Overview of Industrial-Organizational Psychology in the Workplace
Industrial-Organizational (I-O) Psychology focuses on studying behavior and mental processes in work settings, applying psychological principles to enhance work behavior. It covers various specialties such as industrial selection, training, performance measurement, organizational development, motiva
1 views • 33 slides
The Strengths and Weaknesses of the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic faced a turbulent period with strengths like introducing proportional representation but also weaknesses such as political instability and economic struggles. Kaiser Wilhelm II's actions, the impact of WW1, and the challenges faced by the new government are discussed in the conte
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding X-Ray Radiation: A Comprehensive Overview
X-ray radiation, discovered by Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen in 1895, is a high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a frequency range of 3.10^16Hz to 3.10^19Hz and a corresponding wavelength range from 0.01nm to 10nm. This form of radiation has applications in various fields, and its properties make it
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Gaussian Elimination Method in Linear Algebra
Gaussian Elimination and Gauss-Jordan Elimination are methods used in linear algebra to transform matrices into reduced row echelon form. Wilhelm Jordan and Clasen independently described Gauss-Jordan elimination in 1887. The process involves converting equations into augmented matrices, performing
4 views • 14 slides
Affinity Chromatography: A Breakthrough in Biochemical Research
Affinity chromatography, developed in the 1930s by A. Wilhelm Tiselius, is a vital technique for studying enzymes and proteins. It relies on the specific affinity between biochemical compounds and utilizes matrices like agarose for binding sites. Ligands such as amino and hydroxyl groups play crucia
1 views • 27 slides
The Discovery and Impact of X-Ray by Wilhelm Conrad Rontgen
Wilhelm Conrad Rontgen accidentally discovered X-rays in 1895, leading to a revolutionary way of seeing inside objects and the human body. X-rays are powerful electromagnetic radiations that penetrate matter and have diverse applications in medicine and industry.
0 views • 19 slides
Historical Events and Learnings in World War I Era
In this collection of historical topics, explore events such as the three brothers in a marathon, war strategies in World War I, and GCSE History lessons covering Germany and Britain. Learn about significant battles, alliances, and key figures from this era, including Kaiser Wilhelm II. A starter qu
0 views • 21 slides
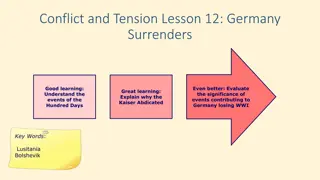
Events Leading to Germany's Defeat in WWI: Hundred Days & Kaiser's Abdication
Evaluate the significance of events that led to Germany losing WWI, such as the Hundred Days offensive and the abdication of Kaiser Wilhelm II. Learn about the impact of U-boats, convoys, the Battle of Jutland, and the blockade on Germany's defeat. Discover key moments like the Black Day of the Germ
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Accountability and Transparency through the Story of Wilhelm Röntgen
Explore the journey of Wilhelm Röntgen's discovery of X-rays in 1895 and delve into the concept of accountability through God's omniscience. Uncover the positive and negative aspects of being under God's watchful eyes, drawing parallels to Röntgen's revolutionary findings and their implications on
0 views • 66 slides
Exploring the History and Properties of X-rays in Condensed Matter Physics
X-rays, discovered by Wilhelm Roentgen in 1895, are highly penetrating rays with unique properties such as electrical neutrality, masslessness, and the ability to travel at the speed of light. They are valuable in medical treatments due to their absorption characteristics and ability to cause photoe
0 views • 4 slides
Origins of Psychology: From Wundt to the Emergence of a Science
Psychology, emerging in 17th to 19th century philosophy, shifted from experimental philosophy to a science. Influenced by Descartes, Locke, and Darwin, it explored the mind-body connection, empiricism, and evolutionary theories. Wilhelm Wundt, termed the father of psychology, pioneered the field by
0 views • 18 slides