Basics of Battery, Charge Controller & Inverter Overview
Batteries are crucial components in a solar system, providing stored energy to power devices. Understanding battery technologies, capacities, and terminal voltages is key. Charge controllers and inverters play vital roles in managing power flow and protecting equipment. This guide covers battery basics, types, and the functions of charge controllers and inverters in a solar setup.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Basics of Battery, Charge controller & Inverter
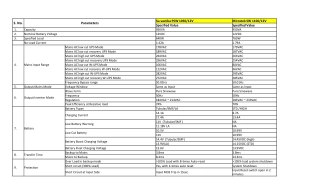
Batteries are the delicate part of the solar system Battery is a tank of charge. When charge goes down in a battery we have to refill it again. Battery charge capacity is given in Ampere-hour(Ah). Battery charge capacity that is available in the market are 2Ah, 10Ah, 100Ah, 200Ah etc. Small battery charge capacity is given in terms of mAh. Example:- Mobile battery ratings are 1000mAh, 4000mAh, 5000mAh Battery has got two terminals. Positive and negative. Terminal voltage is the potential difference between two terminal of battery. Bigger terminal voltage indicates higher driving force. The batteries available in the market have terminal voltage of 2V, 4V, 6V, 12V. Energy stored in the battery is the product of terminal voltage and Charge capacity
The name of battery technology is based on the name of the material used to make battery cell. There are 2 commonly used technologies: Lead-acid batteries These are used for large applications Depth of discharge is 50 %. It s battery life is 3 to 5 years. It s price is 8 to 10 Rs per Wh. Lithium-ion batteries These are used for small applications Depth of discharge is 80-90 %. It s battery life is 4 to 8 years. It s price is 17 to 20 Rs per Wh.
Inverter converts DC power into AC power. Power rating of Inverter should be sum of power of all appliances. Inverter power rating is given in terms of kVA. i.e. 1kVA, 2kVA, 3 kVA, 5 kVA Efficiency of Typical inverter is 80-90 %. Cost of Inverter is Rs. 4 to 8 per Watt. The role of Inverter is as follows:- It helps to extract maximum power from solar panel. It helps to protect battery from over-charge and over- discharge. It helps to supply right voltage and current to appliances.
It manages DC power in and DC output power. Power rating of charge controller should be sum of power of all DC appliances. Efficiency of charge controller is higher than inverter i.e. 85 to 95 % The role of charge controller is as follows:- It extracts maximum power from panel It manages the battery to be over-charged or over- discharged. It provides appropriate DC power to appliances.