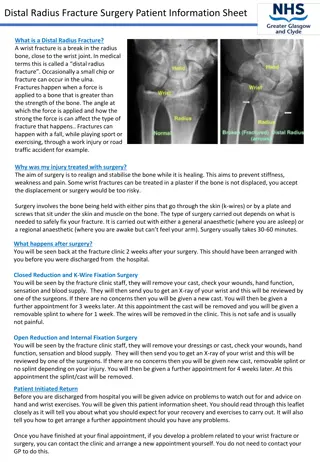
Assessment of Mrs. McDonald's Right Wrist Injury: Colles Fracture Case Study
Mrs. McDonald, a 68-year-old female, presented to the emergency department with a painful and swollen right wrist after falling in her kitchen. She described a mechanism of injury involving a fall on an outstretched hand. Further evaluation revealed limited wrist function, significant pain, and a history of knee replacement and pneumonia. With details on her pain, function, medical history, medications, and allergies, this case suggests a possible Colles fracture.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Distal fracture with dorsal angulation / Colles fracture CBL Regina Sumarlie Y4 Medical Student
Mrs. McDonald Mrs. Mary McDonald: 68 year old female She came to the emergency department after a fall at home this morning. She presented to the Emergency department after falling on to her hand in the kitchen. She is not complaining of painful and swollen right wrist.
What further questions would you like to ask Mrs. McDonald? Mechanism of Injury Pain Function Any other injuries Past medical history Drug and allergies Family history Social history
Mechanism of Injury Mrs. McDonald was cooking in the kitchen, she mentioned that she turned around too quickly and fell on an outstretched hand. She was able to get up afterwards and there was no other injuries that was sustained After an hour or so she realised that her right wrist is increasingly sore and a bit deformed. It looked so different from my left wrist, I was really worried!
Pain SOCRATES Pain around the right wrist Sharp pain that is limiting her movement Pain does not radiate anywhere Movement worsen the pain Haven t tried anything to relief this Severity is around 7/10
Function Can t seem to move her wrist freely Limited by pain Can t lift anything heavy too - pain limits this as well Other injuries? No
Past medical history She is generally quite healthy and active Had a right knee replacement in the past in 2020 Her DXA scan then showed: T score of -5.2 Z score of -3.3 In 2021 was admitted to the hospital due to a community acquired pneumonia Otherwise fit and healthy
Drugs and Allergies Vitamin D, calcium supplements Takes Alendronic acid 10 mg once daily Used to smoke marijuana in her 20s but none since then Allergic to Penicillin She get hives and itching
Family history Mother: passed away due to breast cancer when she was 75 year old Father: high blood pressure, passed away due to old age
Social history She lives by herself in a bungalow Has 2 dogs Smoke 10 cigarettes a day for 30 years Alcohol only on special occasion No recent travel history She drives a car Is usually quite independent, doesn t need any carer Mobilise with no aid Daughter lives 1 hour away from her
Do you think this is a high impact or a low impact fracture? Based on the mechanism of injury described by the patient this sounds like a low impact injury. Low impact fracture Or fragility fracture Is a fracture that result from mechanical forces that would not ordinarily result in a fracture. Also said to be low energy trauma. High impact fracture Are types of bone fractures occurring due to high-impact trauma Example would be car accident
Can you think of anything in Mrs. McDonalds history that could be causing this? She is osteoporotic! DXA scan result showed that she is osteoporotic. We will discuss more about this after we assess Mrs. McDonald!
DXA Scan T-score: T score: compares bone density to average healthy 30 year old adult Z score: compares bone density to average values for a person of same gender and age
Examination Look Feel Move Neurological examination
Look Ecchymosis and swelling Right wrist is diffusely tender Visible deformity is apparent For illustration purposes- this is not a picture of Mrs. McDonald s wrist but this image will aid the understanding on how the deformity may present in cases like hers!
Feel It is really sore and swollen. Mrs. McDonald will try to pull her hand away from you when you toucher the area around the wrist due to pain It also feels like there is a lot of soft tissue swellings all around
Move Very limited movement due to pain She refuse to move her wrist
Neurovascular examination Are these present? The 3Ps: Paraesthesia : tingling, pins and needles or loss of sensation in the hand (?nerve injury) Pain: disproportionate to the injury (? Compartment syndrome) RARE in colles fracture, although there is still a small risk- check if patient is able to move their finger and is appropriately sore Pallor: or duskiness of the hand (? Vascular injury) In Mrs. McDonald s case She has pain but not disproportionate and is able to move her fingers Doesn t seem to have any altered sensation except for some reduced sensation on the swollen area which may happen due to the swelling around. Some bruising present but normal CRT and temperature + palpable radial pulse
Neurological examination Assess: Median, ulnar and radial nerves!
Osteoporosis Osteoporosis: is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, with a consequent increase in bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture. Osteoporosis itself is asymptomatic and often remains undiagnosed until a fragility fracture occurs.
Risk factors for osteoporosis Female sex Increasing age Menopause Oral corticosteroid Smoking Alcohol Previous fragility fracture Rheumatological condition: RA and other inflammatory arthropathies Parent history of hip fracture BMI of <18.5 kg/m2
A 10 year fragility fracture risk score should be calculated prior to arranging DXA scan to measure bone mineral density or starting bisphosphonate, except in: - >50 year old with a hx of fragility fractures DXA scan should be offered - <40 years of age with a major risk factor for fragility fracture DXA scan should be offered Fragility fracture risk can be calculated using Qfracture or FRAX online assessment
What would you like to do next? Xray! Recommended views: AP Lateral
How would you describe this XR? Lateral and AP view Presence of extra-articular fracture of distal radius with dorsal angulation and impaction. Dinner fork deformity How we can describe the dorsal angulation
Other options to further assess: CT XR is usually sufficient but may consider this if there is a concern of intra- articular extension Evaluate intra-articular involvement Surgical planning If considering fixation and to characterise the intra-articular involvement MRI To evaluate soft tissue injury, rarely needed for straightforward wrist fractures Can be considered if signs of complex ligamentous injury present
Distal radial fracture with dorsal angulation/ Colles fracture Are very common extra-articular fractures of the distal radius Usually as a result of FOOSH/ fall on outstretched hand Consist of: Fracture of distal radial metaphyseal region Dorsal angulation And impaction Usually without the involvement of the articular surface
Who? Usually in patients with osteoporosis sustaining an injury due to low impact trauma Or in younger patient usually due to a high impact trauma such as skiing/ contact sports/ etc. How? FOOSH Proximal row of the carpal bone transfer the energy to distal radius In both dorsal direction and along the long axis Hence the presentation of colles fracture
Management Non-operative Closed reduction and cast reduction If extra-articular <5 mm radial shortening Dorsal angulation <5 or within 20 of contralateral distal radius Operative ORIF If XR findings indicate instability Dorsal angulation >5 or >20 of contralateral distal radius Severe comminution Associated ulnar fracture If unable to reduce fracture or there is a loss of position at follow up
How would you manage Mrs. McDonald? Closed reduction and casting in the first instance! Can consider fixation if unable to reduce fracture There is a loss of position at follow up Or if there is significant comminution at presentation How long? Cast for 6 weeks
Recovery Bone healing and smoking Talk to Mrs. McDonald how smoking can affect fracture healing Pain management Physiotherapy Aggressive physiotherapy is quite crucial for her recovery Most distal radius take 3 months or so to heal Full recovery may take up to 1 year and the function they have at 1 year mark is what they have long term.
References https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/multimedia/table/wrist-fractures-colles-and-smith https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg146/chapter/introduction https://americanbonehealth.org/bone-density/understanding-the-bone-density-t-score- and-z-score/ https://www.sportsfitphysioandhealth.com.au/news/bone-health/t-score-bone-health/ https://geekymedics.com/fractures-of-the-distal-radius-wrist-fractures/ https://radiopaedia.org/cases/41322/studies/44157?lang=gb&referrer=%2Farticles%2Fc olles-fracture%3Flang%3Dgb%23image_list_item_17712170#findings https://radiopaedia.org/articles/colles-fracture?lang=gb#image_list_item_17712170 https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/distal-radius-fractures-broken-wrist/ https://orthosho.com/distal-radius-wrist-fractures/