Understanding Credit Reporting and Credit Scores in CARE Presentation
Explore the essential concepts of credit reporting and credit scores in the context of Credit Abuse Resistance Education (CARE). Learn about credit history, its impact on financial decisions, ways to establish credit, the significance of credit reports, and how credit behaviors affect one's financial future.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Introduction to Credit Reporting and Credit Scores Credit Abuse Resistance Education (CARE) Presentation carechicago.org
Warm-Up What is the first thing that comes to mind when I say the word: Credit? how about Credit Report? and finally - Credit Score? Raise your hand or type your response in the Chat. 2 carechicago.org
Lets Review What is Credit Credit is the ability to borrow money Borrowing money creates debt Debt is what you owe It costs money to borrow money Adults can t fix everything How to rescue your credit - before it needs saving! 3 carechicago.org
Your Credit History Affects Whether You Can Buy Things, and How Much they ll Cost You Credit history begins when you choose and use credit services Credit cards Car loans / leases Student loans Mortgages Insurance Rent leases Employment 4 carechicago.org
Your Credit History Matters! A good history will help you get what you need to improve your quality of life A bad credit history will hold you back, and your missteps will follow you for as long as 10 years 5 carechicago.org
How Do You Get Credit? An adult includes you as an Authorized User on their account (such as a credit card) An adult co-signs a loan (such as a car loan) You may be able to open a Secured Credit Card account with a bank by using a savings account for collateral, or an Unsecured Card (such as with a store like Target Once you have credit, the credit reporting agencies will learn about it and will open a file for you 6 carechicago.org
What is a Credit Report? YOUR ADULT REPORT CARD! It is prepared by credit reporting agencies for use by stores, banks, landlords, and other businesses that give credit Tells lenders how much credit you have used and whether you are seeking more credit It lists the type of credit you use, the length of time your accounts have been open, and whether you have paid your bills on time Summary of your financial reliability 7 carechicago.org
How can you get a Copy of Your Credit Report from the Three National Credit Reporting Companies? You can get one free report every 12 months: Visit AnnualCreditReport.com to download 8 carechicago.org
Free Reports or Scores You can also get free reports or scores from sources such as: c c c c c c c c c 9 carechicago.org
Who Creates and Maintains Credit Reports? A The B C C Banks Credit Reporting Companies Social Media Companies Government 10 carechicago.org
What is a Credit Score? YOUR ADULT G.P.A.! A number calculated by a special company that is used by stores, banks, and other businesses as an indicator of how likely you are to repay your debts Each company that gives credit has its own strategy for using credit scores, and there are many different scores A Snapshot of your current financial situation If a company denies credit, it must disclose the reasons Generated by a mathematical formula 11 carechicago.org
Whats in a Credit Score? These ARE in a credit score: These are NOT: Demographic information Age, race, religion, national origin, gender, sexual orientation, marital status, residence, child / family support obligations Payment history Outstanding debt (balances) Credit account history and usage Employment information Salary, occupation, title Recent hard inquiries* Other credit information Interest rates, soft inquiries*, usage of a credit counseling company Types of credit used * Hard inquiries are typically applications for credit and they ARE used in a score; soft inquiries are usually for marketing prescreening and are NOT used in credit scoring 12 carechicago.org
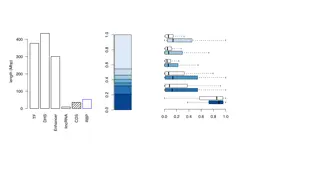
Sample Data Research & Pie Graph Paying on-time and keeping balances low are most important! Payment history New Credit Account payment information Number of recently opened accounts Bad public records 10% Number of recent inquiries Amount of past due accounts 35% Number of past due items 15% Credit history length Types of credit used Number of various types of accounts Time since accounts opened 10% 30% Amount owed Outstanding balances on accounts Proportions of balances to total credit limits Proportion of installment loan amounts 13 carechicago.org
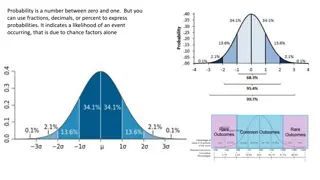
Whats a Good Credit Score? Depends on the score; typically, the higher the score the better 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 Each company decides what it thinks a good score is You are here For example, your credit score might be 690 Very poor Very Good Poor Fair Good Based on one system, here is how you may be viewed by a company that gives credit You are here 14 carechicago.org
Which of these Will Likely Increase your Credit Score A B C C Decrease in overall credit utilization Closed credit card Small missed payment New car loan 15 carechicago.org
Credit Management Tips The single most important part of your credit score is whether you make payments on time Your mom can make a payment for you But your mom cannot make a late payment not late Consider Autopay on your accounts A late payment stays on your credit history and impacts your credit score (up to 10 years) 16 carechicago.org
More Credit Management Tips Set Goals Clean up your records Dispute inaccuracies on your credit report Remove expired debts and collection accounts Consider refinancing a credit balance Guard against identity theft Monitor your transactions Check your credit report at least every three months Improve your credit score 50 points or to above 650 Reduce your credit balances to below 30% of available credit limit Create a budget and stick to it 17 carechicago.org
Top 5 Misconceptions About Credit Scores 4 1 2 3 5 Being a co- signer doesn t make you responsible for the account Paying off a debt will add 50 points to your credit score Once you pay off a bad record, it is removed from your credit report Your credit score will drop if you check your credit report Closing old accounts will improve your credit score 18 carechicago.org
If You Find a Mistake At the conclusion of the investigation, or within 30 days, you ll be notified of the outcome Credit reporting agency will investigate the issue If this does not work, contact the credit reporting agency reporting the inaccurate information Next, contact the company responsible for the inaccuracy and try to resolve the issue First, correctly identify inaccurate information You have the right to dispute inaccurate information on your credit report 19 carechicago.org
Which Element Does NOT Go into a Credit Score? A B C C Hard inquiries Paid-off accounts Home address Zero balances 20 carechicago.org
Which can Happen if a Delinquency is Wrongfully Reported on Your Credit Report A B C C Nothing Credut Score is incorrectly low Denied credit B and C 21 carechicago.org