x 10-3 C and a negative charge of 6.2 x 10-3 C when they are separated by a distance of 15.0 cm? What s due? (homework for a homework check next class) P205 # 1-9 What s next? (What to read to prepare for the next class) Read 5.1 p 196-205