Auto Transformer in Electrical Systems
Auto transformer is a unique type of transformer with a single winding that offers various applications in electrical systems. Unlike traditional transformers, auto transformers do not provide electrical isolation between their primary and secondary sides. They operate similarly to two-winding transformers but with distinct characteristics. Auto transformers can be converted from two-winding transformers by adjusting the polarity. They are useful for applications such as voltage regulation, power transfer, and motor starting. Losses in transformers involve copper losses, core losses (including eddy current and hysteresis losses), and methods for minimizing these losses. Efficiency and load at the maximum efficiency point are crucial aspects of transformer performance. Learn about parallel operation and the necessity of paralleling transformers for transferring large amounts of power efficiently across different locations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
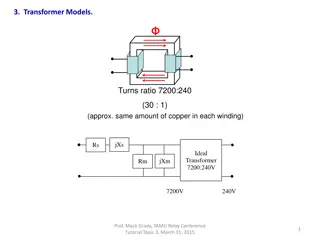
It is a transformer with one winding only, part of this being common to both Obviously, in this transformer secondary are not electrically isolated from each other as is the case with a 2-winding transformer. But its theory and operation are similar to those of a two- winding transformer. primary and secondary. primary the and
Two winding transformer can be converted into auto transformer Additive polarity
Subtractive polarity auto-transformers are used when K is nearly equal to unity
Application As a Variac in Lab/voltage stabilizer or for small work Power transfer through interconnection where two sides voltage level near to same . In Bangladesh ( 132/230kV or 230/132kV) As auto-starter transformers to give up to 50 to 60 % of full voltage to an induction motor during starting.
Losses in transformer 1. CU loss ( loss in the coils) I2R 2. Core loss or iron loss Core loss: a. Eddy current loss b. Hysteresis loss
Loss minimization Laminated core Silicon steel
Mathematics From Text Book
Necessity of parallel operation In some cases very big amount of power( hundreds of MW) can be transferred from one place to another through paralleling the transformer, because big size transformer may not be available.