Applications of Refrigeration in Industrial and Chemical Industries
Refrigeration plays a vital role in various industrial and chemical applications, including food processing, preservation of perishable goods, air conditioning, and separation of gases in petrochemical plants. It helps maintain optimum temperatures for different processes, from freezing food products to condensing gases for storage and transportation. The significance of refrigeration in these industries ensures the quality, safety, and efficiency of various operations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Refrigeration and Air-conditioning Applications Prof. A. D. Kale Vishwakarma Institute of Information Technology, Pune Mechanical Engineering Department Qualifications: ME, Mechanical, Heat Power from COEP, Pune Doing Ph-D in Cold Storages for Vegetable Preservation. 1
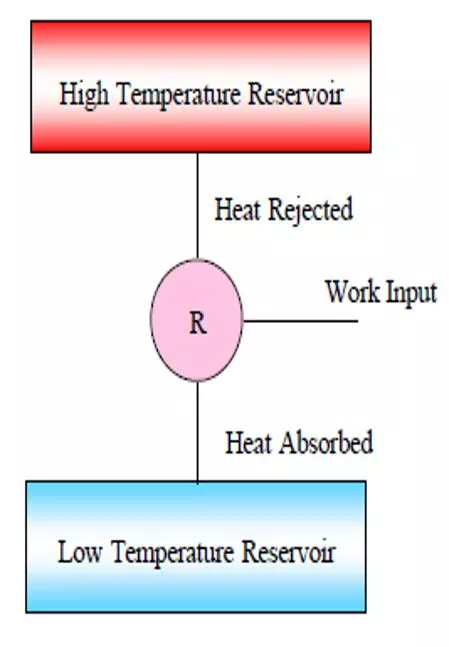
Refrigeration Refrigeration The term refrigeration is used to denote maintenance of a system or body at a temperature lower than that of its surroundings. The system maintained at the lower temperature is known as refrigerated system. Refrigeration is a process of heat transfer from a body at lower temperature to a body at higher temperature with the help of an external agency. The body at low temperature is an insulated space and the body at higher temperature is the atmosphere. 2
1) What are the Industrial Applications of Refrigeration ? 2) Significance of Refrigeration in Chemical Industries ? 3
Applications of Refrigeration: Applications of Refrigeration: 1) Industrial Applications: a) Processing of food products. b) Processing of farm crops. c) Processing of textiles, printing work, photographic materials, etc. d) Cooling of concrete for dams. e) Treatment of air for blast furnace. f) Processing of tobacco, petroleum and other chemical products. 4
Applications of Refrigeration: Applications of Refrigeration: Preservation of Perishable Goods: a) Manufacturing of ice. b) Freezing or chilling, storage and transportation of food stuffs including beverages, meat, poultry products, dairy products, fish, fruits, vegetables, fruit juices, etc. c) Preservation of photographic films, archeological documents etc. Providing comfortable environment: a) Industrial air-conditioning. b) Comfort air-conditioning of hospitals, residences, hotels, restaurants, theatres, offices, etc. 5
App. of refrigeration in chemical and process industries Separation of gases: In petrochemical plant, temperatures as low as 150oC with refrigeration capacities as high as 10,000 Tons of Refrigeration (TR) are used for separation of gases by fractional distillation. Condensation of Gases: some gases that are produced synthetically, are condensed to liquid state by cooling, so that these can be easily stored and transported in liquid state. For example, in synthetic ammonia plant, ammonia is condensed at 10 to 10oC before filling in the cylinders, storage and shipment. This low temperature requires refrigeration. Dehumidification of Air: Low humidity air is required in many pharmaceutical industries. It is also required for air liquefaction plants. This is also required to prevent static electricity and prevents short circuits in places where high voltages are used. 6
App. of refrigeration in chemical industries App. of refrigeration in chemical industries Solidification of Solute: One of the processes of separation of a substance or pollutant or impurity from liquid mixture is by its solidification at low temperature. Lubricating oil is dewaxed in petroleum industry by cooling it below 25oC. Wax solidifies at about 25oC. Removal of Heat of Reaction: In many chemical reactions, efficiency is better if the reaction occurs below room temperature. This requires refrigeration. If these reactions are exothermic in nature, then more refrigeration capacities are required. Production of viscose rayon, cellular acetate and synthetic rubber are some of the examples Cooling for preservation: Many compounds decompose at room temperature or these evaporate at a very fast rate. Certain drugs, explosives and natural rubber can be stored for long periods at lower temperatures. Recovery of Solvents: These can be recovered by condensation at low temperature. e.g: acetone in film manufacture and carbon tetrachloride in textile production. 7
Generally, refrigeration and air conditioning are treated in a single subject due to the fact that one of the most important application of refrigeration is in cooling and dehumidification as required for summer air conditioning. In the form of heat pump, a refrigeration system can also be used for winter heating. Definition of Air-conditioning: A system for controlling the humidity, ventilation, and temperature in a defined envelope e.g: building or vehicle, typically to maintain a cool atmosphere when outside conditions are warm/hot. 10
Applications of Air Conditioning Air conditioning is required for Providing thermal comfort to humans and other living beings - Comfort air conditioning. Providing conditions required for various products and processes in industries - Industrial air conditioning. Comfort Air Conditioning - The objective of this is to provide thermal comfort to the occupants. Thermal comfort may be defined as the state of mind that expresses satisfaction with its surroundings. The requirement of thermal comfort is that human body core temperature to be maintained about 37 degrees. Classification of comfort air conditioning systems : 1. Air conditioning systems for residences. 2. Commercial air conditioning system. 3. Air conditioning system for hospitals. 4. Laptop, mobile air conditioning systems. Window Air Conditioner 11
Industrial Air Conditioning - The objective of this is to provide favorable surrounding conditions so that the required processes can be carried out and required products can be produced. It should also provide at least a partial measure of comfort to the people working in the industries. Industrial air conditioning examples -Textile industries Printing industries Manufacturing of precision parts Semi-conductor industries Pharmaceutics Photographic materials Computer rooms Mines, power plants, etc. 12
Assignment No. 1 Date of Submission: 26 June, 2016 Write Short Note on Topics: 1) Domestic Refrigerator 2) Cold Storage 3) Automotive Air Conditioners 4) Ice Plant 5)Evaporative Coolers Write short note considering following points: a) Labelled Schematic Diagram b) Classification of RAC with tonnage capacity c) Types of Refrigeration Systems d) Typical refrigerants used e) Values of COP, Kw/ton and applications 13
References: 1) NPTEL IIT, Khargpur Dr. Ram Gopal Lectures 2) http://www.enggarena.net/2015/07/applicatio ns-of-refrigeration-and-air.html 14