Asthma Variants: Genetic Insights & Disease Associations
Asthma, a complex syndrome with genetic predispositions, involves variations like the T nucleotide allele at rs7216389 contributing to disease susceptibility. Gene markers, heritability estimates, eQTL associations, and pathways involving interleukins shed light on asthma's molecular underpinnings.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
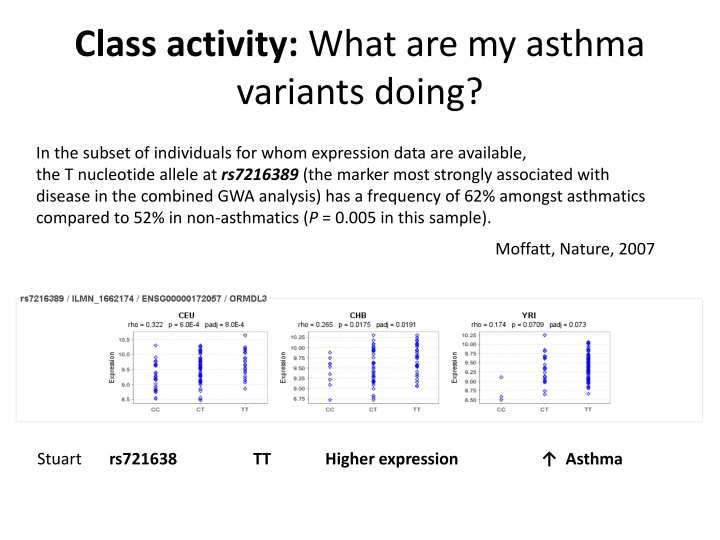
Class activity: What are my asthma variants doing? In the subset of individuals for whom expression data are available, the T nucleotide allele at rs7216389 (the marker most strongly associated with disease in the combined GWA analysis) has a frequency of 62% amongst asthmatics compared to 52% in non-asthmatics (P = 0.005 in this sample). Moffatt, Nature, 2007 Stuart rs721638 TT Higher expression Asthma
Asthma is a syndrome of unknown origins that is characterized by abnormal and inflamed mucosa of the airways, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Asthma runs strongly in families, and its heritability has been estimated as 60%.
Pubmed ID = 17611496 317,000 SNPs in DNA from 994 patients with childhood onset asthma and 1,243 non-asthmatics The SNP with the strongest evidence of association within the interval was rs7216389 (uncorrected P = 9 10-11). Replicated ORMDL3 is the third member of a novel class of genes of unknown function that encode transmembrane proteins anchored in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) rs7216389 is a strong eQTL with ORMDL3 more than one functional SNP underlies the locus
Pubmed ID = 20860503 10,365 persons with physician-diagnosed asthma and 16,110 unaffected persons rs3771166 on chromosome 2, implicating IL1RL1/IL18R1 (P=3 10( 9)); rs9273349 on chromosome 6, implicating HLA-DQ (P=7 10( 14)); rs1342326 on chromosome 9, flanking IL33 (P=9 10( 10)); rs744910 on chromosome 15 in SMAD3 (P=4 10( 9)); rs2284033 on chromosome 22 in IL2RB (P=1.1 10( 8)). Association with the ORMDL3/GSDMB locus on chromosome 17q21 was specific to childhood-onset disease (rs2305480, P=6 10( 23)).
Interleukins/SMAD: indicate pathway that initiates type 2 helper T- cell (Th2) inflammation in response to epithelial damage IL33 activates NF- B and mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases and drives production of Th2-associated cytokines. IL33 may function as an endogenous danger signal to alert the immune system of epithelial damage during trauma or infection.
Area under the receiver-operating-characteristic curve was 0.58 (.50 1.00) Estimation of the population attributable risk fraction for the joint action of the significant loci indicated that 38% (95% confidence interval [CI], 28 to 44) of cases of childhood-onset asthma were attributable to SNP combinations at these loci. These results indicate that although the SNPs would not be effective in classifying the individual risk of asthma, the SNPs (or rather, the downstream functions of which they are markers) do have a substantial effect on the burden of asthma in the community.
Pubmed ID = 20159242 473 cases and 1892 general population controls. 292,443 SNPs. Bonferroni correction is .05/ 292,443 = 1.8 x 10-7 Multiple SNPs in the RAD50-IL13 region on chromosome 5q31.1 were associated with asthma: rs2244012 in intron 2 of RAD50 (P = 3.04E-07). Best SNP is not significant! No strong evidence for SNPs from this paper.
None of the SNPs are statistically significant (p < 1.7 x 10-7)
Class activity: What are my migraine variants doing in different tissues? We identified the minor allele of rs1835740 on chromosome 8q22.1 to be associated with migraine (P = 5.38 10 9, odds ratio = 1.23, 95% CI 1.150 1.324) in a genome-wide association study of 2,731 migraine cases ascertained from three European headache clinics and 10,747 population-matched controls. In an expression quantitative trait study in lymphoblastoid cell lines, transcript levels of the MTDH were found to have a significant correlation to rs1835740 (P = 3.96 10 5, permuted threshold for genome-wide significance 7.7 10 5). Anttila, Nature Genetics, 2011
Pubmed ID = 20802479 Migraine is an episodic neurological disorder with complex pathophysiology, affecting 8% of males and 17% of females Cases: Controls: 5950 50809 Only one marker, rs1835740 on chromosome 8q22.1, showed genome-wide significant association to migraine. (replicated) The proportion of genetic variance explained by the rs1835740 variant was estimated to be 1.5-2.5%.
Possible mechanism Metadherin, also known as protein LYRIC or astrocyte elevated gene-1 protein (AEG-1) AEG-1 acts as an oncogene in melanoma, malignant glioma, breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma. MTDH/AEG-1 down-regulates EAAT2/GLT1, the major glutamate transporter in the brain.
Class activity: What are my BMI variants doing in different populations? rs713586 explained 0.06% of BMI variance Speliotes, Nature Genetics, 2010